wound
Image of a Komodo dragon By Charlesjsharp - Own work, from Sharp Photography, sharpphotography, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Researchers at George Mason University have created a synthetic version of a peptide found in the blood of Komodo dragons (Varanus komodoensis). They dubbed the synthetic peptide DRGN-1. Living up to its name, DRGN-1 proved to be pretty tough against microbes (Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus) as well as biofilms. Bacteria stick together to create biofilms that attach to surfaces and help to protect themselves during an infection. Even infected…
Pictoral abstract showing the use of nanofibers from fish collagen in wound healing. Image from Zhou et al., 2015.
Researchers in China have discovered that collagen isolated from the skin of tilapia effectively reduce wound healing time in mice. The usefulness of collagen, a major structural protein found in connective tussues, in wound healing has been known. Using fish proteins instead of typical mammalian sources reduces the risk for potential pathogens.
Dr. Jiao Sun (Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine) and colleagues isolated collagen from the skin of tilapia and spun…
You might be familiar with tissue regeneration in amphibians and reptiles where limbs can be fully regenerated following an injury. Until now, tissue regeneration following a wound was thought to be limited in mammals (ex: deer shed and regrow their antlers annually; some mice can regrow the tips of their fingers).
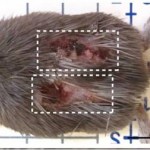
Researchers discovered that African spiny mice are able to regrow skin, complete with hair follicles, after an injury. We are not talking about simple wound healing, but actual skin regeneration without scarring. Researchers suspect this unique ability may have evolved to help them…
For the longest time, people believed that the world's largest lizard, the Komodo dragon, killed its prey with a dirty mouth. Strands of rotting flesh trapped in its teeth harbour thriving colonies of bacteria and when the dragon bites an animal, these microbes flood into the wound and eventually cause blood poisoning.
But that theory was contested in 2005 when Bryan Fry from the University of Melbourne discovered that a close relative, the lace monitor, has venom glands in its mouth. The discovery made Fry suspect that Komodo dragons also poison their prey and he has just confirmed that in…