Antibiotic resistance
A claim that scientists need to quit making:
I've written about these types of claims before. The first one--a claim that antimicrobial peptides were essentially "resistance proof," was proven to be embarrassingly wrong in a laboratory test. Resistance not only evolved, but it evolved independently in almost every instance they tested (using E. coli and Pseudomonas species), taking only 600-700 generations--a relative blip in microbial time. Oops.
A very similar claim made the rounds in 2014, and the newest one is out today--a report of a "super vancomycin" that, as noted…
Most news on the dangers of antibiotic-resistant infections focus on adults. But children are very much at risk too. In fact, a recent study found that U.S. children have experienced a 700 percent surge in infections caused by particular bacteria that’s both resistant to multiple antibiotics and responsible for growing numbers of serious bacterial infections in kids.
“These organisms are scary, they’re hard to treat and respond to few antibiotics…and it’s the type of antibiotic resistance that’s capable of spreading itself to adjacent bacteria even if those bacteria haven’t been exposed to…
Picture of a komodo dragon by CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Researchers studying komodo dragons (Varanus komodoensis) at George Mason University discovered 48 previously unknown peptides in their blood that might have antimicrobial properties. Their findings were published in the Journal of Proteome Research. For the largest lizard, these peptides may help prevent the animals from getting infections from their own saliva, which is host to at least 57 species of bacteria. With this number of bacteria, it is easy to understand why they evolved so many…
A few of the recent pieces I've liked:
Maryn McKenna at National Geographic’s Germination: How We'll Tackle Diseases That Are Becoming Untreatable (“The United Nations just declared antibiotic resistance “the greatest and most urgent global risk.” Here’s what they’re going to do about it.”)
Kelli Garcia in US News & World Report: We Can’t Wait: With Congress unconscionably failing to act, states must move quickly to protect pregnant women from Zika
Kelly Heyboer at NJ.com: The Invisible Workforce: Death, discrimination and despair in N.J.'s temp industry
Alex Campbell and Katie J.M. Baker…
Ever year about 23,000 people die of infections from antibiotic resistant bacterial.
Here is a film of bacteria evolving from regular old bacteria into killer superbugs. On a coffee table size Petri dish.
You can get the story at NPR, where you will learn that
"Getting more people to understand how quickly bacteria evolve antibiotic resistance might help people understand why they shouldn't be prescribed antibiotics. The drug resistance is not some abstract threat. It's real."
Last year, researchers identified a gene that confers resistance to "last-resort" antibiotic colistin. They found it in several E. coli isolates in China, and it didn't take long for other researchers around the world to find the same gene, mcr-1, in stored samples once they started looking for it. Researchers have now found mcr-1 in isolates from 32 countries.
The US wasn't among the initial list of countries finding mcr-1, but it didn't take long for that to change. In May, Walter Reed Army Institute of Research scientists reported finding mcr-1 in E. coli cultured from the urine of a…
The first observation of a bacterial gene called MCR-1 in the United States has scientists worried, if not surprised. The gene provides resistance to colistin, an antibiotic with nasty side effects used to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria. On Aetiology, Tara C. Smith writes "colistin has seen a new life in the last decade or so as a last line of defense against some of these almost-untreatable infections." But now, bacteria wielding MCR-1 threaten to leave humans defenseless. On The Pump Handle, Liz Borkowski explains "MCR-1 is of particular concern because it’s carried on a plasmid, a…
E. coli, from Wikipedia commons
We've been expecting it, and now it's here.
Yesterday, two article were released showing that MCR-1, the plasmid-associated gene that provides resistance to the antibiotic colistin, has been found in the United States. And not just in one place, but in two distinct cases: a woman with a urinary tract infection (UTI) in Pennsylvania, reported in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, and a positive sample taken from a pig's intestine as part of the National Antimicrobial…
On The Pump Handle, Liz Borkowski reports another crack in one of the pillars of modern life—antibiotics. New research in China shows that a family of bacteria called Enterobacteriaceae (which includes E. coli and Salmonella) have acquired a gene that provides resistance to a last-resort antibiotic known as Colistin. These species of bacteria do not have to evolve resistance individually—in fact, they can trade antibiotic-resistant genes with one another using "transmissible pieces of DNA–plasmids, transposons, phage." As Tara Smith writes, "Since the development of penicillin, we have been…
During the holiday season, Kim, Liz and I are taking a short break from blogging. We are posting some of our favorite posts from the past year. Here’s one of them, originally posted on May 27, 2015:
by Kim Krisberg
For more than a decade, biologist Mariam Barlow has been working on the theory that administering antibiotics on a rotating basis could be a solution to antibiotic resistance. After years of research, Barlow had lots of data, but she needed a more precise way to make sense of it all — something that was so specific it could easily be used to treat patients. So, she joined…
A pig flying at the Minnesota state fair. Picture by TCS.
I've been involved in a few discussions of late on science-based sites around yon web on antibiotic resistance and agriculture--specifically, the campaign to get fast food giant Subway to stop using meat raised on antibiotics, and a graphic by CommonGround using Animal Health Institute data, suggesting that agricultural animals aren't an important source of resistant bacteria. Discussing these topics has shown me there's a lot of misunderstanding of issues in antibiotic resistance, even among those who consider themselves…
A groundbreaking study published in PLOS ONE offers hope that scientists can reverse the development of antibiotic resistance among bacteria with the help of "a mathematical model that pinpoints optimal antibiotic cycling patterns." On The Pump Handle, Kim Krisberg writes, "the research comes at a time of widespread concern that without a coordinated, well-funded response to growing antibiotic resistance, medicine could lose some of its most effective, life-saving tools." The collaboration between biologists and mathematicians yielded a piece of software dubbed "Time Machine" that "computes…
For more than a decade, biologist Mariam Barlow has been working on the theory that administering antibiotics on a rotating basis could be a solution to antibiotic resistance. After years of research, Barlow had lots of data, but she needed a more precise way to make sense of it all — something that was so specific it could easily be used to treat patients. So, she joined forces with a team of mathematicians. And the amazing results could help solve an enormous, worldwide problem.
In a nutshell, the team of biologists and mathematicians developed a software program that generates a road map…
I've been working on livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus and farming now for almost a decade. In that time, work from my lab has shown that, first, the "livestock-associated" strain of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) that was found originally in Europe and then in Canada, ST398, is in the United States in pigs and farmers; that it's present here in raw meat products; that "LA" S. aureus can be found not only in the agriculture-intensive Midwest, but also in tiny pig states like Connecticut. With collaborators, we've also shown that ST398 can be found in unexpected…
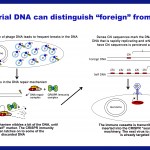
Foreigner or native-born? Your immune system discriminates between them, as do those of bacteria. Yes indeed, bacteria do have immune systems – pretty complex ones at that. And like any useful immune system, the bacterial ones must have a good technique for distinguishing “foreign” from “self.”
You may even have heard of the bacterial immune system: It’s called CRISPR, and it’s used in biology research around the world for DNA engineering and genome editing. CRISPR normally inserts short DNA sequences taken from phages – viruses that invade bacteria – into special slots called spacers within…
As we've written before, the routine use of antibiotics in livestock operations contributes to the global problem of bacteria resistant to antibiotics. So I was delighted to visit Maryn McKenna's Superbug blog and read that Perdue Farms, the US's third-largest chicken producer, has announced that it has stopped using antibiotics for growth promotion or disease prevention, and is no longer using antibiotics important for human medicine in 95% of its birds. (McKenna is always my favorite source for all things antibiotic-related; check out her antibiotics archive to learn more about…
Eleven years ago, two scientists made a bet. One scientist wagered that a new type of antimicrobial agent, called antimicrobial peptides, would not elicit resistance from bacterial populations which were treated with the drugs. Antimicrobial peptides are short proteins (typically 15-50 amino acids in length) that are often positively charged. They are also a part of our body's own innate immune system, and present in other species from bacteria to plants. It is thought that these peptides work primarily by disrupting the integrity of the bacterial cell, often by poking…
After this post on antibiotic resistance, many of you may have seen an exchange on Twitter calling me out for being "knee-jerk" about my call to action to do something about the overuse of antibiotics. In that post, I focused on antibiotic use in agriculture, giving only brief mention to human clinical use. There are a number of reasons for this, and while I didn't discuss them extensively on Twitter, I did want to provide an overview here in order to better explain my position and concern about antibiotic use in agriculture.
How are antibiotics used in animal production?
To start, some…
It's a parent's worst nightmare. Your healthy child is suddenly ill. The doctors you've trusted to treat him are unable to do anything about it. Drugs that we've relied upon for decades are becoming increasingly useless as bacteria evolve resistance to them. New drugs are few and far between. Old drugs, shelved because of their toxic side-effects, are being brought in as last resorts--kidney failure, after all, is better than certain death.
Unfortunately, this is increasingly the state of medicine today, and people are dying from it. The World Health Organization even recently …
For the first time, the World Health Organization has examined antimicrobial resistance globally, and the grim findings won't be surprising to anyone who's been following this issue. (Last year, the US CDC and UK's Chief Medical Officer issued reports with similarly alarming warnings.) The WHO authors write in the report summary:
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is an increasingly serious threat to global public health. AMR develops when a microorganism (bacteria, fungus, virus or parasite) no longer responds to a drug to which it was originally sensitive. This means that standard treatments no…