evolution
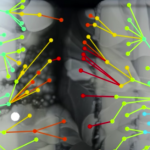
The oldest evidence for microbial life has been found in Greenland, with fossilized 3.7 billion year old stromatolites (layered bacterial colonies) found in the rocks. Here's what they look like:
And here's the abstract of the paper:
Biological activity is a major factor in Earth’s chemical cycles, including facilitating CO2 sequestration and providing climate feedbacks. Thus a key question in Earth’s evolution is when did life arise and impact hydrosphere–atmosphere–lithosphere chemical cycles? Until now, evidence for the oldest life on Earth focused on debated stable isotopic signatures of…
Ever year about 23,000 people die of infections from antibiotic resistant bacterial.
Here is a film of bacteria evolving from regular old bacteria into killer superbugs. On a coffee table size Petri dish.
You can get the story at NPR, where you will learn that
"Getting more people to understand how quickly bacteria evolve antibiotic resistance might help people understand why they shouldn't be prescribed antibiotics. The drug resistance is not some abstract threat. It's real."
It's a standing joke that creationists demand a complete time-lapse recording of evolution before they're going to believe it. Joke no more: we've got one. It's a movie of bacteria evolving antibiotic resistance. I don't even need to explain it, because the video explains everything that's going on.
Different old joke now: But they're still just bacteria.
Also, you should be horrified by the power of evolution. It took 11 days for the bacterial population to evolve resistance to a lethal, thousand-fold increase in antibiotic concentration.
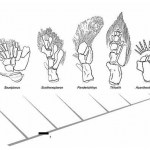
In response to Neil Shubin's recent paper on the subject, and Carl Zimmer's summary, the creationist Michael Denton criticizes evolutionary explanations for the vertebrate limb. It's a bizarre argument.
First, here's the even shorter summary of the Shubin work. Ray-finned fish have, obviously enough, rays in their fins -- rigid bony struts that provide structure. These rays are formed dermally. That is, osteoblasts deposit bone on the surface of a connective tissue matrix to build the rods of bone that prop up the fin. It's called dermal bone because the classic example is the assembly of…
Believe it or not (and you probably won’t believe it), but I never intended to post today, as it’s a holiday, and I had to write my usual level post for my not-so-super-secret other blog. But then one of you had to send me this:
I couldn’t resist at least a quick comment on this.
That’s right. Kent Hovind, one of the world’s most famous young earth creationists and frauds (given that he went to jail for tax evasion) is marrying Marry Tocco, Michigan’s own most annoying antivaccinationist and someone about whom I’ve written several times, most recently in 2014. In the video, he goes on about…
Perhaps we need to think more about human psychology. There's an interesting phenomenon that goes on all the time when people read about evolution: they shoehorn the observations into some functional purpose. There's just something so satisfying to our minds to be able to say "that thing exists for this particular reason", and we find it frustrating to say, "there is no reason for it, it's just chance and circumstance". It shouldn't be so, but our minds just try to fit everything into that particular mold.
Now watch: some people -- maybe even you -- are going to now try and develop an…
You can read this book review, or you can just go HERE and listen to our interview with author Christie Wilcox. I promise you in advance that you will want to read her book!
But, if you want to read the book review, here it is...
Did you ever do anything that hurt, then you had to do it again and you knew it would still hurt, and you didn't like that? Like getting your teeth cleaned, or licking a nine volt battery. OK, maybe you didn't have to lick the nine volt battery, but you get my point.
When I was working in the Ituri Forest, in the Congo, taking a walk in the forest was one of…
Ikonokast interviews Don Prothero.
Don Prothero is the author of just over 30 books and a gazillion scientific papers covering a wide range of topics in paleontology and skepticism. Mike Haubrich and I spoke with Don about most of these topics, including the recent history of the skeptics movement, the conflict and potentials between DNA and fossil research, extinctions and impacts, evolution in general, and the interesting projects Don is working on now.
The interview is here. Please click through and give this fascinating conversation a listen!
The trick to understanding evolution is less about finding good answer to questions, but rather, finding good questions to answer.
Read that sentence twice, because it is very important.
Years ago, Niko Tinbergen developed a method of formulating questions about biology. I'm pretty sure the Tinbergenian method has not been integrated into most science standards and teaching curriculum. It should be.
There are four types of questions one could formulate about a biological system, trait, or observation.
1) Mechanistic. How does this thing work? What cellular processes are involved in a…
Stephen Hsu thinks super intelligent humans are coming. He thinks this because he's very impressed with genetic engineering (he's a physicist), and believes that the way to make people more intelligent is to adjust their genes, and therefore, more gene tweaking will lead to more intelligent people, inevitably. And not just intelligent, but super-intelligent, with IQs about 1000, even though he has no idea what that means, or for that matter, even though no one really knows what an IQ of 100 means. We're going to figure out all the genes that are involved in intelligence, and then we'll just…
The Smithsonian is sponsoring a traveling exhibit called Exploring Human Origins: What Does It Mean To Be Human?, which is going around the country to various libraries. By all accounts, it's an excellent exhibit, and they also promote good education: they offer workshops on human evolution to local teachers (they also offer tours to local clergy -- they're additionally sponsored by the Templeton Foundation).
The exhibit is in Cottage Grove, Oregon right now. You've all seen Cottage Grove -- the big parade scene in Animal House was filmed there. But it's also a nice little town south of…
I have often made the argument that religiosity, a personal belief in god, spirits, the supernatural, etc., would emerge in human societies on its own if it wasn't there already.
Imagine taking an entire generation of people in a geographically isolated region, and wiping out their memory of religion, and also, removing all references to religion that they might ever encounter. They would be religion free for a while, maybe even for a number of generations, but eventually, they would reinvent it.
Everybody has a theory of why religion exists, what purposes it serves, etc. etc. Until proven…
Larry Moran has heard the words of Michael Denton, and has come away with a creationist interpretation of structuralism. I have to explain to Larry that Denton, as you might expect of a creationist, is distorting the whole idea. Here's the Denton/Intelligent Design creationism version of structuralist theory.
As Denton says, the basic idea is that the form (structure) of modern organisms is a property of the laws of physics and chemistry and not something that evolution discovered. He would argue that if you replay the tape of life you will always get species that look pretty much like the…
We've got an interesting seminar coming to Morris next Thursday.
Thursday, February 18, 2016, 5 p.m.
Location: Imholte Hall 109
The origination of novel structures has long been an intriguing topic for biologists. Over the past few decades it has served as a central theme in evolutionary developmental biology, in part to highlight explanatory gaps in the population genetic framework of standard evolutionary theory. Yet, definitions of evolutionary innovation and novelty are frequently debated and there remains disagreement about what kinds of causal factors best explain the origin of…
Sean B. Carroll is coming out with a new book called The Serengeti Rules: The Quest to Discover How Life Works and Why It Matters.
This is the molecular biologist Sean Carroll, as distinct from the physicist (who wrote this).
Homeostasis is one of the basic principles of biology. The term can be applied broadly to mean that certain numbers are maintained within a certain range. This could refer to energy flowing through a system, numbers of specific cellular products like enzymes, numbers of individual organisms in an ecological system, etc. It is not so much that numbers don't change.…
There will be an interesting meeting in London next fall, New trends in evolutionary biology: biological, philosophical and social science perspectives. The description:
Developments in evolutionary biology and adjacent fields have produced calls for revision of the standard theory of evolution, although the issues involved remain hotly contested. This meeting will present these developments and arguments in a form that will encourage cross-disciplinary discussion and, in particular, involve the humanities and social sciences in order to provide further analytical perspectives and explore the…
Why does infection with bacteria or viruses make you feel sick? Prof. Guy Shakhar and Dr. Keren Shakhar have proposed that your symptoms are not just a byproduct of your body’s attempt to get rid of the infection. It is your genes’ way of ensuring they are passed down. The long and short of their argument is that the malaise, loss of appetite and lethargy are all ways of isolating you from your social group – so that your kin, who carry many of your genes, are not infected as well.
That means we share an evolutionary adaptation with such organisms as bees that go off to die far from the hive…
Once upon a time, deep in the Precambrian, this was the planet of worms. Well, actually, this was, is, and always will be the planet of bacteria, but if you filter your perspective to just organisms above a particular size, and if you're an animal writing about it in the modern day with a chauvinistic attitude that allows you to ignore that it was also a planet of algae, that would become a planet of plants, on a world that also is built of soil formed by lichens and saturated with fungus…if you ignore all that, OK, it was a planet of worms.
Late in the Precambrian, the oceans were full of…
I disagree with Razib Khan on a lot of things, but he's exactly right on recent fads in biology.
Periodically I get frankly stupid comments that seem to imply that the incredible swell of results coming out of molecuar genetics and genomics are revolutionizing our understanding of evolutionary and population genetics. Over the past generation it’s been alternative splicing, then gene regulation and evo-devo, and now epigenetics is all the rage. The results are interesting, fascinating, and warrant deeper inquiry (I happen to see graduate school admission applications for genetics, and I can…
In a review of a new book edited by Alan Love, The evolution of “evo-devo”, Adam Wilkins makes a few telling criticisms of the sub-field I enjoy.
Evo-devo has come a long way since 1981 though the Dahlem Conference laid some of the important groundwork for what followed and was, indeed, widely appreciated as having done so. Yet, troublingly, the field remains, for many evolutionary biologists, something of a side-show, a “boutique” subject within evolutionary biology as a whole. Several of us, in the 1990s, warned that this might happen. This is in contrast to some of the early expectations,…