Brain and Behavior
Studies of guppies show that bigger brains may mean "smarter" fish, but less offspring. Credit: Marrabbio2/Creative Commons
...at least for guppies. Dr. Alexander Kotrschal and colleagues at Uppsala University (Sweden) either shrank or grew the brains of guppies over multiple generations to create animals with up to 8-10% variations in brain size. To test for "smartness" they had the fish count by training the animals to look for food where a card with two or four symbols was shown. According to the researchers, the animals with larger brains tended to…
Magnetite in a fish nasal cell. Image: The Scientist from Herve Cadiou, University of Cambridge
In a prior blog, we talked about different animals that are able to sense the Earth's magnetic field. The mystery of how fish, and perhaps other animals, do this may be solved. Animals use the magnetic field like a compass. This is an important skill especially to migratory species who don't have the benefit of Google Maps. It is sort of a built-in GPS system.
Dr. Michael Walker from the University of Auckland discovered that brain cells connected to the nasal cavity of fish can be…
Idiopathic autism has been on the rise in recent years and is thought to be caused by a mixture of genetic risk factors as well as some as yet unknown environmental factors. Research suggests a link between antidepressant use by pregnant women and the development of autism. Further, some unmetabolized psychoactive pharmaceuticals (UPPs) have made their way into drinking water from sources at the surface posing a potential environmental risk of exposure. To study the potential link between UPPs and autism, Drs. Michael Thomas and Rebecca Klaper exposed fathead minnows to a mixture…
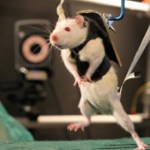
Scientists have been able to restore locomotion in paralyzed rats using a combination of nerve stimulation and engaging the mind by having the rats complete simple tasks (like obtaining treats). In the newly published research, Dr. Grégroire Courtine (University of Zurich and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology) and his team created a rat model of spinal cord injury. After designing a support jacket for the rats, they used a combination of neurotransmitters and electrical impulses to excite the nerves to produce involuntary stepping actions, which alone did not activate…
Elizabeth Norton has an interesting write-up in Science Now. Some years ago, after a long period of suspicion, it was seemingly demonstrated that neurogenesis (the formation of new neurons) happened in the human nose. This research was based on the identification of proteins that would be associated with the early formation of baby neurons. Therefore, it was not possible to prove that full grown and functioning neurons were being grown in the nose, but it was assumed to be a reasonable possibly.
However, it really isn't a reasonable possibility. If there was an Intelligent Designer, then…
I just happen to come across this interesting cameo and snapped this fair use impromptu screen shot...
Who is it, what show is this, and if you are that good, what episode!
___________
posted from my iPad
In a very interesting way.
As a regular reader of this blog, you know that IQ and similar measures are determined by a number of factors, and for most "normal" (modal?) individuals, one's heritage (genes) is rarely important. Putting it another way, variation across individuals in IQ and other measures have been shown again and again to be determined by things like home environment, diet and nutrition, and even immediate social context. Here's another finding supporting this:
Our cognitive abilities and decision-making skills can be dramatically hindered in social settings where we feel…
The presumption being examined here is that humans are divisible into different groups (races would be one term for those groups) that are genetically distinct from one another in a way that causes those groups to have group level differences in average intelligence, as measured by IQ. More exactly, this post is about the sequence of arguments that are usually made when people try to make this assertion.
The argument usually starts out noting that there are dozens of papers that document group differences in IQ. I'll point out right now that most of those papers are published in journals with…
How can we begin to understand the way the brain works? The same way we begin to understand a city: by making a map. In this visually stunning talk, Allan Jones shows how his team is mapping which genes are turned on in each tiny region, and how it all connects up.
Siblings of those diagnosed with autism are more than 20 times as likely as members of the general population to also have autism. Some of these siblings also show evidence of autism-like but less marked cognitive and social communication problems. This suggests that autism has either an environmental cause typically found in all siblings during development or childhood or a strong heritable component, but there is not a known genetic link or a well established biological marker. A biological marker other than observed behavioral deficits would be a neurological phenotype such as might be…
Humans appear to have a reasonable amount of diversity in their sexual orientations, in what is often referred to as "gender" and in adult behavior generally. When convenient, people will point to "genes" as the "cause" of any particular subset of th is diversity (or all of it). When convenient, people will point to "culture" as the "cause" of ... whatever. The "real" story is more complicated, less clear, and very interesting. And, starting now, I promise to stop using so many "scare" quotes.
Prior to birth there are a number of factors than can influence things like gender or sexuality…
Behaviors are not caused by genes. There is not a gene that causes you to be good, or to be bad, or to be smart, or good at accounting, or to like bananas. There are, however, drives. "Drives" is a nicely vague term that we can all understand the meaning of. Thirst and hunger are drives we can all relate to. In fact, these drives are so basic, consistent and powerful that almost everyone has them, we share almost exact experiences in relation to them, and they can drive (as drives are wont to do) us to do extreme things when they are not met for long periods of time. While eating…
Tom Rees reports on a smart new study which tests the effect of religiosity on attitudes toward torture in the US. Using two different large surveys, the researchers first simply examined the correlation between religiosity and support for permitting torture. Realizing that conservative political ideology can also induce greater support for torture and can itself be driven by religiosity, they then compared the direct impact of religion on torture support with the indirect effect as mediated through political ideology.
What they found is that religiosity (measured in one case simply by how…
Peter Freed wants to you to know that Jonah Lehrer is Not a Neuroscientist. Lehrer doesn't claim to be, of course. He's a journalist and science writer who covers developments in neuroscience, and a good one at that.
Freed is concerned about how Lehrer handled a recent study on "the wisdom of crowds" in a recent op-ed in the Wall Street Journal. The wisdom of crowds is a long-standing and often-successful idea that you'll get a better prediction by aggregating the responses from a bunch of people posed with the same question than you'd get by simply asking a given expert, or even…
Richard Tokumei has written a book that is so bad he is ashamed to put his own name on it. "Richard Tokumei" is the pen name of a 'writer/editor in Southern California [with] degrees in Humanities and Phychology from the University of California Berkeley" and he has produced a book designed to anger everyone who hears of it in order to create needless sensation and thus, sell copies. Which, once people get their hands on, will make rather low quality toilet paper.
Monkeys On Our Backs: Why Conservatives and Liberals Are Both Wrong About Evolution includes an inexplicable mix of "correct"…
Via USA Today, we learn about a study showing that people who meditate frequently behave in a more rational manner than non-meditators, and they do so because different parts of their brain take charge of certain kinds of decisions.
The study was based around a common test of rational behavior called the Ultimatum Game. Two people sit at a table. One of them is given a sum of money ($20 in this case), and is told to split that however she wants with the other. Before she makes that decision, the other subject is told that if he rejects the share offered to him, neither player will get any…
There is no evidence that they did, but abundant evidence that they didn't. One example of this is found in how business in the US handle the inevitability of future rising costs of energy, and along with this collection of individual behaviors, the way the free market, the most intelligent and powerful of human activities, optimizes our economy.
It is interesting to see how often proof of the non-existence of anything like a Free Market (anywhere) and proof that humans should stop taking credit for being an "Intelligent Large Brained Hominid" come together. Over the last few weeks, we…
There are human universals. There, I said it. Now give me about a half hour to explain why this is both correct and a Falsehood. But first, some background and definition.
Most simply defined, a human universal is a trait, behavior or cultural feature that we find in all human societies. Men are always on average larger than women. All humans see the same exact range of colors because our eyes are the same. The range of emotions experienced by people is the same, and appears in facial expressions and other outward affect, in the same way across all humans.
The term "Human Universal"…
Human infants require more care than they should, if we form our expectations based on closely related species (apes, and more generally, Old World simian primates). It has been said that humans are born three months early. This is not accurate. It was thought that our body size predicted a 12 month gestation, and some suggested that Neanderthals would have had such, but this research conclusion has been set aside based on new analysis. But it is still true that developmentally, human children do not reach a stage of development that allows some degree of self care for a very long time…
Or, when the hunting season is closed, watch teh game (the guys), or when there are no sales, admire each other's shoes (the gals)?
This is, of course, a parody of the sociobiological, or in modern parlance, the "evolutionary psychology" argument linking behaviors that evolved in our species during the long slog known as The Pleistocene with today's behavior in the modern predator-free food-rich world. And, it is a very sound argument. If, by "sound" you mean "sounds good unless you listen really hard."
I list this argument among the falsehoods, but really, this is a category of argument…