Today’s new articles involve flow: the flow of positrons through the Universe and the flow of particles around the tiny cilia of corals. They involve beauty and mystery, as well. The particle flow, imaged in brilliant colors, won first place in the photography category of the 2013 Science/National Science Foundation International Science & Engineering Visualization Challenge.
And positrons – the anti-matter opposites of electrons – have been found in large numbers flowing in near-Earth space. Weizmann Institute research points to an answer to one riddle: Why did a satellite…
Perovskite (say it: pə-ˈräv-ˌskīt, -ˈräf-). It may never become a household word, and the chemical formulas (eg., CH3NH3PbI3−xClx ) are as long as the name. But if you find yourself, in the not-so-distant future, adding new-and-improved solar panels to your roof, they may well contain a perovskite layer. If they do, it will be these “wonder materials” that will make your panels cheap enough to make your investment worthwhile and efficient enough to make you feel smug when you get your electricity bill.
You may ask: Aren’t solar panels dropping in price all the time? What is special…
The next time you reach into the fridge for a midnight snack – take heed: New research by Weizmann Institute scientists has shown that the time at which you eat your meals might have a profound effect on your liver triglyceride levels. Their research was conducted on mice, but if found to be true for humans as well, it may have clinical implications in the way patients could be treated for fatty liver and other metabolic diseases, which are characterized by abnormally elevated levels of lipids in blood and liver cells.
Our bodies are naturally cued to carry out various biological…
“Billions of dollars are being spent on weapons of mass destruction. A small fraction of that could go so far to engage more Israeli and Arab scientists in collaborative projects in order to create a critical mass that will bring about peace.” The speaker is Dr. Zafra Lerman, President of the Malta Conferences Foundation, which organizes conferences in nonaligned Malta for Israeli, Palestinian and Middle Eastern scientists. These bi-annual conferences, attended by researchers from Egypt to Saudi Arabia, focus such neutral topics as materials science, as well as common interests like water and…
Today's guest post is by Weizmann Institute physicist, Prof. Micha Berkooz. Berkooz, a string theorist, recently organized a conference at the Institute on "Black Holes and Quantum Information Theory." We asked him about Hawking's recent proposal, reported in Nature under the headline:"There are no black holes."
Celebrated theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking has opened a can of worms in his 1976 paper on black holes. In a recent article, he is trying to put the worms back into the can. It may prove a little trickier than expected.
Black holes are solutions of Einstein's equations of…
A recent paper by Weizmann Institute scientists suggests that we might be able to break the third law of thermodynamics. This is how that law was originally formulated in 1908 by Walther Nernst: “It is impossible for any procedure to lead to the isotherm T = 0 in a finite number of steps,” (source: Wikipedia). To elaborate, the entropy of a system approaches nil as the temperature closes in on absolute zero, so that extracting further energy becomes increasingly difficult. According to the third law, you can get very close – temperatures of less than a billionth of a degree have already been…
Prof. Mario Livio takes the long view on science. In his newest book, Brilliant Blunders, he points out some of the mistakes made by some icons of science -- Einstein and Pauling among them. More importantly, he insists that researchers must be free to make mistakes.
Livio recently gave us a taste of his subject matter in a talk at the Weizmann Institute (in English):
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sYaMlTn275A
More science-themed haikus. I seem to keep writing them because we tend to put out three “mini press releases” at a time (a relic of the days when they were printed on two sides of a fold-up page and mailed). So I could pick just one to blog about, or I could try to fit all three into one post (which tends to get muddled when it is on subjects as varied as physics, neurobiology and genetics). Or else I can leave these little breadcrumbs inviting you to follow them back to our website, where the fuller explanation awaits (or, from there, you can follow the links in the releases to get to the…
In the future, stem cells created from our own skin cells will be used to renew damaged organs or grow new ones. We know this promise has often been made before, but the latest research in the lab of Dr. Jacob (Yaqub) Hanna is producing some solid findings that may make you believe in the possibility.
Just a little over a month ago, we reported that Hanna and his group had discovered a “brake” that keeps our cells from easily reverting to an embryonic-stem-cell-like state (induced pluripotent stem cells, or iPS cells). Removing that brake enabled them to ramp up the conversion process – in…
Of the four new articles online on our website, three happen, purely by accident, to be on physics research. The three are very different, and yet each is an illustration of the ways that basic physics research changes our world – in small and large, practical and enlightening ways. And each is situated at a different intersection between the technological and the theoretical – a technological breakthrough that resulted from a successful attempt to provide proof for a theoretical construct, new inventions based on elementary physical principles of light, and a theory substantiated through a…
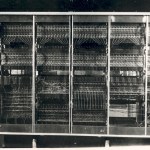
Here is a photo of one of the Golem computers on which Arieh Warshel and Michael Levitt -- this year's Nobel Prize in Chemistry winners, along with Martin Karplus -- did much of their original work.
Golem computer
My dad was a computer programmer at that time, so I have some idea of what their work must have entailed. To this science writer, that makes their feat nothing short of amazing.
The Golem, by the way, which is preserved in the basement of the Weizmann Institute's mathematics building, was not the first computer at the Institute. The WEIZAC (below) was built at the…
Cancer, we are told, is a disease of the genes. It originates in mutations in the DNA. But a paper published by a Weizmann Institute group in Cell Reports flips that idea sideways by about 90 degrees: For at least some types of the disease, the healthy, non-mutated version of a gene is no less of a driving force behind the development of cancer than its mutated form.
Prof. Yoram Groner, who led the research, describes the situation as a “balance of terror.” Until now, researchers have assumed that, when a mutation causes cancer it becomes dominant in the cell, overriding the second copy of…
First, there was the great hope of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), and then there was the inevitable letdown. When the announcement came, in 2006, that simple adult skin cells could be reprogrammed – reverted back to an embryonic stem cell state by the addition of just four genes – it seemed like an almost magical solution to the problems of using stem cells from embryos. But then some studies started to find that the reprogramming process was not perfect – iPSCs were similar, but not identical, to the cells from early embryos. More critically, only about 1% of the cells treated with…
What effect does a constant stream of engaging stimuli have on our relationships? On our social structure as a whole? What percentage of our actions is influenced by others, and how does this translate, at some point, into group behavior?
Neurobiologists Prof. Alon Chen and Dr. Elad Schneidman of the Weizmann Institute and their team members have been using mice to investigate these questions. Chen and Schneidman approach the group as a network composed of the joint behavior patterns of mice that had had their fur dyed in bright, glow-in-the-dark colors. Among other things, this enables the…
Last month we reported on the first people who, around twelve thousand years ago, were lining their loved ones’ graves with flowers. This month, we have a piece on the “extinct” frog that was “resurrected” and then discovered to be a living fossil.
Both of these studies were led by Israeli researchers from other institutions. The Weizmann contributions were what you might call technical: precise radiocarbon dating and x-ray micro-tomography. While the findings, themselves, were publicized in many scientific and popular publications, the technological advances that make these findings possible…
Since the haiku post was well received, and since we have another three pieces online today – each on a different finding and each interesting in its own right – I have decided to return to the haiku format. Among other things, there is something quite satisfying about distilling complex scientific findings down to 17 little syllables – like writing the perfect tweet, but more so.
In any case, follow the links to read more:
A burst of enzymes:
A transcription traffic jam
Watch for gene speed bumps
Genetics can rid
The poison from potatoes
Or add it elsewhere
image: Thinkstock…
Right above the tree tops -- where most people might think there is just air -- Prof. Dan Yakir sees a distinctive atmospheric layer in which all sorts of complex exchanges are taking place. CO2, of course, is one of the important ones, and we still don’t understand all of the ins and outs of its flux through the forest, soil and atmosphere. Moisture, heat (and by extension light) and oxygen all cycle through the interface between the forest canopy and the lower atmosphere, as do a number of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) released by many trees. These compounds may contribute to the…
Take a bunch of peculiar individuals, put them all together in one setting; film their every move, every second of the day. Sound familiar? Dr. Tali Kimchi is explicit about the resemblance of her experiments to a well-known reality TV show. The difference, of course, is that Kimchi’s subjects are mice. She places large groups of animals in a common pen in her lab, which is fitted out with video cameras, infrared lighting for nighttime filming and electronics to continuously record information from the ID chips implanted in each mouse. And while no one can deny that our enjoyment at seeing…
Google's official blog has a post today on the first computer in Israel: WEIZAC, built at the Weizmann Institute in the 1950s. Prof. Aviezri Frenkel gives a charming description of the project, including the fireworks when the machine was first turned on, in the presence of the VIPS who had come to see the new wonder.
http://googleblog.blogspot.co.il/2013/06/remembering-weizac-beginning-of.html
The foresight of the scientists who decided to build the computer is mentioned. But we can also thank them for their foresight in preserving this piece of computing history once newer computers…
The world – or at least a large swathe of Israel – was their classroom. An unusual international conference for science teaching experts started out at the Clore Garden of Science, on the Weizmann Institute campus. From there the “nomadic” conference made its way down to Eilat at the southern tip of the country, Jerusalem in the east and points in between.
Outdoor Learning Environment conference at the Ramon crater
Participating in the first international Outdoor Learning Environment conference were science education researchers from the US, UK, Canada, Denmark, Germany, Sweden, Portugal,…