cholera
Two or three thoughts about the current crisis.
When there is a major climate disaster in the US, people move. Since the US is big and has large gaps in population, it looks different than when a disaster happens in some other places. Five million (or more) Syrians leaving the Levant left a major mark across the globe. A half million leaving the Katrina hit zone was barely noticed on a global, or even national, scale, not just because it was one tenth the amount, but because of our size and space as well.
Something close to half the 400K or so displaced by Katrina (over half of them from…
Months after a severe earthquake devastated Haiti in 2010, UN peacekeeping troops exacerbated Haitians’ suffering by introducing cholera to the country, via waste that leaked from a UN housing base into the Artibonite river. The disease sickened 800,000 people and killed more than 9,000 – although a study at four sites in northern Haiti found the actual death toll could be substantially higher than the official count. In August 2016, UN Secretary General Ban Ki-Moon acknowledged the UN’s role in Haiti’s cholera epidemic, accepting moral but not legal responsibility.
The UN was working to…
Some thoughts for today: the bad news and good news for World Water Day. [First, I think every day should be World Water Day, not just March 22nd, but hey, that’s just me.]
Stop taking your tap water for granted. Go to your tap, draw a glass of water, and drink it. Then remember that nearly a billion people still do not have reliable access to safe, affordable tap water and cannot do what you've just done.
Stop taking your toilet for granted. Nearly 2.5 billion people (more people than lived on the planet in the 1930s) don’t have safe sanitation.
Do you know anyone who had cholera…
In a previous post here, I discussed the scourge of cholera – a waterborne disease largely vanquished in the wealthier nations by our water and wastewater treatment systems. Unfortunately, it remains widespread and lethal. Cholera is perhaps the most common and serious water-related disease, directly associated with the failure to provide safe drinking water and adequate sanitation to billions of people. Millions – mostly young children – die unnecessary deaths each year from these diseases.
This week is the 200th anniversary of the birth of the man who would help settle, once and for all,…
Haiti's cholera epidemic began in October 2010, as the country was still reeling from the devastation of the January 2010 earthquake. The epidemic has now claimed nearly 8,000 lives, and although transmission has slowed, more than 1,500 new cases are still reported each week. Evidence suggests the cholera bacteria arrived in Haiti via UN peacekeepers from Nepal and spread because of an inadequate sanitation system in peacekeeper housing. Last month, however, the UN responded to a compensation lawsuit by invoking immunity under section 29 of the Convention on the Privileges and Immunities of…
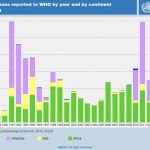
We’re bombarded with numbers every day. But seeing a number and understanding it are two different things. Far too often, the true “significance” of a figure is hidden, unknown, or misjudged. I will be returning to that theme often in these blog posts in the context of water, climate change, energy, and more. In particular, there is an important distinction between accuracy and precision.
Here is one example – reported cases of cholera worldwide. Cholera is perhaps the most widespread and serious water-related disease, directly associated with the failure to provide safe drinking water and…
Deborah Sontag's New York Times piece "Haiti's Cholera Outraced the Experts and Tainted the UN" is a reminder that while public attention to the earthquake-ravaged country has waned, cholera still presents a major threat to the country's people. It's also just a sad story about how one apparently small malfunction can have disastrous consequences for an entire nation.
The UN's independent experts concluded that the strain of cholera now afflicting Haitians had come from South Asia, and originated in the tributary behind a base used by Nepalese UN peacekeeiping troops, most likely from a…
Two years ago, a 7.0 earthquake struck Haiti, killing 300,000 Haitians and leaving 1.5 million homeless. Nine months later, a cholera epidemic began -- its first victim a 28-year-old man who bathed in and drank from a river that was likely contaminated by raw sewage from an encampment of UN peacekeepers from Nepal. Half a million people have been stricken by cholera since then, and 7,000 have died. New cases are being reported at a rate of roughly 200 per day.
Cholera is also spreading in the Dominican Republic, which shaires the island of Hispaniola with Haiti. Officials from CDC, UNICEF,…
Thailand is experiencing its worst flooding since 1942, and millions of people are affected. The death toll has reached 533, due mostly to drowning but also to electrocutions. CNN reports that more than 113,000 people have arrived at 1,700 government shelters set up across the country, and Bangkok officials have warned residents of interruptions to electricity and tap water.
In addition to immediate dangers like drowning, the potential for widespread disease outbreaks is worrisome.
Citing concerns about water-borne diseases spreading through contaminated floodwater, UNICEF announced that it…
Cross-posted from the American Geophysical Union's GeoSpace blog.
Even though the deadly cholera epidemic in Haiti is now spreading more slowly, health officials are still working to prevent as many new cases as possible. Detailed models of the disease's spread help those in charge of making public health decisions understand the effectiveness of control measures, from vaccines to investments in clean water supply and education.
A new study by Enrico Bertuzzo and colleagues just accepted for publication in Geophysical Research Letters looks at how the Haitian cholera outbreak is likely to…
Cholera has killed roughly 3,800 people in Haiti and sickened another 189,000, and it will continue to circulate in the population for the foreseeable future. The good news is that the number of new cases per week has dropped from 12,000, which it reached in November, to about 4,700, and the mortality rate has also decreased. Intensive treatment and prevention efforts (including provision of clean water and educational campaigns) have saved thousands of lives, and will have to continue even as the attention of the international community wanes.
David Cyranoski of Nature News points out that…
One year after a 7.0-magnitude earthquake killed more than 200,000 Haitians and left 1.5 million homeless, conditions in the Western Hemisphere's poorest nation are still grim. Cholera has killed 3,600 people and weakened many more; the UN warns that 650,000 may be affected over the next several months, and the death rate from the disease is an "unacceptably high" 3.6%. Elections in November were accompanied by widespread charges of fraud and voter intimidation, and it's still unclear which candidates will face off in an upcoming runoff.
More than a million Haitians still live in makeshift…
In Monday's post I mentioned how much I loved London when I visited - but London wasn't always such an appealing place. During the Industrial Revolution, it was filthy and polluted. The stench was appalling, and an episode of particularly foul smells from the Thames River in 1858 was known as the "Great Stink." Life expectancy in England's urban areas was markedly lower than in the countryside.
This filthy environment was the site of a public health breakthrough. During the 1854 cholera epidemic in London, the physician John Snow mapped the cholera cases from an outbreak in the Soho district…
Given that Haiti is suffering from the devastation of a major earthquake and a cholera epidemic, it's not surprising that voters yesterday encountered disorganized polling places where many were told their names weren't on the rolls. But there were also reports of violence and intimidation, polling places being ransacked and ballot boxes ripped open, and ballot-stuffing. In the afternoon, 12 of the 19 candiates for president joined together and called for the election to be canceled.
Meanwhile, the cholera epidemic continues. Haitian authorities report that more than 1,600 people have died…
When severe flooding in Pakistan left millions of people without food, shelter, and water, I wrote a post wondering why that disaster was getting less attention than Haiti's earthquake. I suspected the gradual nature of the disaster was part of the problem, and commenters had additional suggestions, ranging from Haiti's closeness to the US to the US public's overall view of Pakistan as a nation.
Last week, The New York Times' Lydia Polgreen put some numbers on the Haitian earthquake vs. Pakistani floods comparison and delved into reasons for the disparity:
In all, $3.4 billion has been…
Haiti's health ministry has reported that the death toll from the cholera epidemic has reached 917, and 14,642 victims have been hospitalized. The disease has been detected in six of the country's ten provinces, and the World Health Organization predicts that 200,000 Haitians will fall ill with cholera over the next six to 12 months.
The UN has made a plea for nearly $164 million in order to supply doctors, medicines, and water-purification equipment. The BBC points out that less than 40% of the aid for Haiti's post-earthquake reconstruction has reached the country, and the first portion of…
The United Nations humanitarian office reports that 9,971 cases of cholera have been confirmed in Haiti, and 643 people have died from the disease.
The Associated Press reported earlier this week that the epidemic has spread into Port-au-Prince, where close to half of the city's nearly 3 million residents are living in tent camps erected for those left homeless after the January earthquake. Conditions in the camps have deteriorated as a result of Hurricane Tomas, and many fear the disease will spread quickly through Port-au-Prince's camps and slums.
Haitian healthcare workers and…
It's a relief that Hurricane Tomas didn't destroy the camps in and around Port-au-Prince where 1.3 million survivors of Haiti's January earthquake are crowded. The storm hit western Haiti hardest, causing flooding and killing 20 people.
There are still concerns about how flooding will affect Haiti's cholera outbreak. The outbreak's official death toll is 544, CNN reports, and more than 8,000 cholera cases have been confirmed. So far, none of the confirmed cases is in Port-au-Prince, but 91 residents of a Port-au-Prince slums are being tested to see if they've been infected.
Cholera…
Months after it was hit by a devastating earthquake, Haiti is now battling an outbreak of cholera. So far, more than 1,500 cases have been reported and 142 victims have died of the disease, which causes severe diarrhea. The treatment is straightforward - rehydration therapy to reverse potentially deadly dehydration - but relies on hospitals being able to handle surges of weakened patients. It's been a century since Haiti last faced cholera, and until now everyone had been relieved that the earthquake hadn't spurred an outbreak.
The Guardian's Rory Carroll reports that the outbreak is taking…
Mark Pendergrast writes: To kick off this book club discussion of Inside the Outbreaks, I thought I would explain briefly how I came to write the book and then suggest some possible topics for discussion.
The origin of the book goes back to an email I got in 2004 from my old high school and college friend, Andy Vernon, who wrote that I should consider writing the history of the EIS. I emailed back to say that I was honored, but what was the EIS? I had never heard of it. I knew Andy worked on tuberculosis at the CDC, but I didn't know that he had been a state-based EIS officer from 1978…