Biomatics
Could artificial sweeteners be helping cause the very thing they are supposed to prevent? They may well do so, and you can probably blame your microbiota – those masses of mostly-friendly bacteria that live in your gut. According to a paper by Weizmann Institute scientists that appeared today in Nature, artificial sweeteners not only encourage the wrong kind of bacteria to expand their numbers, they also induce mix-ups in the cross-communication between these bacteria and your body. Those mix-ups can lead to glucose intolerance – the first step toward metabolic syndrome and diabetes. So,…
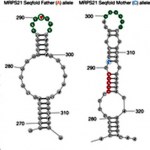
At the level of biomolecules, life boils down to two basic principles: sequence and folding. We know, for example, that the sequence of nucleotides in the DNA contains our genetic blueprint, but the way that our DNA is folded and wrapped up in each chromosome helps determine which genes are easily accessible for copying. Proteins – sequences of amino acids – fold into intricate shapes before assuming their duties. So it is no surprise that the third main molecular sequence in the cell – the RNA, made up of single strands of nucleotides – folds as well. Nucleotides are built to pair up – DNA…
More science-themed haikus. I seem to keep writing them because we tend to put out three “mini press releases” at a time (a relic of the days when they were printed on two sides of a fold-up page and mailed). So I could pick just one to blog about, or I could try to fit all three into one post (which tends to get muddled when it is on subjects as varied as physics, neurobiology and genetics). Or else I can leave these little breadcrumbs inviting you to follow them back to our website, where the fuller explanation awaits (or, from there, you can follow the links in the releases to get to the…
DNA testing can reveal how closely related you are to a group of people halfway around the world or, if you're doing evolutionary research, where organisms fit on taxonomic trees. The same DNA tests, when performed on the cells in a single human body, can be used to reconstruct lineage trees that can trace the cells' ancestry back to the embryo.
The principle in all three cases is the same: DNA amasses mutations over time, and these mutations can be used to assess how far back two people, organisms or cells shared a common parent.
The idea for the cell lineage trees comes from the group of…