symbiosis
(Orac note: I was away at Skepticon over the weekend, where I gave a talk entitled The Central Dogma of Alternative Medicine. (When the talk’s up on YouTube, I’ll provide a link, of course.) Because of all the fun and travel delays I didn’t get a chance to turn my slides and notes into a blog post yet. Also, I’m on vacation this week. However, this gives me the opportunity to resurrect a blog post from 2007, because I think the concept is interesting. I even use it in a slide that shows up in many of my talks (above). I’ve updated dead links and added some text to include relevant links to…
Symbiosis is everywhere. From the Greek for "living with," symbiosis is simply a close association between two different species in nature. These relationships can be mutualistic, parasitic, or somewhere in between. Bacterial symbionts live inside bodies, like the bacteria that help us and other animals digest our food, and they live inside cells, like the bacteria that live in plant roots and provide their hosts with nitrogen. They can be metabolic, hygienic, or photosynthetic; ectosymbiotic, on the host surface, or endosymbiotic, inside the host's cells. Back in the 1860's biologists…
Yesterday I mentioned Symbiotic Households, an art project imagining genetically engineered mosquitoes that provide mood stabilizing compounds to a population plagued by worries caused by climate change. Today on twitter I saw a link to a US patent application filed by Microsoft about engineering parasites to monitor and maintain human health. The possible engineered parasites covered in the application include:
mosquitoes, fleas, ticks, bed bugs (Cimicidae Cimex lectularius), midges (such as Ceratopogonidae), other blood sucking arthropods, annelids or leeches, nematodes such as Ascaris…
With The Symbiotic Household, Elliott P. Montgomery seeks to find answers to problems caused by climate change. Low-cost, low energy solutions are proposed through complex genetic engineering of domesticated insects--"What better way to deal with a future need than with a future technology?"
The project is deliberatively provocative; "By offering a problematic answer, I want to encourage viewers to question the entire scenario and thereby take part in the discussion." What do you think?
via we make money not art
This year's Cambridge iGEM team has made a tiny, wireless lightbulb filled with bioluminescent bacteria! There are two main ways of engineering luminescence in E. coli (I assume these are E. coli, correct me if I'm wrong!). One is to express the luciferase gene from fireflies, which adds ATP and oxygen to the chemical luciferin, producing oxyluciferin and yellow, green, or red light.
Since the lightbulb is blue, this bacteria is probably expressing the Lux operon from Vibrio fischeri, which use their bioluminescence in an awesome underwater symbiosis. From the Cambridge iGEM wiki:
Some…
My good friend and labmate just published an awesome paper: "Emergent cooperation in microbial metabolism." His experiment started with 46 strains of E. coli that had mutations in their metabolic pathways that prevented them from being able to grow without supplementing the media with extra metabolites. Alone they died, but grown together in the same tube, many pairs of mutants were able to feed each other the missing metabolite. Metabolic cooperation was the key to survival.
Measuring and understanding metabolic cooperation can be used to build stronger, more predictive models of metabolism…
A delightful lunch conversation about fruits introduced me to what may be my new favorite symbiotic relationship! Figs are not actually fruits but a mass of inverted flowers and seeds that are pollinated by a species of tiny symbiotic wasps. The male fig flower is the only place where the female wasp can lay her eggs, at the bottom of a narrow opening in the fruit that she shimmies her way through. The baby wasps mature inside the fig into males that have sharp teeth but no wings and females ready to fly. They mate, the males chew through the special fig pollen holders and drop them down to…
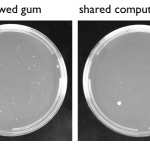
The past few days I've been learning a lot about the bacteria that surround me and realizing just how labor intensive an actually well-controlled handwashing experiment can be! Here is a little bit more of the data I've collected about bacteria on everyday objects:
Dusty corners (unsurprisingly?) have the most bacteria, followed by chewed gum, then pens and computer mice. These data also show that the medium of bacterial transmission has a huge effect on what shows up on the plate. Leaving the actual object on the plate--in this case a dust bunny--allows for a lot of bacterial transfer, as…
Commenter JohnV asked me whether I had let any of my silkworms crawl on an LB plate (what microbiologists use to grow colonies of bacteria) to see what kind of bacteria is living on them in case I ever suffer from catastrophic experiment contamination. I hadn't thought of what kind of bacteria could be living on my silkworms (we are thinking about what kind of bacteria live in their digestive systems that help them digest leaves) so I tried it out! I let one of my wormies crawl on a plate, and I touched one with my relatively clean fingers as a pseudo-control.
I let the plates incubate at 37…
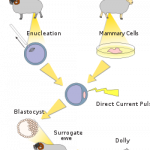
New in vitro fertilization technology is making it possible for someone to have two moms--one that provides the genome in the nucleus of the cell, and one that provides the rest of the egg cell, including the mitochondria. Since all mitochondria are passed down from the mother in the egg (sperm are just too small to provide anything but the father's genetic material to the fertilized embryo), transplanting the nucleus from a fertilized embryo to an egg from a different woman can bypass the transmission of any mitochondrial diseases that the mother carries. Because mitochondria have their own…
My two great thesis project loves are hydrogen and symbiosis, and as such, the recent news of a multicellular organism that lives in a completely oxygen free environment and gets its energy from hydrogenosomes instead of mitochondria is totally fascinating.
Hydrogenosomes are organelles that are evolutionarily related to mitochondria. Mitochondria generate energy for the cell by transferring electrons pulled off of sugars molecules to oxygen (this is why we breathe oxygen). The energy from this electron motion is transferred to the production of ATP, the energy currency of the cell, through…
Animal cells are made up of many smaller membrane-bound compartments called organelles that perform highly specialized functions necessary for life. Incredibly, several of these organelles have been shown to be evolutionarily related to free-living bacteria, captured and incorporated inside a larger cell billions of years ago in a complex mutually beneficial relationship, known as endosymbiosis (a partnership between two species where one of the species is inside the other). The mitochondria that power our cells, generating energy by breaking down sugars are in fact relatives of regular old…
Cooperation and altruism are widespread in biology, from molecules and genes working together in a cell, to bacterial communities that require coordinated behavior to survive in a tough environment, to human relationships and societies. Our human cultural perspective (perhaps even more specifically our American cultural perspective, focused as it is on individuality, free markets, and the American Dream), however, treats cooperation as an outright anomaly that has to be explained away by science (or often, religion). If natural selection is about the "survival of the fittest" how can a…
I am kind of obsessed with symbiosis and the idea that cooperation between different species can be a driver of evolutionary change. I learned about these symbiotic green sea slugs a while back from a colleague whose mom is a zoologist who studies the evolution of symbiosis between invertebrates and photosynthetic microorganisms. A review article from her lab beautifully introduces the amazing properties of Elysia chlorotica:
Faced with life without a protective shell in a predatory environment, some sea slugs evolved a protective mechanism dependent largely upon camouflage pro- vided by…
Many animals in the ocean seek shelter from predators by living on or among other animals. Among fishes, members of the Damselfish family (Pomacentridae) often seek protection this way. Some of these relationships also are commensal or even symbiotic.
One of the most well known symbiotic relationships in the marine world is that between anemones and fishes commonly known as 'clownfish' or 'anemonefish'. Clownfish form a subfamily, Amphiprioninae, of the Dameselfish family. Each of the twenty-some species in this subfamily lives symbiotically with one or more anemone species.
Both the…
If millipedes were not adorable enough on their own, they are often teeming with special little mites. The millipede and the mites typically have a symbiotic relationship wherein the millipede provides the mites with a home and the mites provide an extra layer of terror in the event that an elementary school child on a field trip actually builds up the courage to hold the Giant African millipede.
Who's seen Cloverfield?
tags: symbiosis, humor, The Onion
Those of you who haven't noticed this yet, The Onion has a really amusing article about symbiosis that you have got to read .. it might even make a really amusing "extra reading" for the classroom!
Devouring horsefly larvae embedded in her 3,000-pound partner's back, the tickbird seemed to agree that there was little fire left in their symbiotic relationship. At worst, she said, it feels like she and the rhino have been trapped in the same dead-end symbiosis for "countless millions of years."
"We just go through the motions, and there's hardly any…