glioma
Here we go again.
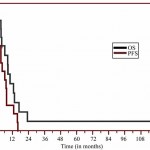
Two months ago, I noted that Dr. Stanislaw Burzynski, the Polish expatriate physician who started out as a legitimate medical researcher and then in the late 1970s took a turn away from science-based medicine and towards being a "brave maverick doctor" through his discovery in blood and urine of substances he called antineoplastons with—or so Burzynski claims—major anticancer activity, had finally published the results of one of his clinical trials. Actually, he published the results of 42.5% of one of his clinical trials, given that he had, without adequate explanation,…
A drug currently used to treat colon cancer in people successfully treated a type of brain tumor, called a glioma, in a dog named "Petey". After removing the tumor, Dr. Simon Platt administered the drug to the brain where it prevented the tumor from returning. The next step is to conduct a larger study that includes more dogs. If successful, the drug may be used in clinical studies of humans to treat glioblastomas, a similar form of brain cancer that affects roughly 13,000 people annually and for which there is currently no cure.
REMOVAL of specific parts of the brain can induce increases in a personality trait which predisposes people to spirituality, according to a new clinical study by Italian researchers. The new research, published earlier this month in the journal Neuron, provides evidence that some brain structures are associated with spiritual thinking and feelings, and hints at individual differences that might make some people more prone than others to spirituality.
Cosimo Urgesi of the University of Udine and his colleagues combined pre- and post-surgical personality assessments with advanced lesion…