future
Many people in synthetic biology, including myself and much of my lab, are working on using biology to make things more efficiently, renewably, and sustainably. Being able to make plastic replacing biomaterials, chemicals, medicines, and fuels in living cells from renewable resources (especially in photosynthetic organisms that need only sunlight and water) will undoubtedly decrease our dependence on fossil fuels and with a lot of work in policy and process and infrastructure engineering may one day become truly sustainable. It's difficult to not notice, however, how unsustainable most…
I got a lot of interesting responses to my post about DIYbio and how modeling innovation in biotech on computer hacker culture may lead to a science that is less "democratized" than what is being proposed. My friend Adam pointed me to Jaron Lanier's work criticizing the "open" and "free" culture movements online as both unfair and leading to cultural stagnation. While I don't agree with all of Lanier's arguments about the prospects of an open digital culture, he makes a lot of really important points that resonate with my feelings about the future of science based on the open online model, in…
Last week's issue of Nature focused on the progress (or lack thereof) in genomics and related fields since the Human Genome Project (HGP) was completed ten years ago. In many ways, the era of genomics has yet to fulfill many of the promises made twenty years ago, but the investment in science and technology has at the same time made a valuable impact on many fields in basic science. Understanding this recent history of the genomics bubble is crucial to how we approach current science and technology investments in areas such as personal genomics and importantly, synthetic biology.
In a…
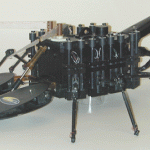
Because of my recent interest in autonomous, biologically inspired robots, my friend Tami sent me some fascinating links about designs and concepts for future flesh eating robots.
From New Scientist, furniture that captures vermin and uses the biomass to power fuel cells that run small electronics:
From Wired, Human corpse powered robots being developed by the Defense Department:
From the file marked "Evidently, many scientists have never seen even one scary sci-fi movie": The Defense Department is funding research into battlefield robots that power themselves by eating human corpses. What…
Cellularity is a new project by James King, a speculative designer working on biotechnology and interaction design. The project focuses on the potential future of smart pharmaceuticals, drug molecules surrounded by membranes that over time as technology advances may come to more and more closely resemble actually living things. He proposes a cellularity scale from totally non-living to really alive artificial cells. This quantification of "aliveness" in a way is something that may need to be done if some of the proposals of synthetic biology come to fruition. When does a membrane surrounding…
Synthetic biology deliberately equates genetic networks to electronic circuits, cells to machines, organisms to factories. In synthetic biology, every living can be thought of as a cyborg, a living machine that can be manipulated, changed to meet our needs, parts swapped in and out like a computer. Some projects in synthetic biology and biologically inspired engineering hope to bring the analogy a step further, combining biological and actual electronic and mechanical components into a single engineered unit, with the goal of essentially making tiny autonomous cyborgs.
There are a lot of…
The future potential of synthetic biology is usually discussed in terms of applications in fields like medicine, food science, and the environment. Genetically engineered life forms are being designed to make medicines cheaply, to target tumor cells, to make more nutritious food, or to make agricultural plants that are easier to grow with less of an environmental impact, to clean up pollution or produce sustainable biofuels. What if synthetic biology systems were instead designed for use in culture or entertainment?
David Benqué, a student in the Design Interactions program at the Royal…
"The history of any given technology is extraordinarily complex."
--Rob Carlson, Biology is Technology.
Analyzing the history of a technology requires a complex look at the social, economic, and political context in which it emerged, and the reciprocal influences that the developing technology exerts on these factors. Predicting what the future of a technology will be like, how it will affect the economy and understanding the potential risks and payoffs is much much harder. Rob Carlson's new book, Biology is Technology: The Promise, Peril, and New Business of…
Synthetic biology is still a new field, and victories are small and incremental. Much of the promise and peril of synthetic biology still lies in the future: genetic devices made to order, computer aided genome design, organisms specially constructed for specific industrial purposes. Will we use this biological technology for good--new more affordable and accessible drugs, better vaccines to emerging diseases, and clean energy--or evil--new deadly pathogens and immortal super soldiers? I think it's safe to say that almost everyone hopes that we'll get all of the good stuff without any of the…
I spend much of my life making the case for changing one's life (and not just one's life - for supporting political and social change that is associated with it) in fairly radical ways, very quickly. I spend a lot of my time writing, and periodically I get on a train or a bus or something and go stand up in front of people and make the same case. I know this is a diffcult thing for many people, whose infrastructure envelopes them and pushes them powerfully towards a particular way of life, so I try to make good arguments for doing it now. I make moral arguments, about the use of a fair…
How would you fancy a holiday to Greece or Thailand? Would you like to buy an iPhone or a new pair of shoes? Would you be keen to accept that enticing job offer? Our lives are riddled with choices that force us to imagine our future state of mind. The decisions we make hinge upon this act of time travel and a new study suggests that our mental simulations of our future happiness are strongly affected by the chemical dopamine.
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter, a chemical that carries signals within the brain. Among its many duties is a crucial role in signalling the feelings of enjoyment we…
ScienceWoman notes: Last week I gave away a couple of books to readers who enthusiastically promised to review the books. The books were mailed on Friday and I've already gotten the first review back. Talk about enthusiasm! Here's a review from Courtney of Courtney's Blog.
What Are You Optimistic About is one of Edge.org's "celebration of the ideas of the third culture" (for further information, read C.P. Snow's classic, The Two Cultures). There is an introduction by the famed scientist/philosopher Dennett, who says, "It can't all be true, but we need to test them."
Fig. 1. Courtney's…
In this week's Science Saturday, science writers Chris Mooney and Carl Zimmer look ahead at the scientific controversies and discoveries of the coming year. Will Craig Venter finally produce artificial life in 2009? Will NASA find proof of Martian life? Will the public become even less informed about science? And perhaps most importantly, will Obama's science policy improve on Bush's?
tags: SEED magazine, sciencebloggers, Universe in 2008
Have you read your February 2008 copy of SEED magazine yet? I have received my copy and discovered that I have finally been published in a magazine after years of rejection letters (yippee) because the editor included a few of my responses to two questions they asked that were included in their "Universe in 2008" piece (p 69). The questions;
What would you like to be blogging about in 2008?
What do you fear you'll be blogging about in 2008?
My responses (only a very very few of which appeared in SEED) are below the fold;
In 2008, I…