neuroscience
You don't have to be brain-damaged to feel the presence of God, but it just might help. On Neurophilosophy, Mo analyzes a recent study into feelings of "self-transcendence" among individuals afflicted with brain lesions. Those with tumors in the posterior regions of the brain were more likely to identify as religious, and feelings of "creative self-forgetfulness," "transpersonal identification" and "spiritual acceptance" increased after surgical removal of "the left inferior parietal lobule and the right angular gyrus." The posterior regions of the brain are strongly associated with…
REMOVAL of specific parts of the brain can induce increases in a personality trait which predisposes people to spirituality, according to a new clinical study by Italian researchers. The new research, published earlier this month in the journal Neuron, provides evidence that some brain structures are associated with spiritual thinking and feelings, and hints at individual differences that might make some people more prone than others to spirituality.
Cosimo Urgesi of the University of Udine and his colleagues combined pre- and post-surgical personality assessments with advanced lesion…
Listen to the podcast, post comments, ask questions - the new forum is now live and will go on for the next week:
How the Hidden Brain Controls Our Lives
We like to think of ourselves as conscious, rational beings.
But human behavior is largely driven by unconscious attitudes.
These attitudes reside in the deep recesses of the brain, and we ignore them at our own peril.
So says Washington Post journalist Shankar Vedantam.
Vedantam is the author of a new book, The Hidden Brain: How Our Unconscious Minds Elect Presidents, Control Markets, Wage Wars, and Save Our Lives.
Vedantam explores how the…
tags: neuroscience, health, medicine, health care, blindness, poverty, India, Pawan Sinha, TEDTalks, streaming video
Pawan Sinha details his groundbreaking research into how the brain's visual system develops. Dr Sinha and his team provide free vision-restoring treatment to children born blind, and then study how their brains learn to interpret visual data. The work offers insights into neuroscience, engineering and even autism.
TEDTalks is a daily video podcast of the best talks and performances from the TED Conference, where the world's leading thinkers and doers give the talk of their…
FYI: the winners of the AAAS Science and Engineering Visualization Challenge are up! You may recognize some of them - including PhD (Piled Higher and Deeper) cartoonist Jorge Cham. Check 'em out and share your opinions; I'll have more to say when I'm back from blogcation!
Just a quick post on an article that caught my eye: Jazz Pharmaceuticals of Palo Alto, CA, has announced that the US FDA has accepted their new drug application (NDA) filing for JZP-6, or sodium oxybate, for the treatment of pain and fatigue associated with fibromyalgia.
The NDA was based on positive outcomes of two, Phase III clinical trials - those randomized, placebo-controlled double-blind trials that serve as the gold standard for drug efficacy. The company expects an approval decision from FDA by October 2010.
Jazz has already garnered approval for sodium oxybate under the brand name…
WHEN it comes to making decisions, timing can be everything, but it is often beneficial to conceal the decision that has been made. Take a game of poker, for instance: during each round, the player has to decide whether to bet, raise the stakes, or fold, depending on the hand they have been dealt. A good player will have perfected his "poker face", the blank expression which conceals the emotions he feels and the decisions he makes from the other players sitting at the table.
Increasing numbers of researchers are using brain scanning techniques to perform what is commonly referred to as "…
The social interactions that come naturally to most people are difficult for people with autism and Asperger syndrome. Simple matters like making eye contact, reading expressions and working out what someone else is thinking can be big challenges, even for "high-functioning" and intelligent individuals. Now, a preliminary study of 13 people suggests that some of these social difficulties could be temporarily relieved by inhaling a hormone called oxytocin.
The participants, who either had Asperger or high-functioning autism, experienced stronger feelings of trust, showed stronger social…
I profiled neuroscientist Eric Kandel for Scientific American Mind a while back; a huge pleasure. Two things stand out.
First, Kandel's work makes a wonderful foundation for an understanding of neuroscience, as his mid-20th-century insights into the dynamics of memory underlie much of the discipline.
Second, Kandel is a gas -- gracious, funny, and stunningly brilliant. When I interviewed him for about 90 minutes in his office at Columbia, he was 73. As he described to me the history of his work, and of modern neuroscience, he seemed to have complete and effortless…
From the Cold Spring Harbor Archive (click for larger image). From Micklos, The Science of Eugenics, pg 116 (1930).
Well, not quite. I got an intriguing abstract in my inbox earlier today, to this new paper from BMC Neuroscience:
Here using a new conditioned suppression paradigm, we investigated whether the ability of a foot-shockpaired conditioned stimulus to suppress chocolate-seeking behavior was antagonized by previous exposure to a chronic stressful experience, thus modeling aberrant chocolate seeking in sated mice. Our findings demonstrate that while Control (non-food deprived) animals showed a profound conditioned suppression of chocolate seeking during presentation of conditioned stimulus,…
IF a rapid series of taps are applied first to your wrist and then to your elbow, you will experience a perceptual illusion, in which phantom sensations are felt along the skin connecting the two points that were actually touched. This feels as if a tiny rabbit is hopping along your skin from the wrist to the elbow, and is therefore referred to as the "cutaneous rabbit". The illusion indicates that our perceptions of sensory inputs do not enter conscious awareness until after the integration of events occuring within a certain time window, and that the sensory events taking place at a certain…
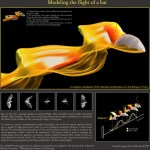
Modeling the flight of a bat (click to enlarge)
Dave Willis et. al., Brown University and MIT
Visual complexity is a paradox. On the one hand, complexity is a compelling feature known to capture a viewer's attention and stimulate interest. . . . On the other hand, complexity only arouses curiosity up to a point. When a visual is extremely complex, viewers may tend to avoid it altogether. -- Connie Malamed
I had a great time this weekend devouring Connie Malamed's oversized treasury of data visualization, Visual Language for Designers. The book couldn't be more appealing: it's like someone…
In Western films, the gunslinger that draws first always gets shot. This seems like a standard Hollywood trope but it diverted the attention of no less a scientist that Niels Bohr, one of history's greatest physicists. Taking time off from solving the structure of the atom, Bohr suggested that it takes more time to initiate a movement than to react to the same movement. Perversely, the second gunslinger wins because they're responding to their opponent's draw.
Now, Andrew Welchman from the University of Birmingham has found that there's something to Bohr's explanation. People do indeed have…
Matthew Albanese makes miniature dioramas out of everyday materials and photographs them, producing Uncanny Valley landscapes that seem almost, but not quite, real. His Paprika Mars, above, is made of 12 pounds of charcoal and spices (paprika, cinnamon, nutmeg, chili powder). Fields, After the Storm, below, is mostly faux fur and cotton.
Albanese's scenes are convincing precisely because they're so paradigmatic - the standard desolate planetary surface, Western grassland, etc. His work exploits our cognitive tendencies to interpret stimuli against the backdrop of our experience, especially…
href="http://www.researchblogging.org">
src="http://www.researchblogging.org/public/citation_icons/rb2_large_gray.png"
style="border: 0pt none ;">Objective diagnosis is in some
ways the holy grail of medicine. It has been maddeningly elusive
in psychiatry. Now comes a paper in which the authors suggest
that they may have found this treasure.
The paper details a method of using magnetoencephalography to assess
human brain function. They claim that, in a select population, it
can correctly identify patients with PTSD with 90% accuracy.
href="http://www.iop.org…
HOW does the brain encode the spatial representations which enable us to successfully navigate our environment? Four decades of research has identified four cell types in the brains of mice and rats which are known to be involved in these processes: place cells, grid cells, head direction cells and, most recently, border cells. Although the functions of most of these cell types are well characterized in rodents, it remains unclear whether they are also found in humans. A new functional neuroimaging study, by researchers from University College London, published online in the journal Nature,…
"WHEN a man sits with a pretty girl for an hour," said Albert Einstein, "it seems like a minute. But let him sit on a hot stove for a minute, and it's longer than any hour." Einstein was describing one of the most profound implications of his Theory of General Relativity - that the perception of time is subjective. This is something we all know from experience: time flies when we are enjoying ourselves, but seems to drag on when we are doing something tedious.
The subjective experience of time can also be manipulated experimentally. Visual stimuli which appear to be approaching are perceived…
On Oscillator, Christina Agapakis lays out some of the history of synthetic biology. While in the last century this field has employed molecular and informational toolkits, in centuries past inventors relied on grosser modes of simulation. Such was the case with eighteenth century wetware, which aspired "to make machines look and feel more like living things—soft, flexible, moist." One of the grails of early synthetic biology was the simulation of the human voice, and to this end we see such terrors as a fake face attached to a phonetic keyboard, which allowed "an operator to play a '…
OUR ability to use and manipulate numbers is integral to everyday life - we use them to label, rank, count and measure almost everything we encounter. It was long thought that numerical competence is dependent on language and, therefore, that numerosity is restricted to our species. Although the symbolic representation of numbers, using numerals and words, is indeed unique to humans, we now know that animals are also capable of manipulating numerical information.
One study published in 1998, for example, showed that rhesus monkeys can form spontaneous representations of small numbers and…