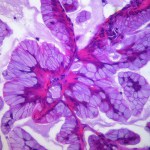
cell division
This new year, researchers concluded that 2/3 of the difference in cancer risk between different parts of the body can be attributed to the number of stem cell divisions those parts undergo. More cell divisions reflect a higher risk as errors that occur naturally during the DNA replication process can contribute to the development of cancer. In other words, the same genetic mutability that enables evolution also ensures that many people will be afflicted by a terrible disease. On Pharyngula, PZ Myers suggests this is one reason our cells naturally get old and stop dividing:…
This week's Weizmann news stories: A "steam release valve" for inflammation, a "brake" for cell division and an "amplifier" for quantum signals.
The steam release valve mechanism also involves an amplifier - one that ramps up the inflammation signal in response to viral attack on a cell. When the signal reaches its peak, it trips a nearby protein called caspase-8, which then kills the amps, damping the signal back down. The scientists think that failures in this mechanism could be behind various inflammatory diseases.
The brake on cell division turns out to be our old friend p53. Thirty…
What? Is this a joke, Ethan? Have you been watching Jurassic Park again, drinking Dino DNA or something? No, I got an interesting question from startswithabang.com reader and ichthyophobe Lucas:
Over the years a few intact, frozen woolly mammoth have been found and procured by different scientists and governments, most recently Japan. What are they doing with these ancient popsicles? Cloning? Could a frozen woolly mammoth be effectively cloned?
Aaah, the woolly mammoth, something we think of as ancient, but really it only went extinct an estimated 3,700 years ago, with the last mammoths dying…