dinosaur
If you have not already had a chance to see it, the T. Rex Autopsy airing on the National Geographic channel is a must-see! They literally created a model of T. Rex based on available evidence about T. Rex and other dinosaurs as well as evidence from modern birds and then performed an "autopsy". The conclusion: T. Rex was basically a 'big angry chicken' - Love it!!
It will be airing again tomorrow night at 10/9 central.
For more information and a sneak preview:
Images from National Geographic website.
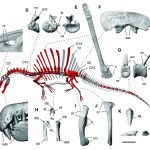
It is called Spinosaurus aegyptiacus but it sounds a bit more like Godzilla. Spinosaurus is a theropod dinosaur (that's the groups birds evolved within) found in what is now NOrth Africa, between about 112 and 97 million years ago. It was first discovered about one century ago, though those bones were destroyed during WW II. Spinosaurus aegyptiacus might be the only species of this genus, or there may be two. It is probably the largest carnivours dinosaur, up to 18 meters in length. Up top of the post is the picture from Wikipedia. Although the head looks a lot like a crock, you can see…
This newly discovered feathered dinosaur, Changyuraptor yangi, was built like a modern airplane. Illustration by S. ABRAMOWICZ, DINOSAUR INSTITUTE, NHM.
Photo of fossil by: Luis Chiappe Dinosaur Institute, NHM as published in the USA Today
The discovery of this non-avian dinosaur, Changyuraptor yangi, that lived 125 million years ago suggests that flight came before birds. The fossil was discovered in the Liaoning Province of northeastern China by Luis Chiappe from the Natural History Museum in Los Angeles, CA. At nearly 4 feet long, it is the largest so-…
This was just too cute (and funny!) not to share. I came across a blog in Scientific American that discussed a "standardized test" created by Hannah Bonner, illustrator and children's writer, to help determine whether someone (or some creature) is a mammal:
Excerpt from "When Dinos Dawned, Mammals Got Munched, and Pterosaurs Took Flight"
The test is part of her book called "When Dinos Dawned, Mammals Got Munched, and Pterosaurs Took Flight." What a great educational tool. It is published by National Geographic Children's Books. Kudos to you Hannah!
Source:
Scientific American
Rubber dino, you're the one,
You make bathtime lots of fun
Rubber dino, I'm awfully fond of you
Doo-doo doo-de-doo
Rubber dino, fearsome roar,
Good thing you're a herbivore
Rubber dino, I'm awfully fond of you
doo-doo doo-de-doo
Every day when I,
get undressed next to the sink,
I find a
Little fella who's,
cute and yellow and extinct
When I squeeze you, water squirts,
Then I giggle, 'til it hurts
Rubber dino, I'm awfully fond of you
Doo-doo doo-de-doo
You're my favorite bathtime toy,
Watch out for that asteroid!
Rubber dino, I'm awfully fond of
Rubber dino, I'm awfully fond of,
Rubber dino…
A toe bone from a Cretaceous ornithischian dinosaur, just laying on the ground. Photographed at Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument, Utah.
My contribution to the Sb-wide Zombie Day will soon be posted, but if you need something to sink your teeth into before then, check out today's new issue of the Times of London science magazine Eureka (included inside the Times, for UK readers). Inside you will find two stories by me - one on paleobiology in the 21st century and the other on our changing view of tyrannosaurs - and you can access them online behind a free registration wall. It was a wonderful opportunity to write for Eureka, and I am indebted to editors Mark Henderson and Antonia Senior for their support and the freedom to…
A few weeks ago I started prep work on a Tyrannosaurus rex toe bone recovered from Montana's Hell Creek Formation and kept at the New Jersey State Museum. This is how the gypsum-encrusted bone looked when I started...
... and this is how it looked at the end of last week. There's still a lot of work to do, but it is encouraging when you start seeing more bone than gypsum.
tags: evolution, evolutionary biology, UV light, flight, dinosaur, dromaeosaur, theropods, Microraptor gui, paleontology, fossils, birds, researchblogging.org,peer-reviewed research, peer-reviewed paper, journal club
Figure 1. The holotype of Microraptor gui, IVPP V 13352 under normal light. This shows the preserved feathers (white arrow) and the 'halo' around the specimen where they appear to be absent (black arrows). Scale bar at 5 cm. [larger view]
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009223
It has long been known that when exposed to ultraviolent light, fossilized bones and shells -- and even…
Hold your arms out with your palm oriented vertically, as if you were trying to shake someone's hand. Now without moving your forearm, bend your hand downwards towards the floor. Unless you are freakishly flexible, you will only have managed to a measly acute angle. But if you were a bird, you could bend your wrist so that your hand pointed back towards your body. These incredibly flexible wrists allow birds to fold their wings and they help with flying. And many dinosaurs could do something similar.
Many older depictions of small raptors, including the Jurassic Park films, have them…
Snakes have been around for nearly 100 million years and scientists have found many fossils of extinct species. But this astonishing specimen is different. This serpent is Sanajeh indicus. It is sitting in a dinosaur nest and its coils surround three eggs and the body of a hatchling.
There are many reasons to think that this prehistoric tableau represented a predator caught in the act of hunting, rather than a mash-up of unconnected players thrown together by chance. The snake is perfectly posed, with its head resting atop a coil and its body encircling a crushed egg. All the pieces are…
Dinosaur books have become more colourful affairs of late, with the dull greens, browns and greys of yesteryear replaced by vivid hues, stripes and patterns. This has largely been a question of artistic licence. While fossils may constrain an artist's hand in terms of size and shape, they haven't provided any information about colour. But that is starting to change.
The fossils of some small meat-eating dinosaurs were covered in filaments that are widely thought to be the precursors of feathers. And among these filaments, a team of Chinese and British scientists have found the distinctive…
It's a dinosaur tooth, and clearly one that belonged to a predator - sharp and backwards-pointing. But this particularly tooth, belonging to a small raptor called Sinornithosaurus, has a special feature that's courting a lot controversy. It has a thin groove running down its length, from the root to the very tip. According to a new paper from Enpu Gong of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, it was a channel for venom.
Thanks to a certain film that shall remain nameless, a lot of people probably think that we already know that some dinosaurs are venomous. But the idea that Dilophosaurus was…
Tyrannosaurid Skeletal Design First Evolved at Small Body Size:
Tyrannosaurid dinosaurs comprised nearly all large-bodied predators (>2.5 tons) on northern continents during the Late Cretaceous. We show that their most conspicuous functional specializations--a proportionately large skull, incisiform premaxillary teeth, expanded jaw-closing musculature, diminutive forelimb, and a hindlimb with cursorial proportions--were present in a new small-bodied, basal tyrannosauroid from Lower Cretaceous rocks in northeastern China. These specializations, scaled up in Late Cretaceous tyrannosaurids…
Meet Raptorex, the "king of thieves". It's a new species of dinosaur that looks, for all intents and purposes¸ like the mighty Tyrannosaurus rex, complete with large, powerful skull and tiny, comical forearms. But there's one very important difference - it's 100 times smaller. Unlike the ever-shrinking world of music players and phones, it seems that evolution crafted tyrannosaur technology with much smaller specifications before enlarging the design into the giant predators of the late Cretaceous.
Raptorex is a new species of meat-eating dinosaur, discovered in northwest China by Paul…
tags: What's Wrong with Philip, comedy, humor, funny, streaming video
This video is a touching vignette about the difficult moment where a woman breaks up with her beau, Philip. As you'll notice in this video, Philip suffers from a common problem: he doesn't listen. However, that said, I sure wish I had a Philip to deal with my parents and family .. although I could do without his farting [2:45]
H/T: Travelgirl.
There is a reason why there are no dinosaur geneticists - their careers would quickly become as extinct as the 'terrible lizards' themselves. Bones may fossilise, but soft tissues and molecules like DNA do not. Outside of the fictional world of Jurassic Park, dinosaurs have left no genetic traces for eager scientists to study.
Nonetheless, that is exactly what Chris Organ and Scott Edwards from Harvard University have managed to do. And it all started with a simple riddle: which came first, the chicken or the genome?
Like almost all birds, a chicken's genome - its full complement of DNA…
tags: paleontologists, fossils, scientists, dinosaur hunters, pervatasaurus, humor, funny, satire, streaming video
Paleontologists recently discovered a new dinosaur fossil in Argentina: they believe the intact skeleton could shed light on the bizarre fetishes of this pervert dinosaur [2:10]
There are two posts on ScienceBlogs which highlight two perspectives on the Dinosaur mass extinction, What Wiped Out The Dinosaurs? and K-T extinction debates: cranky "skeptics" or reasonable science?. I'd assumed that the Asteroids-from-the-sky was the clear consensus, but please see this old BloggingHeads.TV clip where Peter Ward seems to imply that the waters are muddier than you'd think:
These cells look like fairly typical bone cells. They appear to be connected to each other by thin branch-like projections and are embedded in a white matrix of fibres. At their centres are dark red spots that are probably their nuclei. But it's not their appearance that singles out these extraordinary cells - it's their source. You're looking at the bone cells of a dinosaur.
They come from an animal called Brachylophosaurus, a duck-billed dinosaur that lived over 80 million years ago. By looking at one of its thigh bones, Mary Schweitzer from North Carolina State University has managed to…