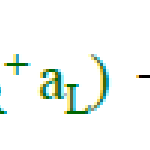Condensed Matter
It's been a while since I last rounded up physics posts from Forbes, so there's a good bunch of stuff on this list:
-- How Do Physicists Know What Electrons Are Doing Inside Matter?: An explanation of Angle-Resolved Photo-Electron Spectroscopy (ARPES), one of the major experimental techniques in condensed matter. I'm trying to figure out a way to list "got 1,800 people to read a blog post about ARPES" as one of my professional accomplishments on my CV.
-- The Optics Of Superman's X-Ray Vision: Spinning off a post of Rhett's, a look at why humanoid eyes just aren't set up to work with x-rays…
I was at the APS March Meeting last week, because I needed tp give a talk reporting on the Schrödinger Sessions. But as long as I was going to be there anyway, I figured I should check out the huge range of talks on areas of physics that aren't my normal thing-- in fact, I deliberately avoided going to DAMOP-sponsored sessions.
This also affected my blogging, so the last few weeks' worth of posts at Forbes have mostly been on March Meeting-related areas:
-- How Cold Atoms Might Help Physicists Understand Superconductors: A post about the connection between ultra-cold atomic physics and…
I'm going to be at the March Meeting of the American Physical Society in Baltimore next week. This is the largest physics meeting of the year, with an emphasis on condensed matter physics (which is actually the largest single area of study within physics, though media overemphasis on particle physics and astrophysics might lead you to think otherwise). The program for the meeting is, um, kind of intimidating.
So, this post has two purposes:
1) If you're also going to be at the March Meeting, let me know, and maybe we can arrange some kind of bloggy-people meet-up.
2) More importantly, if…
I've been really busy with year-end wrap-up stuff, but have also posted a bunch of stuff at Forbes. which I've fallen down on my obligation to promote here... So, somewhat belatedly, here's a collection of physics-y stuff that I've written recently:
-- Using Atoms To Measure Tiny Forces: A post reporting on some very cool atom interferometry experiments, one working to measure the very tiny (but known to exist) force of gravity, the other searching for a possible "fifth force" sort of thing.
-- Making And Shaking New Materials With Ultracold Atoms: A post reporting on a couple more DAMOP…
One of the things I struggle with a bit when it comes to writing about cool modern physics is how much to play up the weirdness. On the one hand, people just can't get enough of "spooky action at a distance," but on the other hand, talking too much about that sort of thing makes quantum physics seem like a completely bizarre theory with no applications.
Which is unfortunate, because quantum physics is essential for all manner of everyday technology. For example, as I try to explain in a new post at Forbes, quantum physics is essential to the cheap alarm clock that wakes me up in the morning.…
Back in December, The Parable of the Polygons took social media by storm. It's a simple little demonstration of how relatively small biases can lead to dramatic segregation effects, using cute cartoon polygons. You should go read it, if you haven't already. I'll wait.
This post isn't really about that. I mean, it is, but it's using it for something dramatically different than the intended purpose of the post. You see, I am such a gigantic dork that when I looked at their toy model, the first thing that came to mind was physics.
(And, in fact, I sat on this post topic for the better part of a…
I've decided to do a new round of profiles in the Project for Non-Academic Science (acronym deliberately chosen to coincide with a journal), as a way of getting a little more information out there to students studying in STEM fields who will likely end up with jobs off the "standard" academic science track.
Sixth in this round is an "adult-onset engineer" working at NASA on some cool stuff.
1) What is your non-academic job? I am a thermal engineer at NASA's Jet Propulsion Lab, working in the Cryogenic Systems Engineering group. Our group provides thermal engineering support (both cryogenic…
The third of the videos I wrote for TED-Ed is now live: Schrödinger's Cat: A Thought Experiment in Quantum Mechanics.This is using basically the same argument I outlined in this post, but with awesome animation courtesy of Agota Vegso. I'm impressed by how close the images that ended up in the video are to the pictures I had in my mind while I was writing it.
As I said in that old post, I dithered for a bit about whether to run with this argument, but decided I liked it enough to go ahead. You can legitimately quibble about some of the phrasing being a little too definite (or that Schrödinger…
The 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics has been awarded to Isamu Akasaki, Hiroshi Amano and Shuji Nakamura for the development of blue LED's. As always, this is kind of fascinating to watch evolve in the social media sphere, because as a genuinely unexpected big science story, journalists don't have pre-written articles based on an early copy of a embargoed paper. Which means absolutely everybody starts out using almost the exact words of the official Nobel press release, because that fills space while they frantically research the subject. Later in the day, you'll get some different framing, once…
The latest in a long series of articles making me glad I don't work in psychology was this piece about replication in the Guardian. This spins off some harsh criticism of replication studies and a call for an official policy requiring consultation with the original authors of a study that you're attempting to replicate. The reason given is that psychology is so complicated that there's no way to capture all the relevant details in a published methods section, so failed replications are likely to happen because some crucial detail was omitted in the follow-up study.
Predictably enough, this…
I'm working on some short pop-quantum explainers for reasons that I'll be a little cagey about. In casting around for a novel way to introduce Schrödinger's cat states, I hit on something that probably works, but illustrates the problems inherent in being both a professional physicist and a pop-science writer.
The hook, as I mentioned on Twitter a little while back (early on a weekend morning, so nobody read it) is that you have Schrödinger's cat to thank for the computer you're reading this on. The core idea of the infamous cat paradox is that it's both alive and dead at the same time,…
Topping the looooong list of things I would give a full ResearchBlogging write-up if I had time is this new paper on a ultra-cold atom realization of "Dirac Monopoles". This is really cool stuff, but there are a lot of intricacies that I don't fully understand, so writing it up isn't a simple matter.
The really short version, though, is that a team of AMO physicists have created particles that are analogous to magnetic monopoles-- that is, to a particle that was only a "north" or "south" pole of a magnet, not both together like a conventional bar magnet (leading to my favorite social-media…
The very last section of the book-in-progress (at least the draft that's with my editor right now...) is titled "Science Is Never Over," and talks about how there are a nearly infinite number of phenomena that you can investigate scientifically. The universe is a never-ending source of amazement and wonder, with surprisingly rich dynamics in the simplest of things. I mean, look at the thousands of words I've gotten out of talking about sticky tape...
This is why I sigh heavily whenever I see a title like Ashutosh Jogalekar's "Should Physicists Stop Looking for Fundamental Laws. This is, at…
Two papers with a similar theme crossed my social media feeds in the last couple of days. You might think this is just a weird coincidence, but I'm choosing to take it as a sign to write about them for the blog.
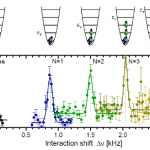
So, what are these papers, and what's the theme? One is the final publication of some results I saw at DAMOP and alluded to back in June, and the other is from this post by Doug Natelson. Both look at the transition from few-body to many-body physics.
And this is interesting, why? I mean, isn't it obvious that you just add some more bodies? OK, I guess that does need a little more…
As noted in a previous post on Monte Carlo simulation in 1960, we recently came into possession of a large box of old Master's theses. The bulk of these are from the 50's and 60's, but there are some going back much farther. As I pass these every day I'm in the office, I thought it might be amusing to take a look at these for the blog, now and again. I don't plan to do a detailed examination of the quality of the science (at least, not necessarily), but to use this to look at how things have changed over the decades.
The first of these, pictured above, is one of the oldest: Secondary Emission…
Through some kind of weird synchronicity, the title question came up twice yesterday, once in a comment to my TED@NYC talk post, and the second time on Twitter, in a conversation with a person whose account is protected, thus rendering it un-link-able. Trust me.
The question is one of those things that you don't necessarily think about right off-- of course an atom is a particle!-- but once it gets brought up, you realize it's a little subtle. Because, after all, while electrons and photons are fundamental particles, with no internal structure, atoms are made of smaller things. But somehow we…
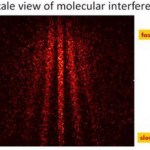
Last time in our trip through the cold-atom toolbox, we talked about light shifts, where the interaction with a laser changes the internal energy states of an atom in a way that can produce forces on those atoms. This allows the creation of "dipole traps" where cold atoms are held in the focus of a laser beam, but that's only the simplest thing you can use light shifts for. One of the essential tools of modern atomic physics is the "optical lattice," which uses patterns of light to make patterns of atoms.
OK, what do you mean "patterns of light"? Well, remember, light has both wave and…
One thing I left out of the making-of story about the squeezed state BEC paper last week happened a while after publication-- a few months to a year later. I don't quite recall when it was-- I vaguely think I was still at Yale, but I could be misremembering. It's kind of amusing, in an exceedingly geeky way, so I'll share it, though it's also a story of an embarrassing mis-step on my part.
So, the physical situation we were studying is described by the "Bose-Hubbard Hamiltonian": Bose because it's dealing with bosons (there's also a Fermi-Hubbard version, I believe); Hubbard after [mumble]…
Yesterday's write-up of my Science paper ended with a vague promise to deal some inside information about the experiment. So, here are some anecdotes that you would need to have been at Yale in 1999-2000 to pick up. We'll stick with the Q&A format for this, because why not?
Why don't we start with some background? How did you get involved in this project, anyway? I finished my Ph.D. work at NIST in early 1999, graduating at the end of May. I needed something to do after that, so I started looking for a post-doc by the don't-try-this-at-home method of emailing a half-dozen people I knew…
Hey, dude? Yeah, what's up?
I'm not normally the one who initiates this, but I was wondering: When you were at DAMOP last week, did you see any really neat physics? Oh, sure, tons of stuff. It was a little thinner than some past meetings-- a lot of the Usual Suspects didn't make the trip-- but there were some really good reports from a lot of groups.
Anything really surprising? Well, there was one talk that I really liked a lot, that I went to on a lark, because I didn't understand what the session title could possibly mean, and there was no abstract for the talk: Experimental Studies of…