silicosis
I felt a little like Claude Rains (as Capt. Louis Renault) in the film Casablanca. He's the actor with the famous line "I'm shocked, shocked to find that gambling is going on here." On Sunday my neighbor asked me: “What do you think about all those coal miners with black lung?”
“Shocked, shocked,” I was tempted to say, but I’m not the least bit shocked.
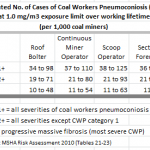
My neighbor was referring to the latest story by NPR’s Howard Berkes about nearly 2,000 cases of progressive massive pulmonary fibrosis (PMF) diagnosed in the last six years among Appalachian coal miners. Two thousand cases is a hefty…
At the Center for Public Integrity, Talia Buford and Maryam Jameel investigate federal contractors that receive billions in public funds despite committing wage violations against their workers. In analyzing Department of Labor data on more than 1,100 egregious violators, the reporters found that federal agencies modified or granted contracts totaling $18 billion to 68 contractors with proven wage violations. The Department of Defense contracted with the most wage violators.
Under Obama, labor officials had attempted to address the problem with the Fair Pay and Safe Workplaces rule, which…
Mining is one of the most dangerous jobs in America, with more than 600 workers dying in fatal workplace incidents between 2004 and the beginning of July. And many more miners die long after they’ve left the mines from occupational illnesses such as black lung disease, while others live with the debilitating aftermath of workplace injuries. Today, researchers know a great deal about the health risks miners face on the job, but some pretty big gaps remain.
Kristin Yeoman and her colleagues at the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) hope to begin closing that knowledge…
This post is dedicated to J.T. Knuckles. He died in 1998 at age 58 from silicosis.
JT Knuckles, foundry worker from Saginaw, MI (1996).
I first met J.T. Knuckles in 1996. He spoke at a press event at which former Labor Secretary Robert Reich announced a national campaign to eliminate silicosis. “If it’s silica, it’s not just dust” was the campaign slogan. Today, 20 years after I met J.T. Knuckles, current Labor Secretary Tom Perez announced an OSHA standard designed to prevent silicosis.
I watched this morning a live stream of Secretary Perez's announcement. He shared some of…
The U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration is no stranger to budget cuts — the agency is already so underfunded that it would take its inspectors nearly a century, on average, to visit every U.S. workplace at least once. In some states, it would take two centuries. Unfortunately, appropriations bills now making their way through Congress don’t bode much better for OSHA.
Earlier this month, the National Council for Occupational Safety and Health (National COSH) and Public Citizen, along with 74 fellow organizations that care about worker health and safety, sent a letter to…
This week, the Center for Public Integrity launched a new investigative series into the failure of regulators to protect workers for toxic exposures. The series begins with the story of a bricklayer who developed acute silicosis after exposure to silica, a deadly substance that threatens more than 2 million workers and that OSHA has been struggling to regulate for 40 years. The bricklayer, Chris Johnson, is just 40 years old and can expect to survive less than five years. Reporters Jim Morris, Jamie Smith Hopkins and Maryam Jameel write:
An 18-month investigation by the Center for Public…
While silicosis-related deaths have declined, it remains a serious occupational health risk and one that requires continued public health attention, according to recent data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
In the Feb. 13 issue of CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), researchers noted that while annual silicosis deaths have dropped from 164 in 2001 to 101 in 2010, dangerous silica exposure has been newly documented in occupations related to hydraulic fracturing (fracking) and the installation of engineered stone countertops. Overall during the 2001-2010 time…
This week will mark the next big step in efforts to institute a federal regulation to protect workers who are exposed to respirable crystalline silica. Tuesday, March 18 will be the first of 14 days of testimony and debate about a proposed silica rule which was released in September 2013 by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration’s (OSHA). The “deadly dust” is associated with malignant and non-malignant respiratory diseases and other adverse health conditions. The hazard has been recognized for centuries, but the U.S. does not have a comprehensive rule on the books to protect the…
Two economists, funded by right-wing, university-housed think tanks, recently submitted their views on OSHA's proposed rule to protect silica-exposed workers. Michael L. Marlow with George Mason University’s Mercatus Center, and Susan Dudley of George Washington University’s Regulatory Studies Center, describe OSHA's proposal as flawed, sloppy, weak and unsubstantiated. Funny, those are some of the terms I used to describe their analyses.
Marlow offers a litany of cockamamie reasons that OSHA should scrap its proposed rule. He says, for example, that OSHA needs to consider a wider set of…
At least 1.7 million US workers are exposed to respirable crystalline silica each year, this according to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). These exposures occur in a variety of industries, among them construction, sandblasting, mining, masonry, stone and quarry work, and in the rapidly expanding method of oil and gas extraction known as hydraulic fracturing or fracking. This exposure can lead to silicosis, an irreversible, and sometimes fatal, lung disease that is only caused by inhaling respirable silica dust. Silica exposure also puts exposed…
Who paid for the study? That's an important piece of information to have when considering a study's methods and reported findings. Financial ties are the most obvious conflicts of interest, but others include pre-publication review and other requirements imposed by a study’s sponsors.
Scientists publishing papers in the leading biomedical journals have, for at least ten years, been providing readers with disclosures of real or potential conflicts. The editors of more than 1,300 medical journals require authors to comply with specific disclosure policies. Researchers from…
Earlier this month, the long-awaited, three-year delayed OSHA silica proposal was published. It's a proposed regulation designed to protect workers employed in construction, foundries, glassmaking, road building and other industries from silicosis, lung cancer and other silica-related diseases.
The proposal does not cover, however, some of the most heavily exposed workers in the U.S.: those employed in the mining industry. These are the workers who routinely drill, cut and load tons of quartz, some of whom work day after day in clouds of silica-laden dust. Protections for…
Occupational health hazards are often hidden, and may not even be appropriately disclosed to workers who are exposed. They are usually shielded from public view, meaning they don't get the attention needed to ensure protections are put in place to address them. But every once in a while, hazards to workers' health are right in front of you.
Yesterday morning, I was driving on FM 1626 in Kyle, TX and passed this scene: Two construction workers standing in a nasty cloud of dust. The men were working at the new campus of Austin Community College in Hays County, TX and…
As Liz Borkowski noted yesterday, we are following up on a tradition that we started last year to mark Labor Day. We released our second annual review of U.S. occupational health and safety for Labor Day 2013.
Liz explained in her post our objectives in preparing the report. She also highlighted its first section which profiles some of the best research from the year published in both peer-reviewed journals and by non-profit organizations. Here’s a peek at section two of the report on activities at the federal level:
Sequestration and other budget cuts have affected our…
President Obama's regulatory czar, Howard Shelanski, has been on the job for a month. During his confirmation hearing Shelanski expressed his commitment to transparency. He suggested it was one of his key priorities within the White House's Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs (OIRA) which is housed within the Office of Management and Budget (OMB). As noted, however, by CPR scholar Sidney Shapiro and his colleague James Goodwin, OIRA has a long history of secrecy with respect to its role in the centralized review of agencies' regulatory activities. Many in the…
After more than 900 days of "review" by the White House's Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs (OIRA), OSHA announced it was publishing a proposed rule to protect workers who are exposed to respirable crystalline silica. It's a workplace hazard that causes the irreversible and progressive lung disease silicosis, and is also associated with lung cancer, autoimmune disorders and kidney disease. About 2.2 million workers are exposed to the fine dust in their jobs, many of which are employed in the construction industry. I've been writing here for about two years on the…
Employers in British Columbia's (BC) construction industry recognized that workers were exposed to respirable silica and other rock dust. What they needed was a standard from the province's worker safety regulatory body on how to identify and control the hazard. The BC Construction Association, which represents 2,500 companies and the Council of Construction Associations (COCA) formally requested a standard on silica to fill the regulatory gap. In BC, worker safety regulations are proposed and adopted through their Workers' Compensation Board, part of WorkSafeBC. …
A funny thing happened when representatives of U.S. foundries met on March 12 with White House officials to complain about a not-yet-proposed worker safety regulation. The industry group seemed to forget that the targets of their complaints are contained in their own best practices publication.
The American Foundry Society (AFS) requested the meeting with the Office of Management and Budget's (OMB) Office of Information and Regulatory Affairs (OIRA) to discuss a draft proposed rule by the Labor Department's OSHA to protect workers exposed to respirable crystalline silica. AFS…
Imagine an organization that is given 90 days to complete a task, but after two years still hasn't finished the job. When you ask them 'what's taking so long?' or 'when we'll you be done?' they respond with 'no comment.'
That's the frustrating situation encountered by the U.S. public health and worker safety community when it comes to the Obama Administration and a proposed rule to protect workers from respirable crystalline silica. The proposed regulation would potentially affect workers involved in stonecutting, sandblasting, tuckpointing, brickmaking, foundries, and…
I wonder sometimes if House Republicans have the same reading list as former Alaska Governor Sarah Palin. They obviously didn't read the series of articles about black lung disease in U.S. coal miners prepared by Chris Hamby and Jim Morris of the Center for Public Integrity, and Ken Ward Jr., of the Charleston (WV) Gazette. Coal mine workers in their 30's, 40's and 50's are developing the fast-progressing form of the lung disease. The stories lay out in detail some of the reasons for the epidemic, as well as the ineffective regulatory and enforcement system that fails to…