pathology
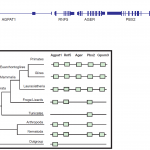
Figure 1 showing RAGE (aka: Ager) expression only in mammals from Sessa et al., PLOS ONE. 9(1): e86903, 2014.
RAGE stands for "receptor for advanced glycation end-products", also known as "AGER", and new research shows that it first appeared in mammals (Sessa et al., 2014). Despite the name, the receptor also binds other signaling molecules such as HMGB1, S100 proteins, beta-amyloid, phosphatidylserine, among others (Xie et al., 2013). RAGE is reportedly involved in diabetes, cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, osteoarthritis, cancer, Alzheimer's disease, as well as liver and renal…
THIS is the left cerebral hemisphere of an 18-month-old infant who lived some 800 years ago. Such finds are extremely rare, because nervous tissue is soft and normally begins to decompose soon after death, so this specimen is unique in that it has been far better preserved than any other. Although reduced by about 80% of its original weight, many of its anatomical features have remained intact. The frontal, temporal and occipital lobes have retained their original shape; the gyri and sulci (the grooves and furrows on the surface, respectively labelled G and S, above) are easily recognizable…
photo: Philip Todeldano for the New York Times
Part of any real healthcare reform will be improving practices in hospitals, and -- as Obama's proposed commission on comparative effectiveness would do -- identifying what works and what doesn't. Knowing what works and why people get better or not is vital to good medicine. But amid the talk on improving such knowledge as part of healthcare reform, a vital and fairly cheap way to generate some of it -- the autopsy -- is going ignored. This is too bad, as autopsies yield incredibly good information about the quality of both diagnosis and…