global warming
The Problem with terminology
There is some confusion about the way we talk about global warming. Most of this confusion arises during the communication of science to the public or to policy makers. Part of this confusion rests within the science itself; There is no meaningful confusion about the nature of global warming or how it is observed, but there are some terminological glitches of the kind that arise in science all the time, and that rarely matter to the science itself.
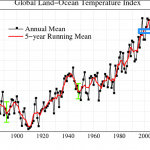
The most commonly used indicator of global warming is a graph that is meant to show the effects of global warming…
Joe and Mary built a house.
They built it on an old flood plain of a small river, though there'd not been a flood in years. This was a 500-year flood plain. Not a very floody flood plain at all.
The local zoning code required that for a new house at their location the bottom of the basement needed to be above a certain elevation, with fill brought in around the house to raise the surrounding landscape. But Joe's uncle was on the zoning board, and it wasn't that hard to get a variance. This saved them thousands of dollars, and they built the house without the raised foundation or the fill.…
Recently, a paper published in a Chinese journal of science by Monckton, Soon and Legates attracted a small amount of attention by claiming that climate science models "run hot" and therefore overrepresent the level of global warming caused by human greenhouse gas pollution. The way they approached the problem of climate change was odd. The Earth's climate system is incredibly complex, and climate models used by mainstream climate scientists address this complexity and therefore are also complex. Monckton et al chose to address this complexity by developing a model they characterize as "…
The Earth is warming because of what humans have been doing to the atmosphere. Global Warming has a lot of effects many of which we've discussed here, but the most obvious one is, well, it gets warmer. At present, India is experiencing record breaking heat and people are dying.
It is very difficult to say how many people die from the heat in any region. We can use a standard approach used by epidemiologists to estimate this number. This involves simply looking at mortality rates as they change over time to try to detect a signal, an increase, associated with the variable in question. If…
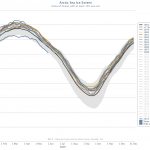
The surface ice in the Arctic has been melting to historic low levels every year for the last several years. The graph above shows the first ten years in the National Snow & Ice Data Center records, meant to indicate what Arctic Sea Ice "normally" does as it melts off during the northern warm months. The thick black line is the average over 1981-2010, and grey shaded area shows two standard deviations above and below that line. The blue line tracking along the lower end of the 2SD shaded area is the ice extent this year. During the period when sea ice is at its maximum, this year's ice…
Human released greenhouse gas pollution changes the climatic system through a variety of mechanisms. Trade winds and jet streams change their patterns of movement, and the distribution of moisture in the air changes, with precipitation either lacking more than usual or being more abundant than usual. The patterns of movement of major air masses and the increased bifurcation of air masses into more wet than usual and more dry than usual can result in long periods where region experiences excess precipitation or a lack of precipitation. When the latter happens, there can be a drought.…
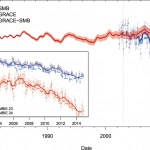
A large portion of the glacial mass in Antarctic, previously thought to be relatively stable, is now understood to be destablizing. This is new research just out in Science. The abstract is pretty clear:
Growing evidence has demonstrated the importance of ice shelf buttressing on the inland grounded ice, especially if it is resting on bedrock below sea level. Much of the Southern Antarctic Peninsula satisfies this condition and also possesses a bed slope that deepens inland. Such ice sheet geometry is potentially unstable. We use satellite altimetry and gravity observations to show that a…
A new paper is just out in The Lancet that examines the mortality risk of high and low ambient temperatures. The basic idea is that if it is either to hot or too cold, mortality may increase, possibly with the weather being a factor to augment the effects of other health problems, or as a direct result. The paper is methodologically reasonably well done but leads to conclusions that I think will be misinterpreted and misused. The paper implies that a shift to a warmer world would have lower mortality effects than a shift to a colder world might. Or, more significantly, that a shift to a…
It is a fiction that the right wing, and the Republican party, and their primary philosophical guru (Rush Limbaugh) and mouthpiece (FOX News) are more American, more security-savvy, and more patriotic than Liberals, Progressives, and Democrats. This fiction is part of a common bully tactic you already know about because you were either bothered by the bullies, or you were a bully, in middle school. The bully takes his nefarious trait and projects it on his victim. And now, we see yet another piece of evidence for this, one among many. FOX News has attacked President Obama for his…
A few notes from Week 3 of Denial 101x: Making Sense of Climate Science Denial. These notes are mainly about the science and not the denialism part (unlike my last post, which addressed the central theme of the course, denialism, more.)
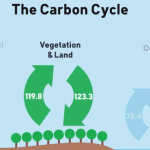
The Carbon Cycle
Atmospheric CO2 concentrations have gone up by about 40%. Simple explanation: Humans are releasing Carbon into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuel. More complex explanation: Humans are affecting the Carbon Cycle in a number of ways, releasing Carbon (burning fossil fuels) as well as affecting natural Carbon sinks.
This became known,…
The title of this post is also the title of a new peer reviewed paper by Stephan Lewandowsky, Naomi Orskes, James Risbey, Ben Newell and Michael Smithson, published in Global Environmental Change. The article is Open Access, available here. Stephan Lewandosky has a blog post on it, in which he notes,
... we examine the effect of contrarian talking points that arise out of uncertainty on the scientific community itself. We show that although scientists are trained in dealing with uncertainty, there are several psychological and cognitive reasons why scientists may nevertheless be susceptible…
Note: The original title of this post was "A Global Warming Fingerprint Confirmed: Upper Troposphere Warming" because I was thinking that upper troposphere warming was a fingerprint. John Cook contacted me to let me know that he didn't think it was. The reason it is not is that more than one thing can cause upper tropospheric warming, not just AGW. However, it does turn out to be more complicated than that. Various people claiming that a lack of UT warming was evidence of no warming have now been shown wrong, but even a lack of warming is not, if you will, an anti-AGW fingerprint. In the…
Global warming is typically measured at the surface, with data from thermometers all across the land areas and sea surface temperatures combined. That isn't the whole story, of course. Much of the added heat, an effect of human generated greenhouse gas pollution, goes into the upper 2,000 meters or so of the ocean. But we use the surface measurements to track global warming because we have the data for a long period of time, and those data in turn have been linked to longer running but less precise paleo data.
Almost every month for way over a year now has been warm, and April 2015 is no…
The Earth's climate is warming. The upper oceans are warming, the sea surface temperatures are elevated, the air in the lower Troposphere, where we live, is warming. This warming is caused almost entirely by the increase in human generated greenhouse gasses and the positive (not positive in a good way) feedbacks caused by that. The effects that increase the global heat imbalance and the effects that decrease it (such as greenhouse gas increase and aerosols -- dust -- from volcanoes, respectively) vary over time in their effect, which causes some variation in the upward march of global…
I'm auditing the EdEx course "Denial101x: Making Sense of Climate Science Denial." This is Week 2: Global Warming ins Happening. The course is covering indicators of warming, what is happening in the Cryosphere, and related matters.
Here is an example lecture segment:
A central theme of this week is the relationship between climate and weather, and how this relationship becomes fodder for the development of myths in service of denial about climate change. The climate is a cherry orchard. Weather is the cherries. Don't pick the cherries!
There are many dimensions the climate system that…
I recently noted that there are reasons to think that the effects of human caused climate change are coming on faster than previously expected. Since I wrote that (in late January) even more evidence has come along, so I thought it was time for an update.
First a bit of perspective. Scientists have known for a very long time that the proportion of greenhouse gasses in the Earth’s atmosphere controls (along with other factors) overall surface and upper ocean heat balance. In particular, is has been understood that the release of fossil Carbon (in coal and petroleum) as CO2 would likely warm…
Dire Predictions: Understanding Global Warming by Michael Mann and Lee Kump is everyperson’s guide to the latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report. The IPCC issues a periodic set of reports on the state of global climate change, and has been doing so for almost two decades. It is a massive undertaking and few have the time or training to read though and absorb it, yet it is very important that every citizen understands the reports’ implications. Why? Because human caused climate change has emerged as the number one existential issue of the day, and individuals,…
I recently posted an overview of a new climate study, Comparing the model-simulated global warming signal to observations using empirical estimates of unforced noise, by Patrick T. Brown, Wenhong Li, Eugene C. Cordero & Steven A. Mauget. That study is potentially important because of what it says about how to interpret the available data on global warming caused by human generated greenhouse gas pollution. Also, the since publication the study has been rather abused by climate contrarians who chose to interpret it very inaccurately. This is addressed in this item by Media Matters.
My…
A group of scientists attending a major conference get together in a bar. They talk, but they agree on nothing because they are critical academics. The server comes along to take the beer order and says, "I noticed you all are constantly arguing. What are you arguing about?"
"Sensitivity," one of them says. "It is the number of degrees C the Earth's surface will warm with a doubling of CO2 in the atmosphere. Is it 2, 3, 4? ... We cant settle on a number"
The server considers their plight for a moment. Suddenly, she rips several sheets out of her order book and hands one to each of the…