genetics
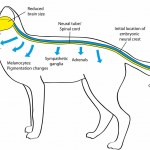
But we have to be clear that it is only a hypothesis at this point. I was reading about domestication syndrome (DS) -- selecting animals for domestication has a whole collection of secondary traits that come along for the ride, in addition to tameness. We are selecting for animals that tolerate the presence of humans, but in addition, we get these other traits, like floppy ears, patchy coat color, shortened faces, etc.; the best known work in this area is by Belyaev (YouTube documentary to get you up to speed) who selected silver foxes for domesticity, and got friendly foxes who also had all…
New genetic disorders pop up all the time -- each one represents a child who may face incredible challenges, or even be doomed to death. A child named Bertrand exhibited some serious symptoms -- profound developmental disabilities -- shortly after he was born, and no one could figure out what was wrong with him. So they took advantage of 21st century biotechnology and sequenced his genome, and the genome of both of his parents, and asked what novel mutations the child carried.
For years, sequencing was too expensive for common use—in 2001, the cost of sequencing a single human genome was…
Dang, I teach all this stuff about genes and chromosomes and epigenetics, but I don't have the advantage of giant floating holographic molecules floating around me. Maybe I'll have to steal this for my classes.
Although it could use some discussion of Blaschko's lines, to explain why you get a stripey pattern rather than just salt-and-pepper.
I first heard about Wade's book when a colleague started talking about bits and pieces of it. He was reading it pursuant to a writing a review. I asked the publisher for a review copy, which they kindly supplied, and started tracking the pre-publication reactions. After reading the first couple of chapters, I realized that I needed to write a review of this book, but I wanted to do something a bit more than a blog post. So, I contacted American Scientist. I had reviewed two books for them earlier. American Scientist is actually my very favorite science magazine (among magazines that are…
This is the paper to read: Palazzo & Gregory's The Case for Junk DNA. It clearly and logically lays out the complete argument from evidence and theory for the thesis that most of the genome is junk. It's not revolutionary or radical, though: the whole story is based on very fundamental population genetics and molecular biology, and many decades of accumulated observations. And once you know a little bit of those disciplines -- you don't need to be a genius with a great depth of understanding -- the conclusion is both obvious and in some ways, rather trivial.
Here's that conclusion:
For…
A confession: I have long disliked Nicholas Wade's science journalism. He has often written about biology in the NY Times, and every time he seems to make a botch of the reporting, because he actually doesn't understand biology very well. For example, in his very last article for the NYT, he described some work that identified 12 genes found on the Y chromosome that are globally expressed — they aren't just involved in testis development, for instance. This is no surprise. There are genes required for sperm differentiation found on autosomes, for instance, and the Y chromosome is not a…
Time to get back to business after yesterday's festivities.
One of the items of Gospel Truth among the "autism biomed" movement, which consists of people who fervently believe that autism is caused by some sort of external "toxin," infection, or vaccines and that subjecting children to various forms of quackery designed either to "detoxify" or reverse whatever physiological derangement believed to be at the root of autism will "recover" these children from autism. Of course, there are a lot of antivaccine believers in the autism biomed movement, and arguably the vast majority of "autism…
I was talking about sex and nothing but sex all last week in genetics, which is far less titillating than it sounds. My focus was entirely on operational genetics, that is, how autosomal inheritance vs inheritance of factors on sex chromosomes differ, and I only hinted at how sex is not inherited as a simple mendelian trait, as we're always tempted to assume, but is actually the product of a whole elaborate chain of epistatic interactions. I'm always tempted in this class to go full-blown rabid developmental geneticist on them and do nothing but talk about interactions between genes, but I…
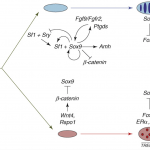
Imagine that there is a trait observed among people that seems to occur more frequently in some families and not others. One might suspect that the trait is inherited genetically. Imagine researchers looking for the genetic underpinning of this trait and at first, not finding it. What might you conclude? It could be reasonable to conclude that the genetic underpinning of the trait is elusive, perhaps complicated with multiple genes, or that there is a non-genetic component, also not yet identified, that makes finding the genetic component harder. Eventually, you might assume, the gene will be…
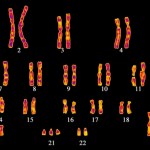
I had known that Jérôme Lejeune was the fellow who had discovered that Down Syndrome was caused by trisomy of chromosome 21, but it seems there were many other things about him I had not known -- he was just a name. But there were a few things that set me aback.
Lejeune became not just a renowned researcher but the darling of the French Catholic right-to-life movement. You can read long flattering Wikipedia biographies in both French and English. He was showered with awards and given a prestigious Chair of Human Genetics at the Paris School of Medicine, bypassing the usual competition…
Razib Khan poked me on twitter yesterday on the topic of David Dobbs' controversial article, which I've already discussed (I liked it). I'm in the minority here; Jerry Coyne has two rebuttals, and Richard Dawkins himself has replied. There has also been a lot of pushback in the comments here. I think they all miss the mark, and represent an attempt to shoehorn everything into an established, successful research program, without acknowledging any of the inadequacies of genetic reductionism.
Before I continue, let's get one thing clear: I am saying that understanding genes is fundamental,…
The one thing you must read today is David Dobbs' Die, Selfish Gene, Die. It's good to see genetic accommodation getting more attention, but I'm already seeing pushback from people who don't quite get the concept, and think it's some kind of Lamarckian heresy.
It's maybe a bit much to ask that the gene-centric view of evolution die; it's still useful. By comparison, for instance, it's a bit like Mendel and modern genetics (I'll avoid the overworked comparison of Newton and Einstein.) You need to understand simple Mendelian genetics — it gives you a foundation in the logic of inheritance, and…
I don't understand how this happens. You've got a good academic position. You're bringing in reasonable amounts of grant money. You're publishing in Nature Genetics and Nature Structural and Molecular Biology. And you don't even understand the basic concepts in your field of study.
For instance, here's a press release titled "Cause of genetic disorder found in 'dark matter' of DNA".
For the first time, scientists have used new technology which analyses the whole genome to find the cause of a genetic disease in what was previously referred to as "junk DNA". Pancreatic agenesis results in…
I'm going to tell you about a paper that was brought to my attention by some poor science journalism, so first I have to complain about the article in the Guardian. Bear with me.
This is dreadfully misleading.
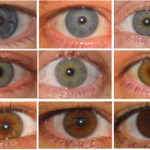
Though everybody's face is unique, the actual differences are relatively subtle. What distinguishes us is the exact size and position of things like the nose, forehead or lips. Scientists know that our DNA contains instructions on how to build our faces, but until now they have not known exactly how it accomplishes this.
Nope, we still don't know. What he's discussing is a paper that…
I'm trying to raise money for the The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, and I promised to do a few things if we reached certain goals. I said I'd write a post microRNAs and cancer if you raised $7500. And you did, so I did. I kept my clothes on this time, though, so here's a more serious picture of yours truly: this is what my students see, which is slightly less terrifying, nicht wahr?
If you want more, go to my Light the Night fundraising page and throw money at it. If we reach our goal of $10,000, I'll organize a Google+ Hangout to talk about cancer. Note that we're also getting matching…
This cat is going to be insufferable
You may have heard we've got this satanic feline padding about the house now, getting into mischief -- she has discovered my collection of cephalopodiana, and her favorite toy is one of my stuffed octopuses that she wrestles and bats around the floor. It's like she's rubbing it in.
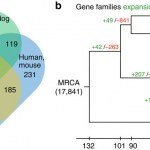
Anyway, a new paper in Nature Communications describes a comparative analysis of the genomes of tigers, lions, snow leopards, and…housecats. I'm not letting her read it, lest she acquire delusions of grandeur (oh, wait, she's a cat — she already has that.)
There's nothing too…
Things have been a bit too serious around here lately. After all, yesterday I wrote about obesity and chemotherapy, while the day before that I did an even lengthier than usual deconstruction of some claims by anti-Obamacare activists, which seemed particularly appropriate to me given that a group of wingnuts has just succeeded in mostly shutting down our government because they are opposed to Obamacare. Come to think of it, given the nastiness that's going on in Washington right now, I could use something light, an easy target even. And who better to serve that role than everyone's favorite…
Let's say you want to do a market-related study in which you gain entry to one thousand homes representing sets of people defined by the usual variables of income, ethnicity, urban-suburban lifestyle etc. The first thing you do is to ask a few people, real nice like, if you can go through their stuff and take a lot of photographs and notes. Most of them say no, and you perhaps even discover that the one or two who actually agree to this are odd ducks. So you go to Plan B. This involves breaking into the homes when the people are out so you can get your data despite the fact that they don't…
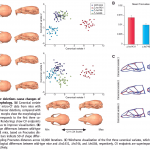
I know you're thinking we've had more than enough discussion of one simplistic umbrella hypothesis for the origin of unique human traits — the aquatic ape hypothesis — and it's cruel of me to introduce another, but who knows, maybe the proponents of each will collide and mutually annihilate each other, and then we'll all be happy. Besides, this new idea is hilarious. I'm calling it the MFAP hypothesis of human origins, which the original author probably wouldn't care for (for reasons that will become clear in a moment), but I think it's very accurate.
A list of traits distinguishing humans…
Don't you hate it when you get up in the morning and the first thing you read on the internet is that the news that your entire career has been a waste of time, your whole field of study has collapsed, and you're going to have to rethink your entire future? Happens to me all the time. But then, I read the creationist news, so I've become desensitized to the whole idea of intellectual catastrophes.
Today's fresh demolition of the whole of evolutionary theory comes via Christian News, which reports on a paper in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution which challenges the ape to human…