oxidative stress
A new article published in Physiological Reviews compared some remarkable similarities and differences between naked mole rats and humans. Both are relatively long-lived, highly social and have low natural selection pressures. But, this is about all they have in common. While humans are prone to developing age-related cancer, diabetes, heart disease and dementias, naked mole rats are rather resistant to these diseases. Instead, naked mole rats appear to maintain a youthful state throughout their long lives of 30+ years, compared to a mere 3 years for a mouse. To top it off, they do not…
Image of goldfish from Wikipedia
Liver failure or congenital defects can lead to a build-up of ammonia in the brain of mammals resulting in life-threatening swelling, convulsions and comas. For goldfish (Carassius auratus), environmental exposure to ammonia causes reversible swelling of the brain. In a new study published in the American Journal of Physiology - Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, researchers wanted to explore how the fish were able to accomplish this. They exposed goldfish to high levels of ammonia for 72 hours which, like mammals, caused…
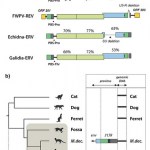
In a phenomenon known as Peto's paradox, large mammals do not develop cancer more often than small mammals, despite having more cells that could go haywire. On Life Lines, Dr. Dolittle writes "Some researchers suggested that perhaps smaller animals developed more oxidative stress as a result of having higher metabolisms. Others proposed that perhaps larger animals have more genes that suppress tumors." But a new hypothesis argues that large mammals have evolved to minimize the activity of ERVs, which are ancient viral elements integrated into our DNA. Active ERVs can cause cancer and possibly…
tags: evolution, evolutionary biology, evolutionary ecology, plumage color,carotenoid-based colour, carotenoids, lipid peroxidation, oxidative stress, sperm motility, sperm quality, sperm velocity, birds, ornithology, Great Tit, Parus major, researchblogging.org,peer-reviewed research, peer-reviewed paper
Great Tit, Parus major.
Image: Luc Viatour, Creative Commons/Wikipedia [larger view]
In some species of birds, males are more brightly colored than females. This phenomenon is due to female choice: females choose to mate with males that have the brightest plumage colors and most…