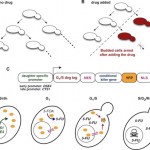
My labmate Bruno's newest paper, "A synthetic circuit for selectively arresting daughter cells to create aging populations" came out today in the journal Nucleic Acids Research (and it's open access!). Using a cleverly designed genetic circuit that activates cell growth arrest in newly divided cells only in the presence of a drug, Bruno was able to create a population of yeast made up of only old cells, called the "daughter arrester."
You would think that yeast, being so single celled and bread-y, wouldn't be able to tell us much about human biology or anything as complex as aging, but many…
BioShock2 came out a couple days ago, the sequel to the wildly successful video game BioShock. BioShock is a first-person-shooter video game set in Rapture, an underwater city overrun by violently insane genetically engineered mutants called "Splicers", creepy zombie-like girls, "Little Sisters", that harvest corpses for "ADAM"--sea slug stem-cells that provide super-human strength, regenerative powers, and the ability to rewrite the human genome with the injection of "plasmids"--and genetically engineered "Big Daddies" that protect them, mentally blank superhumans grafted into enormous…
"The history of any given technology is extraordinarily complex."
--Rob Carlson, Biology is Technology.
Analyzing the history of a technology requires a complex look at the social, economic, and political context in which it emerged, and the reciprocal influences that the developing technology exerts on these factors. Predicting what the future of a technology will be like, how it will affect the economy and understanding the potential risks and payoffs is much much harder. Rob Carlson's new book, Biology is Technology: The Promise, Peril, and New Business of…
Teachers' Domain, a digital media resource for teachers, profiled Karmella Haynes, one of my amazing labmates!
There's a fun video of Karmella talking about her work on synthetic biology devices to track cancer cells and about careers in science streaming on the Teachers' Domain website. You should all check it out, she's an incredible scientist, artist, and teacher--a true inspiration!
Synthetic biology is still a new field, and victories are small and incremental. Much of the promise and peril of synthetic biology still lies in the future: genetic devices made to order, computer aided genome design, organisms specially constructed for specific industrial purposes. Will we use this biological technology for good--new more affordable and accessible drugs, better vaccines to emerging diseases, and clean energy--or evil--new deadly pathogens and immortal super soldiers? I think it's safe to say that almost everyone hopes that we'll get all of the good stuff without any of the…
I'm auditing a really cool class at MIT this semester called "Documenting Science Through Video and New Media." In the first class, we watched some of the earliest science films ever made, microscopic vaudeville performances by cheese mites and flies, made into a little meta-documentary by New Scientist a couple years ago. The videos are really fun, combining a sense of wonder at the beauty and complexity of the natural world with a sense of the excitement and spectacle of moving pictures. Science and nature documentaries like these became a hugely popular hit, and still are today with series…
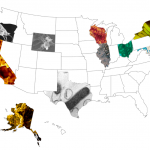
I've had some great suggestions for "Official" State Microbes in comments and via twitter. I'm filling in the map as they come:
So far we have:
Alaska -- Alcanivorax borkumensis for its oil consumption
California -- Ralstonia metallidurans for its gold precipitating qualities (and CA-MRSA as a terrifying runner up)
Illinois -- Penicillium roqueforti for its blue cheese making
Maryland -- Chlamydia trachomatis for UMD research on the bug
Massachusetts -- Escherichia coli for its importance to biotech
New York -- Pseudomonas putida, the first organism to be the subject of a patent case, which…
Wisconsin lawmakers just passed a bill to name Lactobacillus lactis, the bacteria that turns milk into cheese, into its official state microbe! What microbe do you think best represents your state? I think Massachusetts' state microbe should be E. coli, not for the gross make you sick part of course, but because of the importance of the biotech industry to Massachusetts and the importance of the lowly E. coli to biotech. Add your vote for your state microbe in the comments!
The music from the Darwin Electro-Opera I mentioned a while back is now available for free, streaming on Pitchfork!
(via Nick)
Riversimple, a small UK-based company, has designed a tiny, relatively cheap, and remarkably open-source hydrogen fuel cell car. The car will not be available for sale, but people will be able to lease it, with the lease agreement including maintenance, fuel, and the eventual recycling of the car. This unique business model allows for the company to manage sustainability for the life of the car. Check out the video below to see the car in action:
Hydrogen, of course is still hard to make, and there aren't many sustainable hydrogen production options. My lab is working on ways to make…
I sort of love the "KEEP CALM AND CARRY ON" posters that have become the darling of interior decorating bloggers and graphic design jokesters alike in the past few years. I even have one of the posters hanging in my apartment. Then I saw Merlin's version.
At first I LOLed, and then I was like "huh." How did we get here? How did this meme evolve from stoic World War II propaganda to hilarious Richard Dawkins jokes?
And thus, the phylogenetic tree of "KEEP CALM AND CARRY ON" posters was born:
High res here.
Today in my searches for the hot new trends in synthetic biology, I found a news article from Science Daily with an intriguing title: "Scientists Achieve First Rewire of Genetic Switches." Rewiring genetic switches sounds pretty neat, but this headline was intriguing to me first of all because it's kind of late to the party--in fact one of the first papers in modern synthetic biology back in 2000 was about engineered genetic switches: "Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli". When I looked more closely, the article wasn't about this kind of transcriptional switch though,…
Check out these cute hand-embroidered oscilloscope merit badges! Available on Etsy.
There's a funny article over at H+ magazine called "Get Naked: It's Good for Your Brain," telling us exactly that:
Clothing is crushing us! Trapped in tomb-like textiles, we exile our flesh from experiencing the environment. We atrophy the majority of our epidermis. If you put a plaster cast on a broken arm, the skin starves for Vitamin D; muscles weaken due to strangled range of motion; nerve synapses depress to a whimper of their former joy. Twenty-first century hominids shroud the entire skin palette, obliterating symbiosis with the planet except via face, neck and hands. (Burqa-clad…
Things are gearing up for iGEM 2010, and in looking through some of the incredible work of the 2009 teams, I remembered the University of Washington Software team, who made an awesome lego robot that can move small volumes of liquid around in 96-well plates, a crucial and typically very expensive task in high-throughput biology. What makes the team especially remarkable is that the only member is an 11 year old kid, Gabriel See, who designed and built the robot on his own. Gabriel had the flu during the jamboree, so he unfortunately couldn't fly to MIT to share his work, but he did get his…
Cooperation and altruism are widespread in biology, from molecules and genes working together in a cell, to bacterial communities that require coordinated behavior to survive in a tough environment, to human relationships and societies. Our human cultural perspective (perhaps even more specifically our American cultural perspective, focused as it is on individuality, free markets, and the American Dream), however, treats cooperation as an outright anomaly that has to be explained away by science (or often, religion). If natural selection is about the "survival of the fittest" how can a…
Oscillators are huge in synthetic biology. They're an exciting challenge, very hard to make in a controlled, robust way, they have the potential to be useful in many applications, like well-timed drug delivery, and they can tell us a lot about how natural circadian rhythms work. A new paper in this week's issue of Nature from Jeff Hasty's group at UCSD presents a new synthetic biological oscillator in bacteria. While there have been a lot of oscillators designed in the past few years, this one is special because it couples oscillations in fluorescence to bacterial quorum sensing, allowing the…
Nature News has an excellent article about the hype, the challenges, and the potential of synthetic biology. The article quotes Martin Fussenegger, a leader in mammalian cell synthetic biology as saying "The field has had its hype phase, now it needs to deliver." In order to do so researchers will have to overcome five main challenges:
Many of the parts are undefined
The circuitry is unpredictable
The complexity is unwieldy
Many parts are incompatible
Variability crashes the system
The article is a great read, and includes interviews with many of the big names in the field, as well as…
Modern day biological engineering and artificial life research focuses on the microscopic, the molecular, the informational, the stuff of the scientific revolutions of the past one hundred years. Our current synthetic biologies aim to turn the living into the designed, the wet into the computational, the complex into the understandable. In the 1700's, the interplay between the living and the mechanical was reversed; engineers were trying to make machines look and feel more like living things--soft, flexible, moist. Studying these historical artificial life technologies provide a valuable…
Many synthetic biologists cite one of Richard Feynman's many famous quotations as the inspiration for their work: "What I cannot create I do not understand." For synthetic biology the interpretation is clear--only by designing and building living systems will we truly understand the principles underlying the functions of living cells.
This connection between knowing and making that defines much of synthetic biology research today is, however, a much older idea, rooted in the philosophy of the enlightenment and centuries of western science. The 18th century philosopher Giambattista Vico said…