Life Science
While we are on the topic of cute animal stories, here is a family portrait with a newborn baby macaque at the Trentham Monkey Forest in Staffordshire, United Kingdom.
Check out the unique bond between this bear, lion and tiger (i.e. BLT) at Noah's Ark Animal Sanctuary in Locust Grove, Ga:
Visit NBCNews.com for breaking news, world news, and news about the economy
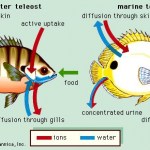
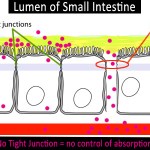
Freshwater fish are in a constant battle with their environment when it comes to maintaining their electrolyte balance as they are continuously losing ions to the surrounding water. Therefore, they have to actively absorb ions such as sodium, calcium and chloride from the water (see figure below). Prior research has shown that acidic environments cause adult and larva zebrafish to increase sodium uptake from their environment.
Depiction of water and salt homeostasis in freshwater and marine fish.
Researchers Kumai et al (University of Ottowa, Ontario, Canada) have provided evidence to…
Just in case you have not seen this viral YouTube video of the family cat saving a boy from a vicious dog attack, I have embedded it below. I think this kitty deserves a nice fresh fish for dinner...every day.
An article was posted today in NBCNews featuring the heroics of other house cats.
Here is one of my favorites:
Image of a clawless house cat named Jack that chased a bear up a tree. Image from NBC News: http://www.today.com/pets/good-kitty-these-6-hero-cats-saved-humans-the…
These brave felines must really believe they have 9 lives!!
You can check out the rest of these heroic…
I have heard of some animals using sugars as antifreeze (check out the prior blog on wood frogs that freeze and survive!), but never lipids.
Image from http://thebuggeek.com/tag/eurosta-solidaginis/
Researchers have discovered that larva of the Goldenrod gall fly (Eurosta solidaginis) shown above survive nearly freezing solid as well, which they hypothesize may be accomplished by accumulating acetylated triacylglycerol, or agTAGs, (i.e. a type of lipid) during winter. They found that the flies accumulate this lipid from September through March and studies of the agTAGs show that this…
Scientists in the jungles of southern India have discovered 14 new species of "dancing frogs" many of which are unfortunately already endangered. DNA analyses have shown that these new species are members of an ancient genus that has been around since the time of the dinosaurs, Micrixalus. There are now 24 known species of dancing frogs. Considering that males outnumber females 100 to 1, these acrobatics are important to attract mates. The tiny frogs are only about the size of a walnut.
Here is a neat video that I watched at the David Bruce Undergraduate Poster session at the Experimental Biology conference last week. It describes the amazing physiology of the avian lung and was created by an undergraduate student researcher, Peter Luu for the Physiology Video Contest sponsored by the American Physiological Society. This video won the Viewer's Choice Award:
To see more of the submitted videos, visit the American Physiological Society website.
Additional highlights from the Comparative Physiology posters presented at the 2014 Experimental Biology conference in San Diego, CA:
TA White, G Evans, GC Verzosa, T Pirtskhalava, T Tchkonia, JD Miller, JL Kirkland, and NK LeBrasseur. "Aging and cellular senescence and disease: The influence of diet and exercise"
Not surprisingly, mice consuming a fast food diet for 5 months gain weight, have impaired glucose tolerance, and blood pressure problems. If they are given a running wheel to use voluntarily, the effects on weight and cardiac function can be prevented. In addition, markers of…
Day 4 of the meeting turned out to be pretty exciting for a comparative physiologist as well.
The first session that I went to was called "RNASEQ approaches to understanding extreme physiological adaptations." Considering the Comparative and Evolutionary Physiology section business and dinner meeting was the night before, I was impressed at my ability to make it to an 8:00am session the following morning.
The first seminar from Dr. Brooke C Harrison (Univ. Colorado, Boulder) was on "Extreme cardiac growth and metabolism in the Burmese python after feeding." He spoke about how the cells…
Day 3 of the Experimental Biology meeting was arguably one of the most exciting for comparative physiology. Here are the highlights from Monday:
Morning Seminars:
Birgitte McDonald from Aarhus University, Denmark presented, "Deep-diving sea lions exhibit extreme bradycardia in long-duration dives." Birgitte and Dr. Paul Ponganis measured the heart rate of California sea lions (Z. californianus) using digital electrocardiogram loggers and found that the heart rate was reduced (bradycardia) during dives along with reduced blood flow to the lungs and periphery. This helps preserve the oxygen…
Check out the world's fastest animal (relative to its size):
This research was featured at this year's Experimental Biology conference!
Another exciting day at the Experimental Biology meeting for physiologists! Although I am a bit nervous about the session on the negative effects of sleep deprivation, "Sleepless in San Diego: Is Sleep Deprivation the New Silent Killer?" Hmmm, maybe I should have gone to bed a bit earlier last night...
Dr. Karen Matthews (Univ of Pittsburgh) has studied the effects of sleep deprivation in teens from low-income families found that less than 6 hours of sleep per night can negatively impact mood, academic achievement and health.
Another talk that I found interesting was on how sleep deprivation…
The meeting is off to a good start.
I attended a session sponsored by the American Physiological Society on Animal Models of hypertension caused by the nervous system, or neurogenic hypertension. While their definition of comparative really only meant rats, dogs and humans, I found it very interesting nonetheless. The speaker, Dr. Olson from the University of Minnesota, explained the pros and cons of trying to develop devices to treat neurogenic hypertension using different animal models. The reason why rodents are not good models is because they are too small to develop devices for in…
I am very excited about the Experimental Biology conference that starts this weekend. I have my bags packed, my poster printed and I am heading to the airport to catch my plane. I can't wait to learn about all of the exciting physiology (especially comparative physiology) research. I will be sure to keep you up-to-date as well!
Image from: bluecrossanimalhospital.ca
The FDA has issued a warning that Easter lilies are toxic to cats. According to veterinarian Dr. Melanie McLean at the US Food and Drug Administration ingestion of even a small portion of the leaves, pollen or flowers of the plant are very poisonous to cats. Initial complications include vomiting but then may lead to kidney failure and death if not treated. If you think your cat may have ingested a lily, then seek immediate medical attention for your pet.
Tiger, Asiatic, Day and Japanese Show lilies are also highly toxic to cats.
Dog owners take…
Sounds kind of like an oxymoron doesn't it? Who knew sponges could be carnivorous? Scientists have described four new species of carnivorous sponges in a newly published article in Zootaxa. Check out this video from the lead author of the study, Lonny Lundsten who is a Senior Research Technician at the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute:
Lundsten L, Reiswig HM, Austin WC. Four new species of Cladorhizidae (Porifera, Demospongiae, Poecilosclerida) from the Northeast Pacific. Zootaxa. 3786 (2): 101–123, 2014.
I am very excited about the upcoming Experimental Biology conference that starts next weekend. I just looked through the Spring newsletter for the Comparative and Evolutionary Physiology section of the American Physiological Society. Check out the exciting programming in comparative physiology at this year's conference:
Monday, April 28
10:30 AM – 12:30 PM
Featured Topic: Abstract-Driven Trainee Session
3:15 PM – 5:15 PM
Featured Topic: Comparative Physiology of Aging and Senescence
Tuesday, April 29
8:00 AM – 10:00 AM
CEPS Symposium: RNAseq Approaches to…
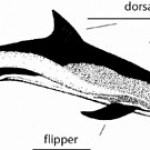
Gray's paradox was originated by the zoologist James Gray in 1936 (J. Exp. Biol. 13: 192–199, 1936). The paradox questioned how a dolphin is able to swim fast (~10.1 meters per second according to his calculations) with what he saw as a limited ability to generate that much power. Therefore, he concluded that dolphins must have some mechanism or adaptation to reduce drag (Davidson College).
More recently, Dr. Frank Fish (West Chester University, Pennsylvania) was quoted in The Scientist saying, “To resolve the paradox was to assume that flow over the dolphin’s body is laminar,…
An river otter was captured on camera taking on an juvenile alligator...and winning. The battle took place at the Lake Woodruff National Wildlife Refuge in Florida in 2011. More images can be seen on their Facebook page where the images were recently posted, impressive! According to National Geographic, the normal diet of a river otter consists of birds, small rodents, frogs, turtles, crabs, and fish. Let's just add juvenile alligators to the list now.
Photo from U.S. FISH AND WILDLIFE SERVICE/FACEBOOK
Perhaps equally impressive is this olive python that was seen…
Image from LiveScience. Credit: Richard Borowsky
Heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) helps keep proteins in the body folded properly and is thought to compensate for variations that occur in proteins over time. In a study published in Science magazine, Dr. Nicolas Rohner and colleagues showed that stress can affect the ability for HSP90 to do its job thereby unmasking these alternative versions of proteins which may lead to adaptation in some cases.
The theory was tested in fish called Mexican tetra (above), some of which adapted to life in caves leading to eventual loss of, or diminished,…