drought
Over the past three years (and indeed, for 10 of the past 14 years) California has experienced a particularly deep drought. How bad is the drought? Is it the worst in the instrumental record? The worst in over a century? The worst in 1200 years? The worst “ever”? And why has it been so bad?
There is no single definition of “drought.” Drought, most simply defined, is the mismatch between (1) the amounts of water nature provides and (2) the amounts of water that humans and the environment demand. As the National Drought Mitigation Center puts it:
“In the most general sense, drought originates…
Guest Post: Matthew Heberger Pacific Institute, Oakland, California
New monthly water use data for California water utilities shows that residential water use varies widely around the state, and that the response to the drought has been uneven. Moreover, in some areas, residential use averages more than 500 gallons per person per day, indicating that we could be doing much more to save water.
In July, the State Water Resources Control Board, or the Water Board, issued an emergency regulation to increase water conservation in urban areas. The new regulations prohibit certain water uses, like…
In a new study just published by the journal Sustainability Science (Springer), analysis from the Pacific Institute (with lead author Dr. Juliet Christian-Smith, now at the Union of Concerned Scientists) shows that many of the fundamental responses of California water users to severe drought actually make the state’s overall water conditions worse – that in the end, many of these actions are “maladaptations.”
Water is a complex resource; and water problems are an equally complex mix of natural resource, technology, social, economic, and political conditions. When water is limited,…
On Significant Figures, Peter Gleick examines the rather relaxed attitudes of some Californians to an extreme drought fostered by three years of dry weather. Gleick writes “reservoirs are at record low levels. Deliveries of surface water to some farmers are lower than at any time in recent history. Streams are drying up and fisheries are being devastated.” Yet he and millions of other residents have been able to run water from their taps freely. Agriculture might only suffer losses of 4% (about .0008% of the state’s total economy). And an expectation of El Niño rains obscures the…
In the past few weeks, I have had been asked the same question by reporters, friends, strangers, and even a colleague who posts regularly on this very ScienceBlogs site (the prolific and thoughtful Greg Laden): why, if the California drought is so bad, has the response been so tepid?
There is no single answer to this question (and of course, it presumes (1) that the drought is bad; and (2) the response has been tepid). In many ways, the response is as complicated as California’s water system itself, with widely and wildly diverse sources of water, uses of water, prices and water rights,…
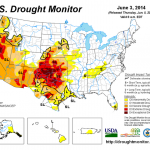
I made a movie you might enjoy. There may be something else out there like this, probably better than this one, but it is still cool. I downloaded all the PDF files from the US Drought Monitor archives, using the version of the connected US that has only the year, month, and day on the graphic. Then I slapped them in iMovie and sped the animation up by 800% over the default 1 sec. per pic. I do not have today's rather horrifying image on it, which I've placed above.
Here's the movie:
Snapshots from the New National Climate Assessment
After three years of intensive effort, research, writing, and review by hundreds of climate scientists, the latest update of the U.S. National Climate Assessment was released today. It includes many long, carefully prepared sectoral and regional studies, and covers the massive range of effects of climate change on the nation, including both changes already observed and expected in the future.
There are hundreds of pages of information, observations, projections, and conclusions to absorb – almost all of it bad news. Here, in short form and in…
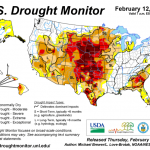
The end of the rainy season in California is arriving in a few weeks, and the April 1st snowpack measurement, which is a key indicator of water conditions, is tomorrow. As we approach the dry spring and summer months, the scope and severity of California’s drought will become more apparent, but it is already clear that California is faced with extraordinarily dry conditions, with impacts to all sectors and every corner of the state.
As part of the Pacific Institute’s Drought Response efforts, here is the March 31st update of the key information and graphics that characterize the current…
In the last few months, as the severe California drought has garnered attention among scientists, policymakers, and media, there has been a growing debate about the links between the drought and climate change. The debate has been marked by considerable controversy, confusion, and opaqueness.
The confusion stems from the failure of some scientists, bloggers, reporters, and others to distinguish among three separate questions. All three questions are scientifically interesting. But the three are different in their nuance, their importance to policy, and their interest to politicians and water…
We’ve entered a new era: politicians can now talk loud and clear about the reality of human-induced climate change and the growing threats to humanity. With strong, unambiguous statements by President Barack Obama, Secretary of State John Kerry, Senator Sheldon Whitehouse, and a growing chorus of other top-level voices, the wholesale denial of climate science is increasingly relegated to a tiny group of industry-funded voices and their followers (directly mirroring the tobacco story decades ago); confused or ignorant politicians; and those who hope to avoid the difficult policy discussions by…
Droughts – especially severe droughts – are terribly damaging events. The human and ecosystem costs can be enormous, as we may relearn during the current California drought.
But they are also opportunities – a chance to put in place new, innovative water policies that are not discussed or implemented during wet or normal years.
In the hopes that California’s warring water warriors open their minds to policy reform, here are some of the issues that should be on the table now, in what could be the worst drought in California’s modern history. But here is what I fear, said best by John Steinbeck…
It is time to recognize the serious California drought for what it is: a bellwether of things to come; a harbinger of even more serious challenges to California water resources allocation, management, and use.
The drought could end next month. It could go on for more years. But it will not be the last drought and it is vital that we take the opportunity -- amidst the serious problems farmers, cities, and the environment all face -- to rethink those aspects of California water policy created in the 1900s and 2000s that no longer make sense in the 21st century.
We must also consider this…
Figure 1: Monthly average precipitation showing the seasonality of precipitation in different parts of California, from the iconic California Water Atlas.
California has a “Mediterranean” climate, which means that each year it has a concentrated rainy season, followed by a long temperate and dry period. California’s rainy season typically runs from early October to late March, with very little precipitation outside of these months. (Figure 1 shows the average monthly rainfall for California.) It is now early 2014 and the rains have not come, for the third year in a row. While the …
Dropping water levels in Lake Mead, behind Hoover Dam. (Source: Peter Gleick 2013)
It is no surprise, of course, that the western United States is dry. The entire history of the West can be told (and has been, in great books like Cadillac Desert [Reisner] and Rivers of Empire [Worster] and The Great Thirst [Hundley]) in large part through the story of the hydrology of the West, the role of the federal and state governments in developing water infrastructure, the evidence of droughts and floods on the land, and the politics of water allocations and use.
But the story of water in the…
(the featured image above is of the once aptly named Rio Grande, now referred to by locals as the "Rio Sand")
The LA Times has a very chilling piece on New Mexico's not so chilling climate change. Here are a few quotes to pique your interest:
"All of New Mexico is officially in a drought, and three-quarters of it is categorized as severe or exceptional."
"The last three years have been the driest and warmest since record-keeping began here in 1895."
"With water supplies at the breaking point and no relief in sight, a domino-effect water war has broken out, which might be a harbinger of…
Here we have a nice new infographic for you to gaze at, share around on your facebook accounts, and so on. (It is below.) Here in Minnesota, we've got a problem getting that last one million acres of corn planted (about 1/8th of the normal amount), not because of drought, but because of excessive rain. However, all that extra rain is not expected to alleviate the effects of our drought long term, so we get to have both. If the price or availability of major food types ("commodities") goes south (up and down, respectively) here and there, adjustments can be made. But if climate change…
There is a long history of conflicts over water – the Pacific Institute maintains an online, searchable chronology of such conflicts going back 5,000 years. There were dozens of new examples in 2012, in countries from Latin America to Africa to Asia. (A full update for 2012 has been posted.) Access to water and the control of water systems have been causes of conflict, weapons have been used during conflicts, and water systems have been the targets of conflict.
One especially disturbing example of a major conflict, with complicated but direct connections to water, has developed over the…
With Masters, Mann, Hayhoe and Douglass. From Climate Denial Crock of the Week.
Although the science is getting cold, the conversation about climate change was warmed over by President Obama on Thursday. On Thoughts from Kansas, Josh Rosenau says “This is a welcome change from the complete silence of the last few years, but falls well short of what the American people and the world deserve.” Rosenau argues that with scientific consensus long established, an attempt at policy is overdue. California, the economic canary in a coal mine, just enacted a cap-and-trade system designed to curb carbon emissions. Meanwhile, climate change denialists strive to maintain a false…