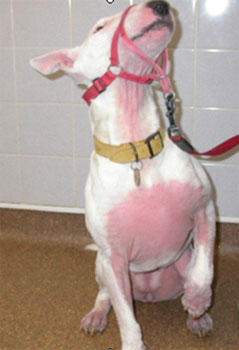
 Image of atopic dermatitis from www.itchfreepet.com
Image of atopic dermatitis from www.itchfreepet.com
Dr. Kerstin Lindblad-Toh at Uppsala University (Sweden) who specializes in comparative genomics and Dr. Åke Hedhammar, SLU (Sweden) recently identified a novel gene in German shepherd dogs, PKP-2, that encodes a protein (plakophilin-2) important for regulating proper skin structure and function. This protein was found to be associated with canine atopic dermatitis (i.e. doggy eczema), a condition that affects 3-10% of man's best friends. Researchers hope that the discovery of this gene relationship may lead to better understanding of, and novel treatments for, eczema in both dogs and the 10-30% of humans who share this condition.
Source:
