Aetiology
As an unprecedented outbreak of Ebola crosses borders in West Africa, people are asking new questions about the virus and its potential to turn into a global pandemic (hint: it's not gonna happen). Greg Laden writes "The disease is too hot to not burn itself out, and it has no human reservoir. Ebola accidentally broke into the human population earlier this year or late last year." The current numbers from the WHO suggest 1800 confirmed and suspected cases of Ebola so far with a mortality rate edging down toward 55%.
Last week some in the U.S. objected to bringing two American patients…
On Aetiology, Tara C. Smith continues her series on the science of The Walking Dead, explaining how diseases spread and how they might cause zombiism. One thing that would be observed in any real contagion would be an incubation period— the time between when a virus (for example) enters your body and you start showing symptoms of infection. For a virus like the flu, this could be about two days during which you don’t feel sick but could still be infecting people around you—even if you don’t bite them. Tara also expresses nerd rage at the show's "doctors" pursuing antibiotics to…
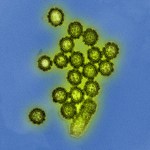
A new strain of bird flu is circulating in China, and authorities are keeping a close eye on a potentially disastrous scenario. On Aetiology, Tara C. Smith writes that by now, "the microbe may have already become established in the population, adapting to humans stealthily before we were even aware of it." Greg Laden writes, unlike H1N1 in 2009, the new H7N9 doesn't sicken birds, making it more difficult to identify reservoirs of the virus. And according to the latest reports, it doesn't make all people sick either. Documented infections are widespread in a populous…
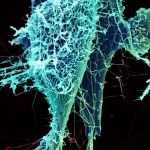
A notorious bacterial foe has made its first documented appearance in the U.S. and is jumping species around the farm scene. First, MSRA—methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus— was found in chickens. Just recently, research conducted by ScienceBlogger Tara Smith from Aetiology found that ST398, a strain found in pigs, was also found in many of the humans who came into contact with the pigs at a large food production farm in Iowa. While this strain seems to spread readily between animals and humans, its potential for lethal infections is still unclear.
Related ScienceBlogs Posts:
Swine…