In A Perfect World, everyone who was infected with HIV-1 would be tested and treated.
1-- People with access to antiretrovirals live longer.
Increases in Adult Life Expectancy in Rural South Africa: Valuing the Scale-Up of HIV Treatment
I really like the introductory paragraph to this paper:
For most of the 20th century, life expectancy increased in nearly every part of the world (1). However, from the late 1980s, the HIV epidemic led to a reversal of this trend in southern Africa, with a large rise in mortality among working-age adults (1–3). In South Africa, life expectancy at age 15 declined from 67.4 years in 1990 to 58.7 years in 2009; and in Swaziland, from 68.1 to 53.4 years (2). In addition to the direct loss of life, these declines in adult life expectancy had profound negative effects on households, communities, and governments, including declines in household wealth; large increases in the number of orphans; the loss of skilled workers, including teachers, doctors, and government officials; and the interruption of intergenerational transmission of knowledge and norms (4).
Read that again.
That is what HIV/AIDS did to Africa. While the rest of the world has seen increases in life expectancies (for comparison, last year Japan was at 83, and the US was trailing at 78), a kid in South Africa could expect to live into their 50s. And HIV/AIDS doesnt stop at death-- the deaths of adults leads to loss of income for the surviving family, increases in the number of orphans, shortages of adults-- teachers, community leaders. So who the hell do the kids have to look up to? What kind of future can they hope for themselves (to the ripe old age of 50-something)?
Antiretrovirals are a beacon of hope, for a future.
Of course it is relatively easy to study individuals who are enrolled in a clinical trial of some kind, who are given medication and monitored and so on. We know people who take the medication as prescribed can live just as long as people who are uninfected. But what is the impact of access to antiretrovirals have on the community? Everyone who lives in a region, HIV+ or -?
Thanks to a program initiated by George W Bush in 2004, PEPFAR, South Africa was able to roll out public access to antiretroviral therapy to as many HIV+ patients as they could (yes, you read that right, W). So this group of scientists picked a community at high-risk for HIV infection, and calculated the average individuals life expectancy before, and after public access to antiretrovirals. They did not pick an 'easy' community:
The study population included all adult resident and nonresident members of all households in a 434-km2 surveillance area in rural KwaZulu-Natal.
...
The community is largely rural and is located in one of the poorest districts in South Africa (25). HIV prevalence is very high; 29% of adults are HIV-positive, with about half of women aged 30 to 49 and about one-third of men aged 35 to 49 living with HIV (12). In the early 2000s, over half of all deaths in this community were attributable to HIV (7).
This is what happened.
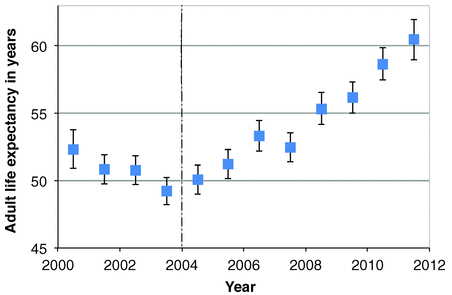 Increases in Adult Life Expectancy in Rural South Africa: Valuing the Scale-Up of HIV Treatment
Increases in Adult Life Expectancy in Rural South Africa: Valuing the Scale-Up of HIV TreatmentScience 22 February 2013: vol. 339 no. 6122 961-965
Life expectancy before PEPFAR: Under 50. Eight years after PEPFAR: Over 60.
To be precise, an 11.3 year gain.
Again, this is not the life expectancy of someone diagnosed with HIV-- This is life expectancy of an Average Person in a community where HIV is present, and antiretrovirals are available.
2-- People with access to antiretrovirals are less likely to infect others.
Again, it isnt so difficult for scientists to enroll discordant couples (monogamous pairs where one person is HIV+ and one is -) and track the effect of medication in the + person on HIV status of the - person.
But not everyone who is HIV+ is in a monogamous relationship.
What is the effect of access to antiretrovirals in a community on HIV spread within a community?
Same community described before. To summarize an entire paper in one sentence: The more HIV people within a community who have access to antiretrovirals, the less chance a negative person has of acquiring HIV.
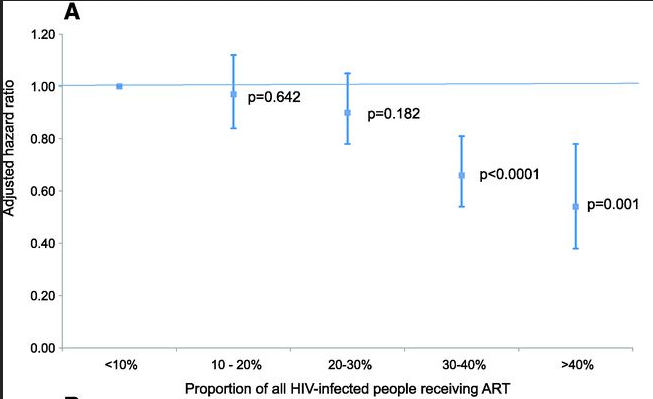 High coverage of ART associated with decline in risk of HIV acquisition in rural KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
High coverage of ART associated with decline in risk of HIV acquisition in rural KwaZulu-Natal, South AfricaScience. 2013 Feb 22;339(6122):966-71
It is not 'only' the HIV+ individuals who benefit from access to antiretrovirals.
The entire community benefits.

Well done, Dubya! :P