Having been trained as an evolutionary biologist, I've always thought that the medical literature avoids using the word evolution: instead, words like emergence, development, spread, and acquisition are used. In PLos Biology, there's an article that quantifies what I've always suspected:
The increase in resistance of human pathogens to antimicrobial agents is one of the best-documented examples of evolution in action at the present time, and because it has direct life-and-death consequences, it provides the strongest rationale for teaching evolutionary biology as a rigorous science in high school biology curricula, universities, and medical schools. In spite of the importance of antimicrobial resistance, we show that the actual word "evolution" is rarely used in the papers describing this research. Instead, antimicrobial resistance is said to "emerge," "arise," or "spread" rather than "evolve." Moreover, we show that the failure to use the word "evolution" by the scientific community may have a direct impact on the public perception of the importance of evolutionary biology in our everyday lives.
The authors present some experimental data showing that there is a 'trickle effect' of the medical use of the word evolution into the popular literature; when the word evolution is used in the scientific literature, it is more likely to be used in the popular literature:
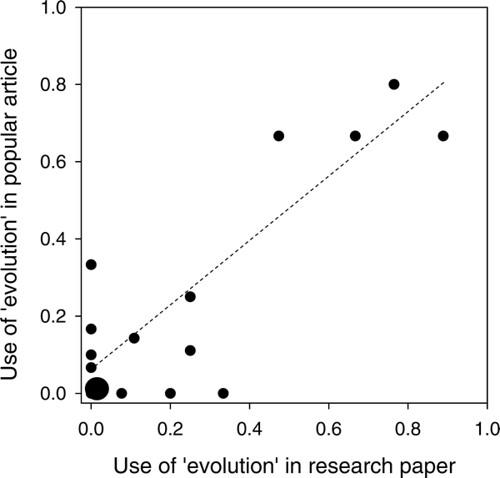
(legend from the paper) This graph shows the relationship between the frequency of use of the word "evolution" in popular press articles addressing antimicrobial resistance and the frequency of its use in the corresponding research article. Most of the articles included were in the biomedical literature (Text S1). The point at the origin represents nine pairs for which "evolution" was mentioned neither in the scientific nor in the popular version. The regression is highly significant (d.f. = 21, p 0.0001, Ã = 0.76; weighted arcsine square root transformed; points and fitted line in figure represent untransformed data).
The whole paper is definitely worth a read (and I think it's quite accessible to non-experts):
Evolution by Any Other Name: Antibiotic Resistance and Avoidance of the E-Word Antonovics J, Abbate JL, Baker CH, Daley D, Hood ME, et al. PLoS Biology Vol. 5, No. 2, e30 doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0050030

Ah, but do they ever used the Intelligent Design term "poof"?