Distance
"I wouldn't know a spacetime continuum or a warp core breach if they got into bed with me." -Patrick Stewart
It's the end of the week once again, and so it's time for another Ask Ethan segment! There have been scores of good questions to choose from that were submitted this month alone (and you can submit yours here), but this week's comes from our reader garbulky, who asks:
Why does gravity decrease the further away you are from the object? I've read that it does decrease with distance squared but not why it does this.
This question seems so simple, and yet the answer -- to the…
"One sees qualities at a distance and defects at close range." -Victor Hugo
A couple of weeks ago we took a look at the most distant galaxy (so far) in the known Universe, a galaxy so far away that it takes exclusively infrared observations from our most power space telescopes (Hubble and Spitzer) in order to detect it. What's perhaps even more remarkable is that the light we do detect from it -- the light we detected in the infrared -- was actually emitted in the Ultraviolet part of the spectrum!
Image credit: NASA, ESA, Garth Illingworth (University of California, Santa Cruz) and…
"We find them smaller and fainter, in constantly increasing numbers, and we know that we are reaching into space, farther and farther, until, with the faintest nebulae that can be detected with the greatest telescopes, we arrive at the frontier of the known universe." -Edwin Powell Hubble
With 110 deep-sky objects scattered throughout the heavens, the Messier Catalogue provides skywatchers across the globe with a number of spectacular targets, from nearby nebulae and clusters to spectacular, distant galaxies. Each Monday, we spotlight a new one right here.
Image credit: Rolando Ligustri,…
“People say sometimes that Beauty is superficial. That may be so. But at least it is not so superficial as Thought is. To me, Beauty is the wonder of wonders. It is only shallow people who do not judge by appearances. The true mystery of the world is the visible, not the invisible.” -Oscar Wilde
Beyond the planet Earth, beyond all the stars in the night sky, and beyond the Milky Way galaxy, there's literally an entire Universe out there.
Image credit: R. Jay GaBany, of http://cosmotography.com/.
The farther away we're able to look, the more galaxies we're able to see. As far as our…
“Because dark energy makes up about 70 percent of the content of the universe, it dominates over the matter content. That means dark energy will govern expansion and, ultimately, determine the fate of the universe.” -Eric Linder
It's been a while since we've spoken about dark energy, and we were just talking about Einstein's greatest blunder, so let's just dive right in.
Image credit: S. Beckwith & the HUDF Working Group (STScI), HST, ESA, NASA.
This is our observable Universe, as unveiled by the Hubble Space Telescope. With hundreds of billions of galaxies stretched out some 41…
What is distance?
There's the distance between people, who subconsciously space themselves apart, providing a reliable visual matrix of intimacy. It's no coincidence we use the word "close" to describe our most intimate relationships: to whisper and caress, we draw near to one another, less than six inches apart. For chatter amongst personal friends, the norm ranges from 1.5 to four feet. The more estranged, the farther away we shrink. Social distance for interactions among acquaintances overlaps with the previous category, but ranges outwards to nearly twelve feet. Of course, we don't always…
"How old would you be if you didn't know how old you are?" -Satchel Paige
Today marks another year and another trip around the Sun for me. For you, and me, and everything on Earth that makes it through another year on this world, there's a whole lot we get to experience.
Image credit: NASA / ISS Expedition 13.
Some things are tiny: the Earth's rotation slows by about two millionths of a second each year, while some are large: we hurtle over 900 million kilometers in outer space as we orbit around the Sun. Our Earth spins just over 366 times on its axis, while our one revolution around…
What's the application? Measuring the distance from the Earth to the Moon by bouncing a laser off one of the retro-reflector arrays left there by the Apollo missions.
What problem(s) is it the solution to? 1) "How does the distance from the Earth to the Moon vary over time due to things like tidal drag?" 2) "Does the strength of gravity change over time?" 3) "What can we do with a laser to really cheese off people who think the Moon landings were fake?"
How does it work? This concept is simplicity itself. You simply point a laser at the Moon, fire off a short pulse of light, and wait for it…
Very simply, parallax is an apparent motion of an object due to a change in observation position. Let me start with an example. Here are two photos. I took a picture of the cabinet in the background from two slightly different positions. In the foreground is a clone trooper that did not actually move.
I added the dotted line so you could see how the clone trooper appeared to change positions with respect to the background. Here is a diagram of the camera in the two positions along with the toy.
Since the camera changed positions, the object that is closer appears to have moved with…
So as a full member of both the American Astronomical Society and the American Physical Society, I get sent issues of the magazine Physics Today. Well, I was going through the April issue, when I saw this article:
Cosmic Sound Waves Rule
by Daniel J. Eisenstein and Charles L. Bennett
That first name sounds familiar. Why? Because he's my boss! The article requires a subscription, but seeing as how this is what my research is, why don't I tell you what the big idea is.
The Universe is full of dark matter, normal matter, and radiation. When it's young, the radiation is more important than matter…
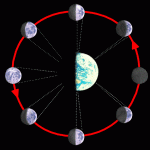
The Moon goes around the Earth, the Earth goes around the Sun, and the Sun goes around the center of the Milky Way. We know the Moon takes about 4 weeks to make its trip around the Earth, and that causes the Moon phases:
We also know that the Earth takes one year to go around the Sun, and that causes the seasons:
We also know that the Earth has been around for about 4.5 billion years, which means it has gone around the Sun about 4.5 billion times. Well, now I ask the question(s):
How long does it take the Sun to go around the Milky Way? How many times has it done that so far, and how many…