Planets
New measurements from NASA's New Horizons spacecraft revealed that Pluto, named for the Greco-Roman god once called Hades, is a little more swollen with ice than previously thought, making it the biggest trans-Neptunian object—more voluminous than rival dwarf planet Eris, which is nevertheless more massive. Greg Laden explains why these orbs are not considered full-fledged planets on his blog.
While Eris orbits the Sun within the 'scattered disc,' Pluto orbits in the Kuiper Belt, a collection of gravelly snowballs that Ethan Siegel says outnumber all the planets in our galaxy. The Kuiper Belt…
“I have announced this star as a comet, but since it is not accompanied by any nebulosity and, further, since its movement is so slow and rather uniform, it has occurred to me several times that it might be something better than a comet. But I have been careful not to advance this supposition to the public.” -Giuseppe Piazzi
So it begins again: the neverending debate about who gets to be a planet and who doesn't. Everyone can bring their own interpretation of the science to the table -- and everyone has their own preferred naming scheme -- but when I think about the Solar System, I try…
"Like all animals, human beings have always taken what they want from nature. But we are the rogue species. We are unique in our ability to use resources on a scale and at a speed that our fellow species can't." -Edward Burtynsky
It's really a romantic notion when you think about it: the heavens, the Milky Way, is lined with hundreds of billions of stars, each with their own unique and varied solar systems.
Image credit: 湖北直行便 of AstroArts, via http://www.astroarts.jp/photo-gallery/photo/13870.html.
But beyond that -- in addition to the stars -- there are hundreds of billions of planets…
The final session in the online discussion of the NASA Astrobiology Roadmap is today from 4-5 pm eastern.
Go to Astrobiology Future to sign in to the live web chat. Questions and comments will be taken both from call-ins and from written questions.
The online discussion will be moderated by Dr Francis McCubbin from UNM, Dr Sean Raymond from Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Bordeaux, and yours truly...
The live session will, as with the other Roadmap sessions, be followed by a week long opportunity to input questions, ideas and topics for discussion at The Astrobiology Future Forum.
The four…
You certainly didn't hear it here first: today NASA, at a press briefing, announced that minerals analyzed by the Curiosity rover indicate that life might, in the galactic past, have survived on Mars. The rover's been poking around an ancient network of stream channels descending from the rim of Gale crater since September of last year; now, after drilling into the sedimentary bedrock nearby, it's hit on a treasure trove of life-supporting minerals: carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and nitrogen. These mineral findings are really just icing on the cake, as the geological…
"Night, when words fade and things come alive. When the destructive analysis of day is done, and all that is truly important becomes whole and sound again." -Antoine de Saint-Exupery
When you look out into the Universe, what is it that you typically think of? Do you think of reliable, fixed stars and constellations? The vast expanse of the Milky Way, with its memorable dust lanes and amorphous shapes?
Image credit: Wally Pacholka of http://www.astropics.com/.
The unchanging nature of the points of light in the sky?
Image credit: Roth Ritter (Dark Atmospheres), of the double cluster in…
"Stuff your eyes with wonder, live as if you'd drop dead in ten seconds. See the world. It's more fantastic than any dream made or paid for in factories." -Ray Bradbury
It wasn't all that long ago -- back when I was a boy -- that the only planets we knew of were the ones in our own Solar System. The rocky planets, our four gas giants, and the moons, asteroids, comets, and kuiper belt objects (which was only Pluto and Charon at the time) were all that we knew of.
Image credit: NASA's Solar System Exploration, http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/planets/index.cfm.
But these were just the worlds…
"You don't drown by falling in the water; you drown by staying there." -Edwin Louis Cole
Our Solar System is -- at least from our perspective -- the most well-studied system of planets, moons, asteroids and comets in the entire Universe.
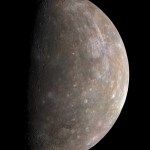
Image credit: Olaf Frohn, from earlier in 2012.
And in this system, the closest planet to our Sun, Mercury, was also one of the most poorly understood planets until very recently. Because Mercury is so close to the Sun, it's very difficult to view it under good conditions with a telescope; the risk of ruining your optics by exposing them to direct…
The space-heads among you have undoubtedly heard about the Curiosity rover's first significant discovery: the remnants of an ancient streambed on Mars, which would seem to indicate the presence of water in the planet's history. This jagged pile of alluvial rock and dust may not look like much, but it brings to mind one of my favorite pieces of Martian historical arcana.
For a time in the late 19th century, it was believed that there were canals on Mars.
The Italian astronomer Giovanni Schiaparelli, who observed Mars in 1877, was the first to describe, name, and lovingly illustrate…
The NASA Mars rover Curiosity just landed on Mars. Those of us who tuned in vicariously via NASA's live coverage watched as a roomful of tense engineers exploded, and heard their disembodied voices whispering and booming through the control room. Holy shit. We did it. Their headsets fell askew, they glad-handed one another, criss-crossing the room, and then, immobilized by a sudden hush as the news spread: We've got thumbnails.
Thumbnails. We watched as a tiny image formed, transmuted across the void of space and into this room. It was black and white, an indistinguishable gesture of light…
"Don't go around saying the world owes you a living. The world owes you nothing. It was here first." -Mark Twain
So, you've been around a while, seen all sorts of things, and learned an awful lot about the world, solar system and Universe that we live in. But how well do you know it, really?
Image credit: NASA / Lunar and Planetary Laboratory.
To scale and in order, these are the eight planets you know so well. There are the four rocky worlds of our inner solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, and the four gas giants that dominate the outer solar system: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and…
A couple of months ago, I wrote a piece here on Universe exploring the ideas of the futurist Gerard K. O'Neill, who designed far-out but ultimately quite pragmatic environments for human habitation in space in the mid-1970s. In that article, I touched briefly on the notion of the "Overview Effect," a phrase coined by the writer Frank White to describe the profound insight -- characterized by a sudden awareness of life's interconnectedness and the frailty of our planet -- experienced by astronauts gazing down at the Earth from space.
Frank White is the author of The Overview Effect: Space…
By Dr. Friedemann Freund; Carl Sagan Center for the Study of Life in the Universe, SETI Institute, and Gail Jacobs
Friedemann Freund doesn't shrink from taking on the really big problems. His research has elucidated such important phenomena as the fact that rocks under stress behave like batteries that can produce currents deep within the crust of the Earth. These are not piddling electron flows, either - the currents could be as large as millions of amperes, sufficient to be measured above ground, and perhaps even from orbit. Understanding and exploiting this phenomenon could lead to a…
"All things move and nothing remains still" -- Heraclitus
The history of astronomy can be read as a story of better and better vision. Over the centuries, we have supplemented our vision with technology that allows us to see further and more clearly; while Ancient astronomers, who relied only on their naked eyes to perceive the universe, managed to make star catalogues and predict comets, Galileo, pressing his to a telescope, saw all the way to the moons of Jupiter.
Optical telescopes and the human eye are fundamentally limited; early astronomers were forced to gaze into telescopes for…
By Dr. Ignacio Mosqueira, an astrophysicist at the Carl Sagan Center for the Study of Life in the Universe, SETI Institute, and Gail Jacobs
Ignacio Mosqueira works with Paul Estrada to piece together the way in which giant planets - such as Jupiter and Saturn -- and their moons and rings formed. Ignacio notes that making moons is similar to forming planets. Understanding moons may have something to tell us about the possible habitats for life, since large moons could, in principle, have both the liquid water and atmosphere necessary for the kind of diverse biology we see on planet Earth.…
By Dr. Rosalba Bonaccorsi
Environmental Scientist at the Carl Sagan Center for the Study of Life in the Universe, SETI Institute, and Gail Jacobs
Rosalba, what first sparked your interest in science?
I've always had big dreams -- even as a young girl. As soon as I started to walk, I took an interest in conducting experiments with whatever was available around such as household plants and various chemical compounds. I'm lucky I didn't end up poisoned or otherwise hurt! I remember dismantling alarm clocks. I was so curious!
As a young girl, I was in poor health and as a result spent a lot of…
By Dr. Paul EstradaPlanetary physicist at the Carl Sagan Center for the Study of Life in the Universe, SETI Institute, and Gail Jacobs
If planets are a dime a dozen, moons are less than a penny each. There are at least 139 moons just within our own solar system. Most of these are the property of the gas giant planets beyond Mars. More than just a nice accompaniment to planets, moons may have habitats in which liquid water could ebb and flow - and possibly be a suitable home for life. Planetary physicist Dr. Paul Estrada investigates how moons around gas giants are formed -- an important…
By Dr. Cynthia Phillips
Planetary geologist at the Carl Sagan Center for the Study of Life in the Universe, SETI Institute
Jupiter's moon Europa could be the best place beyond the Earth to search for life. This small moon, about the size of Earth's Moon, is one of the Galilean moons first discovered 400 years ago by Galileo. The Galilean moons were the first objects observed to orbit another planet, and they revolutionized the way our solar system was understood.
Today, the moons of Jupiter are known to be a scientifically rich part of our solar system, and they are yielding a new revolution…
by Nathalie A. Cabrol
I realize how immodest the title of this first blog may sound and it is certainly not my intention to convince anybody that I will answer this question in the limited space allowed here or even in a lifetime. My hope is, instead, to stir thoughts and invite an exchange of diverse perspectives to make this a thread that we can all pull from time to time. It is an immense subject debated in an abundant literature, but discussing it is certainly not the exclusive privilege of those called explorers. All beings, from the greatest minds to the simplest forms of life on this…
A large part of my affection for science comes from the thrill of terror I get when a particularly insane piece of science news hits the presses. When an article begins with a sentence like, "there is something strange in the cosmic neighborhood," or "all the black holes found so far in our universe may be doorways into alternate realities," my pulse quickens and a dormant paranoia is roused from deep within my breast: a sensation of joyful panic. I used to call this the "fourth-grade nightmare fantasy." This might be because as a long-time science fiction adept, I tend to read science news…