livestock
Last week, the journal Antibiotic Agents and Chemotherapy posted an accepted manuscript that contains some very bad news: an easy-to-spread gene that makes bacteria resistant to an important class of antibiotics has been found in samples from a US pig farm.
A team of researchers from Ohio State University, led by Thomas Wittum, collected samples from pigs and buildings at a pig facility over five months in 2015. They found that several of the samples contained carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE). Back in 2013, CDC Director Thomas Frieden held a press briefing on this "nightmare…
Photo by: Myrabella / Wikimedia Commons, via Wikimedia Commons
With the approach of summer, a timely study was published in the American Journal of Physiology - Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology on whether inflammation plays a role in heat stress-related complications in muscles. Heat stress is a major problem in the livestock industry. In the United States alone it is reportedly associated with a loss of approximately $158 billion annually in the swine industry. To cool off, swine seek shade and often mud baths (which mimic sweating by …
For the first time, the World Health Organization has examined antimicrobial resistance globally, and the grim findings won't be surprising to anyone who's been following this issue. (Last year, the US CDC and UK's Chief Medical Officer issued reports with similarly alarming warnings.) The WHO authors write in the report summary:
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an increasingly serious threat to global public health. AMR develops when a microorganism (bacteria, fungus, virus or parasite) no longer responds to a drug to which it was originally sensitive. This means that standard treatments no…
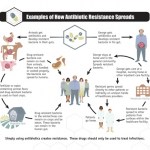
Antibiotic-resistant infections kill 23,000 people in the US and sicken two million each year, and the problem is getting worse, warns a new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States, 2013 ranks several strains of bacteria according to their current and projected health and economic impacts. It describes 18 microorganisms whose threat levels are "urgent," "serious," or "concerning."
CDC identifies three bacteria as urgent threats: Clostridium difficile, Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE), and Drug-resistant…
In a recent study comparing workers at industrial livestock operations and those employed at antibiotic-free livestock operations, researchers found that industrial workers were much more likely to carry livestock-associated strains of drug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, more commonly and scarily known as MRSA.
First, it's important to note that both groups of workers had a similar prevalence of S. aureus and methicillin-resistant S. Aureus (MRSA); however, it was overwhelmingly workers at industrial livestock operations, sometimes known as concentrated animal feeding operations or CAFOs,…
This week is Get Smart About Antibiotics Week, and CDC is promoting awareness about when these important drugs should and shouldn't be used. Overuse of antibiotics speeds the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and infections from these bacteria are much harder to treat.
Many of our readers are probably already familiar with CDC's message, which boils down to the fact that antibiotics don't cure viral infections (colds, flu, most bronchitis) and the reminder that when you are prescribed antibiotics, you need take the entire course of drugs rather than stopping once you feel better.…
If you haven't yet read Maryn McKenna's riveting Atlantic article "How Your Chicken Dinner is Creating a Drug-Resistant Superbug," you should. McKenna, working with the with the Food and Environment Reporting Network, has delved into research that's been accumulating about the association between the extensive use of antibiotics in poultry and the increase in drug-resistant urinary tract infections.
A quick bit of background: For decades, health officials and advocates have been concerned about the overuse of antibiotics. The more you use an antibiotic, the more quickly bacteria resistant to…
Yesterday, the FDA announced a new program that has the potential to slash the routine use of antibiotics by livestock producers. The routine administration of antibiotics to livestock with no signs of sickness helps animals grow more quickly, but it's also a significant contributor to the rise of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. An estimated 70% of the antibiotics sold in the US are given to non-human animals, and most of them are the same drugs that humans rely on to treat our illnesses.
Gardiner Harris's New York Times article about FDA's announcement bears the exciting (to me, anyway)…
No, not the kind used in track and field (although if you really want to jump over them I won't stop you), I mean the sort used to keep livestock in without breaking the budget on fencing. They look cool, and now is the perfect time of year to prune out branches and hurdle making materials. We use low ones to keep chickens out of spots we don't want, and have a few that we use for moving livestock to create chutes - but I'm working on more. As long as it is time to prune trees and cut wood anyway, you might as well make some fence as well!
Two tutorials, first a written one here from the…
Just received an email from Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases saying that my recent article, The Emergence of Staphylococcus aureus ST398, will be available for free online for the next two weeks. It was submitted roughly a year ago so it's already a bit dated in this quick-moving field, but provides an overview of "livestock-associated" MRSA up to mid-2010 or so--including food-associated MRSA.
It is pouring down rain - Tropical Storm Nicole is dumping 5 inches on us - and the dogs are barking out of control. I can't see a thing in the storm, but I suddenly realize what they must be barking at - I forgot to put Blackberry in the barn.
Blackberry, you see, is our pet rooster. He's so gentle than my children carry him around. Isaiah, who has a special rapport with animals snuggles him under his arm. In the winter, the children tried to teach him to ski down the plow piles. In the summer, they come running when Blackberry roams into the road, which for some reason, he does daily…
The Sharks and the Jets are fighting over by the compost pile. Well, ok, maybe not quite, but it has that feel to it. You see, we have two street-gangs of ducks. The first ones, Pekins and one ratty looking Rouen who is shooting for the "oldest living duck record" have been around for a bit. The Rouen was the only duck on our farm for about two years, after his girlfriend succumbed to the siren song of the creek and got eaten by something. Then, this year on Christmas morning (which would make a great Christmas miracle story if a. I were a Christian and b. it weren't ducks ;-)), a group…
A jaguar (Panthera onca). From Flickr user Prosper 973.
One year ago this week Macho B was euthanized. He had been captured in mid-February of 2009, the only known jaguar living inside the United States, but after he was caught and fitted with a radio collar his health quickly deteriorated. When he nearly stopped moving he was recaptured, taken to the Phoenix zoo, and put to sleep when it was discovered that he was suffering from irreparable kidney failure.
At first it seemed as if his capture was a lucky accident, but a later investigation by the Fish and Wildlife Service found that the…
Once You've Got the Chickens, You'll Hardly Notice the Yaks: Re-Inventing the Diversified Small Farm
Over at ye olde blogge, on one of my Independence Days updates, a reader commented on something that I'd posted. I'd mentioned that we are having trouble with goat parasites - most specifically, meningeal worm. Meningeal worm is a parasite is hosted by snails and transmitted by the feces of white tailed deer. It is worst in camelids like llamas and alpacas, but goats are a secondary host, and two of does, Selene and Mina, have it. It is most common after a wet summer and warm fall - this past summer was the wettest in living memory here - we had almost 20 inches of rain in June alone, and…
tags: global warming, humor, behavior, streaming video
According to the Christian Science Monitor, cows are one of the main culprits in global warming. This streaming video shows how [0:39].
Humans have been blamed for the disappearance of species before but never quite like this. Scientists at the University of Oxford have found evidence that two species of bacteria are merging into one. The two species are swapping genetic material at such a high rate that they are on the road to sharing a single, common genome. Their genetic merger is probably the result of being thrust into a new environment - the intestines of heavily farmed chickens, cattle and other domesticated livestock.
The two bacteria in question - Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli - are two of the most…