Consequences
There's more than a few climate bloggers who have a dirty little secret. We like to excoriate those who can't tell the difference between weather and climate, or herald every momentary drop in temperature as evidence that global warming has ended, or revel in each new report that suggests not every single square millimeter of the planet's surface is experiencing dramatic climate shifts. As we should. But many of us take a peek, every morning, at the daily version of a graph from the National Snow and Ice Data Center depicting current sea-ice extent in the Arctic.
We know that what happens…
"I thought I better come see the bears because the next time I am in this country they will be all gone."
-- Polar bear tourist in Churchill, Man.
Ecotourism. Sounds so responsible, or least, non-exploitative. But let's face it: Anyone who flies long-distance to get close to some endangered piece of nature at risk from climate change is doing their bit to push those species that much closer to extinction. A paper published recently in the Journal of Sustainable Tourism tries to quantify the irony. "The carbon cost of polar bear viewing tourism in Churchill, Canada" (Subs req'd) looks at the…
What happened at Three Mile Island in 1979 led to a new regulatory environment that increased the costs of building and running nuclear power reactors in the U.S. The environment was so hostile to the industry that no new reactors have been ordered since then. There are several in the planning stages, but none have been approved. The question now being debated among energy analysts is whether or not what's going on in the Gulf of Mexico at the moment will lead to similar challenges for the oil industry.
Of particular interest is the precedent set this week when BP agreed to pony up $20…
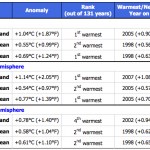
The latest report from the National Climatic Data Center reminds us that the planet is continuing to warm as expected. Most of the attention will be afforded to the global picture, for good reason:
The combined global land and ocean average surface temperature for May 2010 was 0.69°C (1.24°F) above the 20th century average of 14.8°C (58.6°F). This is the warmest such value on record since 1880.
Those of us living in the U.S. Southeast are sweltering through a record-breaking heat wave, so there will be much nodding of heads. Of course, regional weather isn't the point. So it's useful to…
Smoke and Mirrors:
Climate Change and Energy in the 21st Century
By Burton Richter
Cambridge University Press, 218 pages.
Do we really another book summarizing the science of climate change and the available response options? Sure. Why not? What's the harm? In this era of hyperfractionated audiences and echo-chambers, there's no such thing as too many arrows in our collective quiver. This one, by Nobel Prize-winning physicist Burton Richter, doesn't contribute anything new. But at this point in the conversation, there's not much new to contribute, just novel approaches to making the argument…
I've never been completely comfortable using the fate of small island states -- places like Tuvalu and Kiribati and the Seycelles that might be the first to go under as sea levels rise -- as poster kids for the consequences of climate change. For one thing, as difficult as it would be for their populations to abandon their homes, there's just not that many people involved, and so there was never any real chance that their pleas would have much of an effect on industrialized countries. The reality is people react to threats to their own quality of life, not those facing a tiny group on the…
NASA's James Hansen has few peers when it comes to the title of leading climatologist-turned-policy-wonk, but Mike Hulme of the University of East Anglia (yes, that university) is giving him a run for his money. Hulme's latest entry is a cautionary tale involving the challenges involved in geoengineering.
In Yale e360, Hulme argues that the technical obstacles to making the Earth's climate do what we want aside, the politics of trying to change the radiative heat balance of the atmosphere are problematic in the extreme.
Who, he asks,
is entitled to initiate the large-scale deployment of a…
Today marks the official start of North Atlantic hurricane season. So...
One of the key differences between genuine climatology and anti-scientific denialism of anthropogenic climate change is the flexibility of the former and the stubbornness of the latter when it comes to our ever-evolving understanding of how the world works. The connection between hurricanes and climate is a perfect example.
When the "An Inconvenient Truth" crew was filming Al Gore deliver his now-familiar presentation, they couldn't have anticipated that two major hurricanes would, as if on cue, roar through the Gulf of…
A paper in Nature Geoscience published early this month was much derided by the usual suspects in the pseudoskeptic community. Contrary to what many critics of "Methane emissions from extinct megafauna" claim, the research does not lead to the conclusion that humans are solely responsible for a global cooling event known as the Younger Dryas, which saw a brief reversal in the warming trend that brought the last ice age to an end. But it does remind us of just how interconnected are all the elements of the planetary ecosystem, and how dangerous it is to tinker with one of them.
The authors,…
Back in the winter of 1990-91, when I was a between-real-jobs freelancer hanging out in Vancouver with plenty of time on my hands to read, I would cycle down to Stanley Park each rainless day, find a quiet stretch of beach, and read. I went through dozens of books before returning to the working world, but the only book I remember in any detail is Bill McKibben's The End of Nature. It was the first full-length, popular-science take on climate change, and I've spent much of the last 20 years thinking and writing about the subject, thanks to that book. So has McKibben.
eaarth is an oddly…
The Boston Globe has assembled 40 outstanding photographs of what's happening in the Gulf. Click on the shot below to see the rest:
Most of the alarmism generated by climate predictions deals with sea level rise, drought, and biodiversity loss. But what happens to waterfront property, farms and polar bears could be the least of our worries if temperatures rise much more than a few degrees. A new paper in PNAS, "An adaptability limit to climate change due to heat stress," paints a much more dire future for much of the larger mammals on the planet, including humans.
In the paper, Steven Sherwood of the University of New South Wales and Matthew Huber of Purdue University try to estimate how warm the Earth can get before…