metabolic disease
Ziv Zwighaft
Ziv Zwighaft is a research student in the group of the Weizmann Institute’s Dr. Gad Asher. Their new findings reveal some intriguing connections between our circadian clocks – which tick according to cycles of day and night – metabolism and aging. Here is his description:
King Solomon said: “There is a time for everything, and a season for every activity under the heavens.”
Our research tries to take this insight into the condition of living creatures a few strides forward. How strictly does it apply? Our lives are regulated by a biological clock – it’s actually many clocks…
What's in a picture?
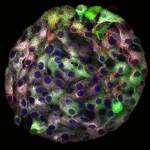
Prof. Benny Shilo knows the value of a good picture. We recently mentioned his book: Life’s Blueprint, which uses photographs of things like bread dough and yeast cells to illustrate the process of biological development. Here is the image from the most recent piece we have uploaded on his research:
This is an individual Islet of Langerhans, as you’ve never seen it before. The white dots are the insulin-containing vesicles inside the beta cells, which both sense glucose levels and secrete insulin. Shilo and his team managed to get “close-up shots” of the individual cell…
Could artificial sweeteners be helping cause the very thing they are supposed to prevent? They may well do so, and you can probably blame your microbiota – those masses of mostly-friendly bacteria that live in your gut. According to a paper by Weizmann Institute scientists that appeared today in Nature, artificial sweeteners not only encourage the wrong kind of bacteria to expand their numbers, they also induce mix-ups in the cross-communication between these bacteria and your body. Those mix-ups can lead to glucose intolerance – the first step toward metabolic syndrome and diabetes. So,…
The next time you reach into the fridge for a midnight snack – take heed: New research by Weizmann Institute scientists has shown that the time at which you eat your meals might have a profound effect on your liver triglyceride levels. Their research was conducted on mice, but if found to be true for humans as well, it may have clinical implications in the way patients could be treated for fatty liver and other metabolic diseases, which are characterized by abnormally elevated levels of lipids in blood and liver cells.
Our bodies are naturally cued to carry out various biological…
You might not think of cell suicide as a sexy subject - but it is actually quite hot. Cells off themselves for any number of reasons: In embryonic development, cell suicide helps shape the growing organism. In adults, suicide is the last resort of a cell whose DNA is too damaged to repair, and its death prevents cancer, among other things. You can think of cell suicide as a prerequisite for the existence of multicellular life.
Prof. Atan Gross has, for the past several years, been focusing on a pair of cell suicide proteins - BID and ATM. The more Gross studies these proteins, the more…
Feel the need to eat chocolate when under pressure? You might be able to blame it on your genes, specifically a gene in the brain that responds to stress. This gene, when active, brings out your anxiety and as well as bringing about metabolic changes that tell your body to burn sugar, rather than fat. The same metabolic changes reduce insulin sensitivity in muscles, raising sugar levels in the blood, and causing the pancreas to churn out more insulin. According to the Institute scientists who revealed the gene's function, if the constant stress of daily life keeps this gene overworked, the…