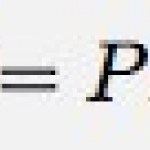As part of the Ask a ScienceBlogger series, reader Jim Swanson asks:
When I open the dishwasher after washing and the contents are still hot, why do the glass and ceramic items dry off more quickly than the plastic items?
This is a great question. Great because it is something most everyone can relate to and great because there is some good science. Really, this shows the difference between temperature and thermal energy. I think the common idea is that temperature is a measure of the energy something has - but this isn't quite true.
Ok, let me first start with a sample case. Suppose you…
thermal energy
A new video from the Red Bull Stratos Jump guys came out. Here it is:
This reminds me of an unanswered question about the Stratos jump that I didn't address on my last post on this topic. Commenter Long Drop asked about how much Felix would heat up as he falls from 120,000 feet. This is a great question. The first, off the bat answer is that he won't heat up too much. Why do I say this? Well, when Joe Kittinger jumped from over 100,000 feet and didn't melt. Still, this is a great thing to calculate.
How do you calculate something like this? I will look at this in terms of energy. For…
The more I think about the last MythBusters' exploding water heater, the more cool things I see. How about I look at the energy of the explosion. There are three things I can look at:
How much energy went into the water heater from the electric source?
How much kinetic energy did the water heater have right after the explosion?
How much thermal energy did the water and water heater have?
How much gravitational potential energy did the heater have at it's highest point?
Hopefully, I can show that the energy in from the electric source is greater or equal to kinetic plus thermal. Also, the…
Note to self: don't do the mechanical equivalent of heat lab again. It doesn't really work that well and there are better labs to do.
So, what is the mechanical equivalent of heat lab? It is actually a pretty cool idea. Take and object and drop it. What happens to the kinetic energy the object had right before it hit the ground? Most of it goes into thermal energy of the object and surroundings. In this lab, the students measure the change in gravitational potential energy for a falling object (where object is really lead shot or something) and then measure the change in temperature in…
I already talked about increasing the temperature of a pool. My father commented that he thought the pool level rose by like half an inch when the temperature increased (by about 10 degrees F). So, this leaves the question: Is my father crazy, or is this possible? Or are both true?
Does water expand when it warms up? Yes, except when it melts. Why does this happen? Liquids are actually very complicated, but here is a basic answer. Take a look at this PhET gas simulator, I know it is for gases not liquids. I think we can make it behave like a liquid if you increase the gravity to the…
It is spring break, so we are at my parents house for a couple of days. The kids like it because there is a pool, a heated pool even. It really isn't that cold outside, but yesterday the water measured at 62 oF. So, with some help from the kids, we cleaned out the pool and turned on the heater. We also put a cover on it, hopefully to help it heat up some more.
This is perfect for a quick calculation. Is it reasonable that the pool could get up to a swimable temperature by tomorrow? Let me first make some assumptions and data:
15,000 gallons of water in the pool. This is about 57 m3.…
Temperature is a pretty weird thing if you think about it. How do you best define temperature? Let me go ahead and give you my favorite definition:
Temperature is the thing that two objects have in common when they have been in contact for a long time.
Yes, that is a good definition. Maybe now you can see why temperature is weird. Doesn't it have something to do with energy? Well, something - yes. Let me take an example. Suppose pour some hot coffee into a paper cup (I use paper because styrofoam(TM) is trademarked). Further suppose that this is super hot coffee from McDonald's. Can…
Heat. You have heard it before. You have used it. I have even used it. Do we need this word? No. Is this a useful word? No.
Let me start with the definition as usually stated in a physics type text: (this is from [dictionary.com](http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/heat))
*heat:* a nonmechanical energy transfer with reference to a temperature difference between a system and its surroundings or between two parts of the same system.
This definition is fine. It is not wrong, but is it needed? Not really. Couldn't we just say energy transfer? Actually, I like to use this in the…