synthetic biology
Unlike many of my colleagues, I'm not really interested in the whole "science vs. religion" thing, but I do want to point out the very thoughtful analysis of genetic engineering and synthetic biology by the Church of Scotland's Society, Religion, and Technology Project. On GM food, they write:
The official scientific and economic reports support the view of the 1999 Assembly, that GM is not a simple 'yes or no' issue and must be taken case-by-case, weighing up many different factors. Theologically, SRT has found no convincing reason to say it is a wrong act to transfer genes into a crop from…
I'm a little late in posting about the recent work of Tuur Van Balen, a Belgian designer who uses art and design to explore the boundaries between people and technology. His work has explored synthetic biology and biotechnology for years, and I first was introduced to his work through news of his Urban Biogeography project. A recent focus in synthetic biology has been the design of simple biosensors, strains of bacteria or yeast that can sense an environmental pollutant and produce a measurable output such as color change. Thanks to the work of several very creative iGEM teams, the Registry…
My semester in MIT's course on Documenting Science Through Video and New Media has drawn to a close. I've had a wonderful time and learned a lot about how films and science are constructed by different people in different times for different reasons. Most of all I've learned about how challenging it can be to put together an interesting narrative and present a point of view while at the same time ensuring that the science being explained is honest and clear to everyone. I've recently gotten the chance to watch two great recent science documentaries outside of class, Naturally Obsessed and…
Silks are incredible protein fibers produced by many different species of insects. Besides their use in making versatile textiles, silks are currently used in many different medical and engineering applications, from sutures to tissue engineering scaffolds to flexible electrode brain implants. Since I love fabrics and I'm interested in what biological engineers can do with biomaterials, I recently started working on a fun side project to raise and engineer silkworms, the animals used in industrial silk production around the world. We're having a lot of fun learning about silk and how to raise…
Many people in synthetic biology, including myself and much of my lab, are working on using biology to make things more efficiently, renewably, and sustainably. Being able to make plastic replacing biomaterials, chemicals, medicines, and fuels in living cells from renewable resources (especially in photosynthetic organisms that need only sunlight and water) will undoubtedly decrease our dependence on fossil fuels and with a lot of work in policy and process and infrastructure engineering may one day become truly sustainable. It's difficult to not notice, however, how unsustainable most…
Light interacts with and controls biological systems in diverse and fascinating ways. Our eyes are made up of thousands of cells that respond to light, sending signals to our brain as light in different colors and shapes moves across them. Photosynthetic cells are full of receptors that can sense and respond to many wavelengths of light, allowing cells to absorb light for photosynthesis, but also to move towards areas of more sunlight and know when the seasons are changing. Synthetic biology takes these light-responsive systems as parts that can be recombined, shuffled and integrated into…
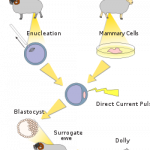
New in vitro fertilization technology is making it possible for someone to have two moms--one that provides the genome in the nucleus of the cell, and one that provides the rest of the egg cell, including the mitochondria. Since all mitochondria are passed down from the mother in the egg (sperm are just too small to provide anything but the father's genetic material to the fertilized embryo), transplanting the nucleus from a fertilized embryo to an egg from a different woman can bypass the transmission of any mitochondrial diseases that the mother carries. Because mitochondria have their own…
As you can probably imagine, there are a lot of very interesting things that pop up when you have a google alert for "synthetic biology." Here is today's special find: a short dubstep song about synthetic biology by Dysoniq, featuring a voice talking about computer chips for your brain from this video, an interesting hour-long BBC presentation about intelligent robots (thanks again, Google!).
Synthetic BiologybyDysoniq
I got a lot of interesting responses to my post about DIYbio and how modeling innovation in biotech on computer hacker culture may lead to a science that is less "democratized" than what is being proposed. My friend Adam pointed me to Jaron Lanier's work criticizing the "open" and "free" culture movements online as both unfair and leading to cultural stagnation. While I don't agree with all of Lanier's arguments about the prospects of an open digital culture, he makes a lot of really important points that resonate with my feelings about the future of science based on the open online model, in…
An interesting paper in BioEssays last month looks at the potential future of xenobiology, totally orthologous biological systems made out of synthetic nucleotide and amino acid bases, new cells that use XNA instead of DNA. The author, Markus Schmidt, argues that while the design of such systems current poses a difficult technological challenge to researchers in synthetic biology, that xenobiological systems will enable a "genetic firewall" between natural and designed organisms, creating a built-in measure of biosafety.
This is something I've argued for before, in reference to creating new…
Last week's issue of Nature focused on the progress (or lack thereof) in genomics and related fields since the Human Genome Project (HGP) was completed ten years ago. In many ways, the era of genomics has yet to fulfill many of the promises made twenty years ago, but the investment in science and technology has at the same time made a valuable impact on many fields in basic science. Understanding this recent history of the genomics bubble is crucial to how we approach current science and technology investments in areas such as personal genomics and importantly, synthetic biology.
In a…
Cellularity is a new project by James King, a speculative designer working on biotechnology and interaction design. The project focuses on the potential future of smart pharmaceuticals, drug molecules surrounded by membranes that over time as technology advances may come to more and more closely resemble actually living things. He proposes a cellularity scale from totally non-living to really alive artificial cells. This quantification of "aliveness" in a way is something that may need to be done if some of the proposals of synthetic biology come to fruition. When does a membrane surrounding…
Synthetic biology deliberately equates genetic networks to electronic circuits, cells to machines, organisms to factories. In synthetic biology, every living can be thought of as a cyborg, a living machine that can be manipulated, changed to meet our needs, parts swapped in and out like a computer. Some projects in synthetic biology and biologically inspired engineering hope to bring the analogy a step further, combining biological and actual electronic and mechanical components into a single engineered unit, with the goal of essentially making tiny autonomous cyborgs.
There are a lot of…
My paper, "Insulation of a synthetic hydrogen metabolism circuit in bacteria" just came out in the Journal of Biological Engineering! And it's open access!
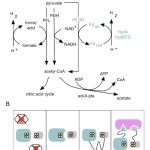
We designed a metabolic circuit in bacteria that produces hydrogen (a potentially useful fuel) from natural precursors in the cell. The proteins in our synthetic pathway work to make hydrogen by transferring high-energy electrons from pyruvate, a common metabolite, to protons that are freely floating in the watery cytoplasm. The electrons transfer between the proteins through quantum-mechanical tunneling, which makes hydrogenases and…
My labmates and I love Lady Gaga. Like, love love love. Enough to make a parody fan video of Bad Romance. It is my pleasure to present to you "Lab Romance", a production of Hydrocalypse Industries. Enjoy!
Lyrics after the jump!
ø⸨°º¤ø⸸âø¤º°¨¸âø¤º°¨ ¨°º¤øâ¸LADYâø¤º°¨ âø¤º°¨ GAGA `°º¤ø¨°º¤ø⸸âø¤º°¨¸âø¤º°¨ ¨°º¤ø
Music by Lady Gaga, lyrics by Tami Lieberman and Jake Wintermute, performed by Jake Wintermute, editing by me and Patrick Boyle, dancing by the Silver Lab.
Oh-oh-oh-oh-oooh!
Oh-oh-oooh-oh-oh!
Caught in a lab romance…
Some of the responses to my post about synthetically expanding the genetic code have highlighted some of the weaknesses in my argument about the safety of using a different genetic code. Namely, that "life finds a way", that we can't really ever know for sure what will happen when we release a synthetic organism in the wild, or how natural selection will act on them. The science fiction scenarios where engineered organisms escape, break out of the designed restrictions on their growth and take over in new and terrifying ways are compelling, frightening, and instructive for thinking about…
Almost every living thing shares an identical genetic code, with three nucleic acids in an RNA sequence coding for a single amino acid in the translated protein sequence. While there are 64 three-letter RNA sequences, there are only 20 amino acids and degeneracy in the code allows some amino acids to be coded by multiple codons. Chemists and synthetic biologists in the past few years have been working to expand this genetic code, with unnatural nucleotides that can be incorporated into DNA and RNA sequences and unnatural amino acids that can expand the chemical functionality of proteins.…
The future potential of synthetic biology is usually discussed in terms of applications in fields like medicine, food science, and the environment. Genetically engineered life forms are being designed to make medicines cheaply, to target tumor cells, to make more nutritious food, or to make agricultural plants that are easier to grow with less of an environmental impact, to clean up pollution or produce sustainable biofuels. What if synthetic biology systems were instead designed for use in culture or entertainment?
David Benqué, a student in the Design Interactions program at the Royal…
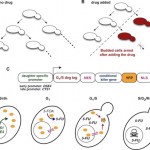
My labmate Bruno's newest paper, "A synthetic circuit for selectively arresting daughter cells to create aging populations" came out today in the journal Nucleic Acids Research (and it's open access!). Using a cleverly designed genetic circuit that activates cell growth arrest in newly divided cells only in the presence of a drug, Bruno was able to create a population of yeast made up of only old cells, called the "daughter arrester."
You would think that yeast, being so single celled and bread-y, wouldn't be able to tell us much about human biology or anything as complex as aging, but many…