Life Science
According to a new statement from the CDC, while Ebola is deadly to humans and animals, it is very difficult to catch. Therefore, they concluded that pets are not at significant risk of Ebola in the US. Moreover, there have been no reports of dogs or cats becoming ill in Africa. For more information, visit the CDC website
http://www.cdc.gov/vhf/ebola/transmission/qas-pets.html
I have. So I surfed the web and found this neat video from Smithsonian that explains it all.
Image from the American Physiological Society's website.http://www.the-aps.org/mm/Conferences/APS-Conferences/2014-Conferences/…
Wednesday was the last day of the meeting that culminated in a closing banquet with an awards session to honor students who had exceptional presentations. What an impressive group of young comparative physiologists! The plenary lecture was given by Dr. Steven Chown (Monash Univ, Australia). He spoke about climate change forecasts and continuing environmental changes and how important it is to understand how animals adapt to changing conditions in order to…
Image from the American Physiological Society's website.http://www.the-aps.org/mm/Conferences/APS-Conferences/2014-Conferences/…
Tuesday was no less exciting than Monday!
Here are some highlights:
I thoroughly enjoyed a session called "Overcoming a Major Physiological Barrier: Adaptation from Saline to Freshwater Habitats" which highlighted the need for several species to shift how they regulate ion balance when they migrate between fresh water (ion absorption from the water) and salt water (ion secretion to the water).
Clements K, Bojarski L, Johnson K, McMillan S, White L, Angert E (Univ…
Image from the American Physiological Society's website.http://www.the-aps.org/mm/Conferences/APS-Conferences/2014-Conferences/…
As anticipated, the meeting today was excellent! Here are some highlights from today:
Dr. Michael Joyner (Mayo Clinic) spoke about how we should reconsider animal models that are used in research as laboratory rodents can be manipulated to match their genotype to their phenotype. In other words, researchers modify the animal's genome to produce a specific disease or attribute they are interested in studying. The problem with this approach is that genes can be…
Image from the American Physiological Society's website.http://www.the-aps.org/mm/Conferences/APS-Conferences/2014-Conferences/…
I am really excited about the comparative physiology conference that starts this weekend in San Diego! Here is a press release about the meeting (author Stacy Brooks from the American Physiological Society):
Bethesda, Md. (September 25, 2014) — More than 400 comparative and evolutionary physiologists will gather to present new research and discoveries in animal physiology at the American Physiological Society’s 2014 intersociety meeting “Comparative…
Depiction of a retrovirus integrating its DNA into the DNA of the host cell. Image from: http://bit.ly/1phzpbR
I read an interesting article in Scientific American that discussed the so-called Peto's Paradox. Dr. Richard Peto (University of Oxford) came up with the idea that if every cell has an equal probability of becoming cancerous, then larger animals would be predicted to develop cancer at higher rates than smaller animals. As it turns out, it is not that simple. All mammals exhibit similar cancer rates, with some exceptions. This is what came to be known as Peto's Paradox.
Some…
Image of eyeless Mexican tetra fish from www.seriouslyfish.com by H-J Chen.
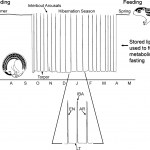
The metabolism of most animals follows a circadian rhythm that differs between the day and night. Mexican cavefish living in constant darkness, lost this circadian rhythm some time ago. In a newly published study in PLOS ONE, researchers compared the metabolic rate of both cave- and surface-dwelling Mexican tetra fish (Astyanax mexicanus). They hypothesized that since the fish living in each location naturally experience differences in food, predation as well as exposure to daily light fluctuations, they might also…
No joke. George (the goldfish) had developed a rather large tumor over the past year and the owners loved the fish so much, they spent $200 to have the life-threatening tumor surgically removed:
Conservationists are trying hard to save the Devils Hole pupfish (Cyprinodon diabolis) from extinction. With less than 100 animals remaining, a captive breeding program was started at the University of California, Berkeley.
As you can imagine from the image below, the geographic range of this fish is smaller than other wild vertebrates. They are only found in the limestone caverns of the geothermal Devils Hole pool in Death Valley, Nevada. The pool is 3m wide, 20m long, 426 feet deep, and a very warm 92-93 degrees Fahrenheit. It is thought to have formed more than 500,000 years ago…
Image of Bretagne from www.eonline.com
On this anniversary of 9/11 we remember not only the victims but also the heroes of that fateful day including countless first responders as well as their rescue animals that searched tirelessly for victims. The last known living rescue dog from 9/11 is Bretagne, a 15-year old golden retriever who returned to the memorial site with her handler Denise Corliss. She was only 2 years old at the time of the 9/11 attacks.
Visit NBCNews.com for breaking news, world news, and news about the economy
According to veterinarian Dr. Cindy Otto who took care of the…
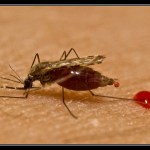
Image of mosquito from http://bloodinurineandpainofca.wordpress.com/
Until now I thought I had come up with enough reasons to dislike mosquitoes, those tiny little blood sucking vectors of disease. With reports of the debilitating mosquito-borne virus chikungunya in the Americas (Carribean), I was ecstatic hear that researchers are working hard to find ways to control mosquito populations. As mentioned in a previous blog, only the females bite to obtain nourishment for developing eggs. According to the study authors, the female mosquito can double her own body weight after just one meal,…
With the help of advice from a manicurist, Dr. Kate Mansfeld (University of Central Florida) has come up with a way to track hatchling sea turtles for the first time. After hatching, the turtles head straight for the ocean where they grow for about 10 years or so before returning to the same beach where they hatched. Until now, researchers have wondered how these juvenile turtles spent their time.
Source:
Scientific American
Researchers in Peru have discovered four new species of tiny so-called "glass frogs" (family: Centrolenidae).
Centrolene charapita: with the yellow splotches on its back, this species was aptly named after little yellow chili peppers. Their hindlegs also had fleshy little zigzag-like protuberances whose purpose is unknown.
Figure 4 from Twomey et al. Zootaxa, 2014.
Cochranella guayasamini: This species is mostly green with yellow encircling its eyes. Interestingly, the tadpoles begin as a reddish pink color. Since they live in streambeds that are low in oxygen, this coloration…
Image of seals from www.fanpop.com/clubs/the-animal-kingdom/images/14060694/title/seal-wall…
Paleogeneticist Dr. Johannes Krause (University of Tübingen, Germany) and colleagues were interested in the origin of tuberculosis (TB) in the Americas. Since strains of TB found in the Americas are related to strains found in Europe, prior theories held that Spaniards may have introduced it to the Americas while colonizing South America. The problem with those theories is that pre-Columbian skeletal remains showed signs of TB much earlier.
Dr. Krause was quoted in Scientific American, “…
Image of a naked mole rat from www.animals.sandiegozoo.org
The naked mole rat is the longest lived rodent species (>31 years). Unlike most mammals, they seem resistant to many age-associated ailments until much later in life, making them an exciting model of healthy aging. They are also resistant to the development of cancer as mentioned in this prior post.
According to the CDC, cardiovascular disease is currently the leading cause of death in the United States, claiming the lives of roughly 600,000 people annually (or 1 out of every 4 deaths). In a new study published in the American…
A new study from researchers at the University of Sydney shows that golden orb-weaving spiders (Nephila plumipes) that live in the city are larger and produce more offspring as compared to country living.
When they say the spiders are big, they mean really big. The females can reach up to 20-25mm (males are only ~5mm).
Image from Spiders of Australia http://ednieuw.home.xs4all.nl/australian/nephila/Nephila.html
The researchers speculate that the urban heat island effect, which is attributed to a lack vegetation and hard surfaces, may lead to the increased body size as invertebrates in…
Image of a green tree python from www.kids.britannica.com J.H. Pete Carmichael—The Image Bank/Getty Images
Dr. Greg Byrnes (Siena College, Loudonville, NY) and Dr. Bruce Jayne (University of Cincinnati, OH) discovered that snakes use more force than is necessary to support their weight when climbing. To climb, snakes rely on friction and repeatedly contract and extend their bodies, a process called concertina locomotion. To study the forces generated by snakes during this type of locomotion, the researchers constructed a vertical cylinder that was covered with textured tennis racket…
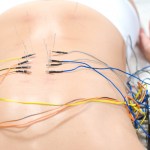
Image of electroacupuncture to the back from www.sandiegohealingarts.com
A new study published in AJP-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology suggests that electroacupuncture to the abdominal region may prevent increases in blood sugar concentrations after a meal by affecting insulin sensitivity and circulating free fatty acid concentrations. Granted this is not comparative physiology research, I find it interesting that electrical stimulation can have such a large impact on metabolism, in mice at least.
Drs. Nicola Abate and Jiande Chen, lead investigators…
Researchers at DARPA are using geckos to create biologically inspired methods of scaling vertical walls.
Check out this video demonstration of "Geckskin":