In a previous post here, I discussed the scourge of cholera – a waterborne disease largely vanquished in the wealthier nations by our water and wastewater treatment systems. Unfortunately, it remains widespread and lethal. Cholera is perhaps the most common and serious water-related disease, directly associated with the failure to provide safe drinking water and adequate sanitation to billions of people. Millions – mostly young children – die unnecessary deaths each year from these diseases.
This week is the 200th anniversary of the birth of the man who would help settle, once and for all, the question of the cause of cholera. In the process, a legend would develop around him, an honorary society would be created in his name, websites would be created to discuss his role in water history, and a pub in London would be named after him.
Snow was born on March 15th, 1813 in York, England (Figure 1). He was not just one of the first scientists to use tools of “epidemiology;” he was also a pre-eminent physician. He was admitted to membership in the Royal College of Surgeons at the young age of 25; and he helped to deliver Queen Victoria’s baby (Prince Leopold) in 1853 using chloroform as an anesthetic, for which she was, apparently, quite grateful. He returned for a repeat performance for the birth of Princess Beatrice.
 Dr. John Snow, in 1857, shortly before his death. (Public domain photo.)
Dr. John Snow, in 1857, shortly before his death. (Public domain photo.)
Snow lived at a time when there was a fierce debate underway about whether cholera (and many other diseases) were caused by dirty air (or “miasmas”), dirty water, or other means of transmission. This was also a time when science was in full flower and advances in human understanding were racing ahead. In 1849, Snow published a treatise “On the Mode of Communication of Cholera,” which argued that it was caused by exposure to contaminated water. That book also cited case studies of the transmission of cholera in polluted waters from Rotherhithe, Manchester, Ilford, Bath, Newburn on the Tyne, and through the Black Sea Fleet. The local medical establishment was not convinced:
“Notwithstanding our opinion that Dr Snow has failed in proving that cholera is communicated in the mode in which he supposes it to be, he deserves the thanks of the profession for endeavouring to solve the mystery. It is only by close analysis of facts and the publication of new views, that we can hope to arrive at the truth”. (London Medical Gazette, 1849)
Snow continued his work on the issue. A breakthrough occurred in the mid-1850s when another in a series of severe cholera outbreaks hit London. He is best remembered today for his work in 1854, when he created a now famous map to show the link between cholera cases and water sources.
I recently wrote a book about the story of bottled water, which includes a discussion of the history of cholera, water treatment, and John Snow. In that book, I described Snow’s experience as follows:
“In the 1850s, the river smelled so bad on hot summer days that Parliament would adjourn because of the stink. Health officials in England had observed that cholera and typhoid mortality were five to six times higher in the poorer districts getting water from the sewage-contaminated Lower Thames compared to wealthier West London, which received cleaner water from upstream. In 1848, the Lambeth Water Company, one of several private water companies supplying London moved its water intake upstream on the Thames, above the worst of the sewage discharges, reducing illness in its service area.
In a now legendary experiment in 1854, Dr. John Snow, a London physician, conducted a simple yet brilliant test that helped to settle the debate about the transmission of cholera. Snow drew a map [see Figure 2 below] of a virulent cholera outbreak in one of the poorest neighborhoods of London – served by central wells and no sewage collection. He plotted the homes and numbers of people affected, and in a flash of insight, mapped the location of the wells that provided water for the hardest hit neighborhoods. The maps he generated and the interviews he conducted with the families of victims convinced him that the source of contamination was the water from the Broad Street well. He received permission from local authorities to remove the pump, which forced residents to go to other, uncontaminated wells for water. Within days, the outbreak subsided.” [from “Bottled and Sold: The Story Behind Our Obsession with Bottled Water” Island Press, Washington DC.]
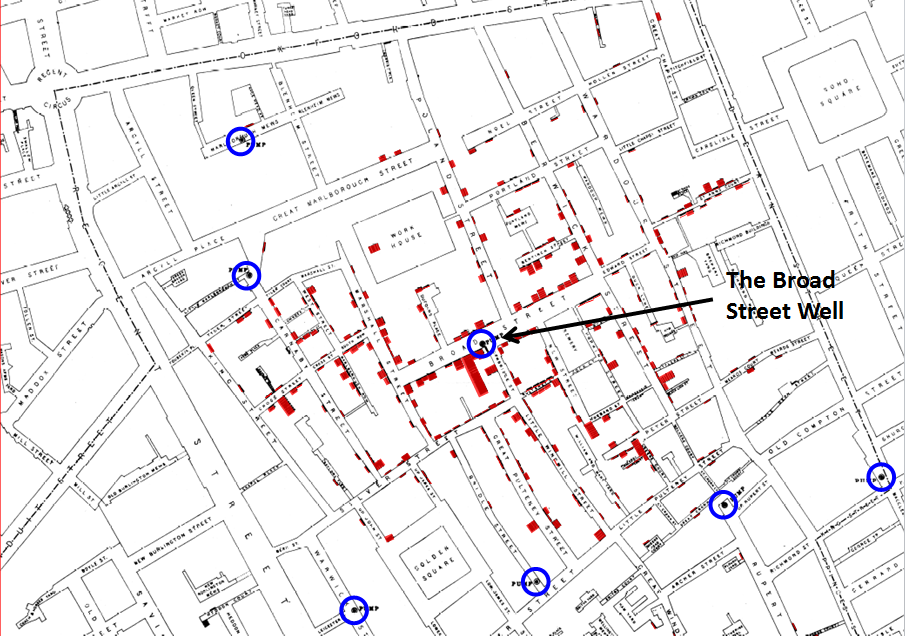 This is John Snow's famous map. On it, I've colored in red his column of bars, each of which represents a cholera death. I've also circled in blue the local water pumps, including the Broad Street pump -- servicing the well that was the source of cholera.
This is John Snow's famous map. On it, I've colored in red his column of bars, each of which represents a cholera death. I've also circled in blue the local water pumps, including the Broad Street pump -- servicing the well that was the source of cholera.
It took several additional decades for the evidence of a water link to cholera to become universally accepted, but that map is considered one of the first, if not the first, examples of mapping epidemiology. Over time, the map, and the additional research around water quality, led to a great expansion of water treatment, enhanced efforts to protect water sources from human and industrial wastes, and dramatic improvements in public health.
Snow died young – at the age of 45 in June 1858. If you’re in London, hoist a pint in his name for me.
Happy Birthday, John Snow.
-----------------------------------------------
Special thanks for some of the above materials, and for his enthusiasm (equal to or even greater than mine) for Snow, to Michael J. McGuire (also tweeting as @CaptDocMike). Here are some other John Snow resources:
Frerichs, R. R. John Snow. http://www.ph.ucla.edu/epi/snow.html (accessed March 11, 2013).
Hempel, S. 2007. The Strange Case of the Broad Street Pump: John Snow and the Mystery of Cholera. Los Angeles, California: University of California.
Johnson, S. 2006. The Ghost Map: The Story of London’s Most Terrifying Epidemic and How It Changed Science, Cities and the Modern World, New York City, New York: Riverhead Books.
Vinten-Johansen, P., H. Brody, N. Paneth, S. Rachman and M. Rip. 2003. Cholera, Chloroform, and the Science of Medicine. New York City, New York: Oxford University Press.

Along similar lines, have you ever read _Dirt: a Social History..._ by McLaughlin? (Cal Berkeley's Public Health library has a copy, otherwise it's expensive to buy online.) Absolutely fascinating for public health geeks, though at times nauseating. For example envision bathing twice a year and using perfume to mask the results of not doing so more often, or consider why barbers were at one time also minor surgeons. Makes one utterly thankful to live in a society where potable public water, sewage disposal, street cleaning, refuse disposal, and soaps and detergents, are reliable and effective.
Also, the collected papers of Col. George Waring, which can be found online with a bit of a search. Interestingly, Waring believed in the miasma theory and was skeptical of germ theory, which goes to show that sometimes one can have the wrong theory but still end up getting the right results ("drainage" aka sewage disposal, and street cleaning). A keyword search of "Waring" + "drainage" will also lead to historic documents on the development of household plumbing, which are interesting in their own right.
The purveyors of bottled water would probably love it if continued budget cutting resulted in the decline of potable public water supplies in the US. Whether or not they pounce on every opportunity to advance that cause remains to be seen, just as with the private prison industry's obvious benefit from cutting budgets for community police.
But there's also a certain misguided sector of the sustainability community that appears to disbelieve in germ theory. I have heard first-hand at meetings, where locally prominent experts, who are ideologically opposed to flush toilets, have strongly advocated self-contained composting toilets in urban apartment units. Aside from the issue that in most cities there is no nearby open land on which to utilize the composted human manure, there is also the *enormous* public health hazard of incompletely-composted manure in conjunction with infectious agents such as norovirus.
Envision some poor soul with intestinal flu, trying to carry a full compost container down a building's main stairway, and tripping, thereby splashing the contents on the walls and carpet. The building becomes a red-hot zone, and the outbreak spreads via the usual carelessness about hand-washing. Similar outcomes could occur with bacterial diseases. Composting toilets may be viable in rural environments where there is sufficient land to use the output, but *not* in cities, and *not* with untrained people handling the material.
As for me, I'm downright militant about drinking clean tap water.
Sanitation + vaccination = civilization.
"Sanitation + vaccination = civilization."
It is disheartening to think about the non-significant number of people who don't think vaccination belongs in that equation.
I just thought someone should point out that Scienceblogs hosts a blog named in honor of Dr. Snow's breakthrough.
In Fairness to John Snow http://wp.me/p2CmCK-8j . This other column offers some additional historical insight into what actually happened: the myth versus the reality of John Snow's effort -- not in an effort to diminish his contribution, but to clarify and support the history. Even I have bought into the myth to some degree! It remains a truly great story!