Eyjafjallajökull
This week has been destroyed by workshops and my last death throes with a paper I am submitting on my research in New Zealand. And to think, I thought it might settle down a little after the students left.
To news!
Ash fall on a taxi cab near Guatemala's Pacaya.
Pacaya in Guatemala erupted yesterday causing evacuations of people near the volcano and the closure of Guatemala City's main airport. Pacaya is a mere ~25 km from the capitol of this Central American nation. Tragically, a news reporter from one of the capitol's TV stations died when they were struck by volcanic debris, again…
Brief news!
Lava flows reaching the sea at Kilauea in Hawai`i. Image from November 2009, courtesy of HVO/USGS.
The Alert Status at Cleveland in the Alaskan Aleutian Islands was raised to Yellow (Advisory) by the Alaska Volcano Observatory after new signs of activity emerged. The latest report from AVO on the volcano says a thermal anomaly has been spotted at the summit, which typically is one of the first signs that the volcano is entering an eruption period. However, there is no real-time seismic monitoring for Cleveland, so that is the only clue (right now) that AVO has. Cleveland is a…
For all of you going into withdrawal now that Eyjafjallajökull seems to have quieted down, there are two eruptions of note that aren't in the North Atlantic:
Undated image of the Barujari cone at Mt. Rinjani in Indonesia.
Arenal in Costa Rica - which is almost always sputtering away - had a more significant explosive and effusive event today. The volcano produced enough ash, bombs and gas emissions - along with 8 lava flows (or avalanches, depending on the source) - to prompt the evacuation of the National Park around the volcano. Arenal has had numerous strombolian eruptions over the last…
The small steam plume from Eyjafjallajökull on May 23, 2010, where explosive eruptive activity has ceased for now.
The big news over the weekend, at least volcanically, was that Eyjafjallajökull seems to have entered a period of relative quiet. The eruption has died down dramatically, with the last ash explosion occurring two days ago. Since then, the vent has still be producing a significant steam plume that reaches 3 km / 10,000 feet, but none of the ash-laden explosions that marked the earlier parts of the eruption have occurred (meaning the airspace over the North Atlantic and Europe…
The ash plume from Eyjafjallajökull, piercing the cloud deck above the volcano. Image courtesy of the Icelandic Met Office, taken on May 13, 2010. See the latest report on the eruption.
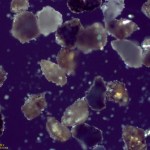
With all the rapid fire news on eruptions as of late, combined with my busy schedule during the school year, I haven't been able to post as many articles on some basic aspects of volcanology. I will try to remedy some of this over the summer and the first will look at volcanic ash and specifically the ash from Eyjafjallajökull. I've taken some photomicrographs of the ash from Eyjafjallajökull (sent to me…
The latest Weekly Volcanic Activity Report from our friends at the Smithsonian Global Volcanism Program and the USGS.
Highlights (not including Eyjafjallajökull - you can check the latest IMO update on that eruption and the latest VAAC ash advisories.):
Villarrica in Chile was raised from Alert Level 1 to 2 by the Chilean SERNAGEOMIN after an increase in seismicity, a rise in the lava lake levels at the summit and more vigorous fumarolic activity.
In the first update in a while, a small ash plume was noticed at Chaiten in Chile, rising to ~1.8 km (8,000 feet) from the new domes.
Karymsky in…
News, news, news!
Ash from Eyjafjallajökull piling up on a roof at Seljavellir. Image courtesy of the IMO, by Ari Tryggvason.
The latest from Eyjafjallajökull has the volcano continuing to puff away - producing intermittent airspace closures over Europe. The Icelandic Met Office reports a ~7 km (21,000 foot) ash plume, but they note that the explosivity of the eruption seems to have waned some since a maximum on May 13. Right now, the IMO estimates the eruption rate at ~200 tonnes/second. Lets put that in a little perspective - a Ford F-150 pickup weighs about 2 tonnes, so the volcano is…
Some news for a sleepy Monday:
Mt. Hood in Oregon.
The ash from Eyjafjallajökull is, once again, causing significant airspace closure over northern Europe - close of 1,000 flights today. However, much of the closures are fairly short-lived, but that isn't keeping people happy. The eruption hasn't actually changed much, just that the winds are bringing ash towards Europe. The ash for the next few days will likely effect the England, Scotland, Ireland, Netherlands, France and possibly other parts of northern Europe (along with airspace over Greenland and the north Atlantic). The ash plume is…
Time to play a little catch up ...
Eyjafjallajökull erupting in early May. Image by and courtesy of Martin Rietze.
A brief update on our friend Eyjafjallajökull - the eruption plume from the volcano was considerably taller yesterday, reaching 6-9 km (20,000-30,000 feet), but prevailing winds meant the ash hazard was confined to areas in the middle of the North Atlantic and northern parts of the British Isles. However, even as the ash hazard for Europe wanes (for now), you shouldn't forget the amount of ash being dumped on parts of Iceland. If you want to see some stunning images of the…
An aerial view of Eyjafjallajökull erupting on May 11, 2010, with the extent of the black ash from the eruption on GÃgjökull clearly evident, along with the cracks in the glacier near the lava flow. Photo from the Icelandic Met Office, by Sigurlaug Hjaltadóttir.
Since this past weekend's disruptions due to Eyjafjallajökull, the air over Europe has cleared and most of the airports in Spain, Portugal and Germany (along with those in Morocco) have reopened. The current ash advisory by the London VAAC looks like it will only effect transatlantic flights and Iceland itself, with the ash cloud…
I an in the home stretch for grading exams, so just a quick update for today:
The evidence of floods from the Eyjafjallajökull eruption, taken on May 1, 2010 by Dr. Joe Licciardi.
Airports now as far south as Spain, Morocco and the Canary Islands are facing closures due to the Eyjafjallajökull ash. The latest London VAAC ash advisory has the ash wrapping around western and southern Europe, which I am sure is making life interesting for routing transatlantic flights into Europe. The flights within Europe don't seem to be that effected according to Eurocontrol - and they have even dropped…
A shot of the summit area of Eyjafjallajökull, showing the twin steam-and-ash plumes from the lava flow and active vent. Picture taken by Dr. Joseph Licciardi (UNH).
Over the weekend, the newly reinvigorated ash eruptions from Eyjafjallajökull combined with favorable winds meant that ash from the eruption closed airspace over swaths of Europe, including Ireland, Spain, Portugal, Italy, Austria and Germany. These disruptions are continuing into the new week, although most of the disruption is for transatlantic flights. However, the threat of ash is more present than ever, as Ryanair…
The GÃgjökull outlet glacier on Eyjafjallajökull, showing the steaming lava flow carving its way through the glacier. Image taken May 5, 2010 by Dr. Joseph Licciardi.
A quick update on the ongoing activity at Eyjafjallajökull:
The activity at the volcano continues to be more explosive during the last few days than it was in the previous week, leading to more potential for airspace closures over Europe if the winds were to shift. Currently, the VAAC ash advisory only seems to suggest that even Spain may get a taste of the ash sometime tomorrow, but most of Europe will be OK. However,…
Grading grading grading!
A webcam capture of the eruptive plume from Eyjafjallajökull on the morning of May 6, 2010.
News:
A quick update on the Eyjafjallajökull eruption: The volcano has been producing an impressive ash plume over the last day (see image above). The current ash plume is reaching 5.8-6 km height (19-20,000 ft) - and causing some trouble over Ireland and Scotland. However, much of airspace closed yesterday has reopened (for now). You can see two new images of the ash plume over at the NASA Earth Observatory. As for the continued fallout from the ash plume from April,…
A shot of the strombolian activity at the vent of Eyjafjallajökull, taken on May 4, 2010. Image courtesy of the Iceland Met Office.
The latest news from the Eyjafjallajökull eruption has the volcano erupting more explosively again (see above), possibly due to an increased influx of water into the vent area - in any case, the ash has become denser (by volume in the air) and the plume is higher (see below) than in the last couple of weeks. The rate of lava flow extrusion has also gone down in the last few days. The latest update from the Iceland Met Office has a lot of details on the current…
The steam plume from a lava flow moving down the slopes of Eyjafjallajökull on May 2, 2010.
A quick note on the activity at Eyjafjallajökull in Iceland: The ash from the ongoing eruption has caused a partial closure of airspace over Ireland from 0600 to 1200 on Tuesday May 4. This is one of the first closures of European airspace since airspace reopened over 10 days ago. This closure is based on the predicted location of ash in flight corridors over Ireland tomorrow.
The Icelandic Met Office has released two interesting updates on the activity at Eyjafjallajökull. The first describes the…
Webcam capture of Eyjafjallajökull erupting on May 2, 2010. You can see the steam plume on the middle flanks of the volcano - this is likely a lava flow coming from the summit vents.
A brief update on activity at Eyjafjallajökull:
Overnight, the lava flows from Eyjafjallajökull could be seen in the crater of the ice cap - some of the images posted by Eruptions readers are simply stunning. You can clearly see the red glow of the strombolian eruptions at the vent, and the glow of the lava flows as they had down the slope of the volcano. This has brought a lot of new melting to the snow/…
News!
Colima in Mexico erupting in 2008.
The current activity at Eyjafjallajökull is more-or-less unchanged, with strombolian activity producing a 3-4 km tall ash-and-steam plume and the lava flows at the crater moving northward towards the GÃgjökull glacier. You can check out an extensive page on the state of this eruption at the Nordic Volcanological Center - along with a new page with thermal and LIDAR information on the eruption from France.
The Icelandic Met Office notes that the lava has been producing meltwater from the glacier - which many Eruptions readers have noticed as floods…
An undated painting of the island volcano of Ischia near the Bay of Naples, Italy.
Guess what? It is the end of the semester (well, school year) here at Denison, so I might be a little busy for the next couple weeks.
Here are some news bits (with special thanks to all who emailed me some of these links):
Boris might have more information or opinion on this, but Italy is back in the news concerning the threat of volcanism to the country. This time the volcano is Ischia, off the coast in the Bay of Naples. Guido Bertolaso of Italy's civil protection agency is quoted as saying that the "magma…
Night image of Eyjafjallajökull erupting on April 24, 2010. Image courtesy of James Ashworth.
A quick update on the Eyjafjallajökull eruption: Not a lot to report in terms of changes in the volcanic activity at the volcano. The update from the Icelandic Met Office last night sums it up nicely:
Overall activity similar as yesterday. Eruption seen from west in the morning - north crater still active. External water has not affected vent activity much since 18 April. Geologists' field observations (2-10 km from vents) show that explosivity is magmatic and that the tephra produced since 18…