domestication
Only 1% of the human genome codes for proteins, which might make you wonder what the rest of the nucleotide sequence is good for. In 2012 the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (or ENCODE) announced that a full 80% of the genome played a biochemical role, interacting with proteins in some way. But a new study says it takes only about 8% of our non-protein-coding genes to make us human. This is the percentage of genes that are 'conserved' by the human species: change one of these genes, and you'll alter the fitness of the individual. These genes evolve slowly (although not as slowly as protein-…
Image of yellow lab from Wikimedia Commons
New genetic analyses supports the argument that the domestication of man's best friend coincided with the advent of argiculture and human settlements. Researchers Erik Axelsson (Uppsala University, Sweden) and colleagues present evidence suggesting that wolves became domesticated as they increasingly scavenged in the human settlements. The researchers sequenced DNA from 12 wolves and 60 dogs to find areas that evolved under selection pressure. What they found were differences in genes relaed to the development of the…
You've probably had a conversation that goes something like this:
Person A: "My dog is sooooo amazing!"
You: "I mean, dogs are awesome and all, but what's so amazing about this particular dog?"
Person A: "He just understands me. It's like he knows what I'm thinking and what I need."
You: "Do you think he's just maybe responding contingently do your overt displays of emotion?"
Person A: "Listen, man, I'm telling you: my dog can read my mind!"
No matter on which side of this sort of argument you tend to fall, the question of whether or not domestic dogs can read human minds is an interesting…
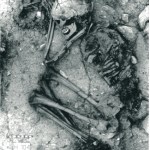
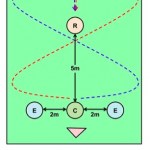
There is a small bit of land, only about a square kilometer, that has added a new wrinkle to the story of animal domestication. This bit of land located in Northern Jordan, just southeast of the Sea of Galilee near the banks of the Jordan River, is home to an archaeological site known as 'Uyun al-Hammam. One key feature of this site, excavated in 2005, is a burial ground containing the remains of at least eleven humans in eight different gravesites. The early humans were buried here sometime during the pre-Natufian period, or around 16,500 years ago.
Layout of the 'Uyun al-Hammam site, and…
Eric M. Johnson and I spent about 45 minutes discussing "evolutionary psychology beyond sex" last night, which you can see today on Bloggingheads "Science Saturday."
Or just watch it here:
I showed this video today as an intro to my 8-week "mini-course" on Canine Cognition.
In it, narrator John Lithgow presents two slightly different versions of the dog domestication story. The first version is essentially the Belyaev story: young wolves would be adopted into the camps of early humans. Only those who were most tame would breed with eachother, and over many generations, the domestic dog would emerge. The second is the version in which wolves "chose" to be domesticated - they noticed a lot of tasty trash around human encampments, and if they were unafraid enough to hang around,…
Cooperation and conflict are both a part of human society. While a good deal of the academic literature addresses the evolutionary origins of conflict, in recent years there has been an increased focus on the investigation of the evolutionary origins of cooperative behavior. One component of cooperative behavior that might be present in other animals is aversion to inequity. Some scientists have suggested that inequity aversion may itself be the main factor driving the enforcement of cooperation. Put simply, inequity aversion is the resistance among partners to unequal rewards following…
At least one dog can be found in forty percent of US households, and forty percent of those owners allow their dogs to sleep on their beds. To put this in perspective, in a family with five children, two of them can be expected to become dog owners, and one of them will probably allow the dog to sleep on his or her bed. In an undergraduate lecture class of two hundred, eighty of those students come from homes with at least one pet dog. So as you might expect, dogs are a big business! In 2007, the pet industry was worth about $40 billion in the US, with dogs responsible for the largest share…
For today's dose of monday pet blogging, head on over to a piece that I wrote for Scientific American that went up today. I used the invitation as an opportunity to a dig a little deeper into the story of Belyaev and his domesticated silver foxes (I previously wrote about them, here and here)
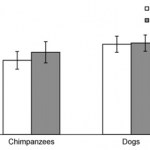
Dogs are pretty smart. They can have huge vocabularies, they can infer meaning in the growls of other dogs, and they can effortlessly figure out if other dogs want to play or fight with them. But their intelligence might be limited to the social domain; indeed, while they outperform chimpanzees in social tasks, chimpanzees outperform them in many other tasks. And they might have developed their impressive social skills as merely an accident of natural and artificial selection.
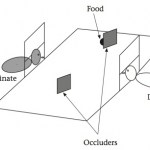
Previous research has shown that dogs can use lots of different forms of human communicative signals to find food,…
I will be reposting some dog-related posts from the archives in the coming few weeks as I prepare for the course I'm teaching this semester on dog cognition. Please let me know if you find something inaccurate or unclear.
Domesticated dogs seem to have an uncanny ability to understand human communicative gestures (see here). If you point to something the dog zeroes in on the object or location you're pointing to (whether it's a toy, or food, or to get his in-need-of-a-bath butt off your damn bed and back onto his damn bed). Put another way, if your attention is on something, or if your…
In general, the ability to attribute attention to others seems important: it allows an animal to notice the presence of other individuals (whether conspecifics, prey, or predators) as well as important locations or events by following the body orientation or eyegaze of others. We've spent a lot of time here at The Thoughtful Animal thinking about how domestication has allowed dogs to occupy a unique niche in the social lives of humans. They readily understand human communication cues such as eye-gaze and finger-pointing, and capitalize on the infant-caregiver attachment system to have their…
It's been a pretty long stressful week around here, and not just because of Pepsipocalypse and the resulting fallout. But, well, I'm back, and I have an awesome paper to tell you about. When I saw it I just KNEW it had to be blogged.
Mythbuster Adam Savage sets the yawning in motion in Mythbusters attempts to start a yawning epidemic across the globe
Did watching that video make you yawn? Chances are it did, and you can thank contagious yawning for it. What is contagious yawning? Contagious yawning is a very well-dcoumented phonemenon wherein yawning is triggered by the perception of others…
You can have a pet domesticated fox of your very own - from the Russian fox farm I've previously written about - for the low low price of just $5,950.
Figure 1: Isn't he cute? Click to embiggen.
Check it out.
According to the website,
Housing:
Foxes can live outside or inside.They need shade from excessive heat and rain. A bed or blanket is nice, but optional.
If the fox lives outside, the cage should have a bottom or the walls of the cage should be dug in deep enough so that the fox cannot dig a hole and escape.
Inside your house, they will snuggle on a bed like a cat.
During the…
Happy Father's Day, everyone!
I spent a lot of time today thinking back to why I started blogging in the first place, while I was at my parents house doing the other-than-science things that I love to do: playing with the dog, cooking, gardening. I realized that I've not done enough of that stuff lately.
I've only been seriously doing the blog thing (in the current format) since January, and I've now been here at Scienceblogs around two months, so it was time to reflect. The transition from Wordpress obscurity to Scienceblogs prominence happened relatively quickly for me, and I think it's a…
Dogs are particularly good at tasks that involve communicating or cooperating with humans, which has led some researchers to speculate that they are really good at solving social tasks, more generally. For example, dogs can figure out where a human's attention is, are really good at picking up on eye-gaze and finger pointing cues, distinguish among different individual humans (by contrast, humans are really bad at distinguishing among different individual monkeys, for example), and at least in one outstanding case, are capable of "fast mapping."
Relative to non-human primates, domestic dogs…
I've decided I want to cover some recent research on social cognition in domesticated dogs. But first, we need some background. So here's a repost from the old blog.
Today I want to tell you about one of my most favorite studies, ever, of animals. Are you ready? It's a FIFTY YEAR LONG longitudinal study of captive silver foxes in Russia. Gather around, pour yourself a cup of your favorite beverage, get comfortable, and enjoy storytime.
In 1948, Soviet scientist Dmitri Belyaev lost his job at the Department of Fur Animal Breeding at the Central Research Laboratory of Fur Breeding in Moscow…
Yesterday afternoon, I watched the livestream of the "All Creatures Great and Smart" session of the World Science Festival in New York City. The session was absolutely fantastic, and featured Brian Hare, Vanessa Woods, Jeremy Niven, Patrick Hof and Klaus Zuberbühler.
The conversation challenged long-held assumptions about the differences between "animal" and "human", and included fascinating discussion about pin-sized brains that can count, categorize, and hold a grudge against those who've tried to swat them. Does your dog really think and feel like a human? Do our closest primate…
Zen recently wrote mentioned this study on his blog, so I thought it was time to dredge it out of the archives. Also, I've just returned from APS (see my daily recaps here here and here), and I am TIRED.
Domestic animals and their wild counterparts can be different in big ways; there can be differences in morphology (physical characteristics), physiology, and behavior. These changes may depend on spontaneous adaptations to captivity or to artificial selection pressures arising from the motivation for domesticating the animal in the first place.
One change that is often observed as a result of…
Lately, a paper to be published in the June edition of the American Naturalist has been getting some attention. The findings that are getting reported out of this paper didn't make sense to me, but I wondered if this was an issue with accuracy in reporting. So I went and found the paper. Turns out that the reporting is accurate, its the actual findings from the paper that confuse me. I really wanted to make sense of this paper, so I've been waiting a while to blog about it. But I can't make sense of one key finding.
Figure 1: An artist's rendition of me, being confused. If, you know, I were…